the chemistry of organic molecules
... 3) Unsaturated fats-occur when fatty acids contain double bonds between their carbon atoms. These are often referred to as vegetable oils. a) Polyunsaturated fatsb) These types of fats are liquids at room temperature. D. Types of Lipids 1. Phospholipids-contain only 2 fatty acid tails. These are fou ...
... 3) Unsaturated fats-occur when fatty acids contain double bonds between their carbon atoms. These are often referred to as vegetable oils. a) Polyunsaturated fatsb) These types of fats are liquids at room temperature. D. Types of Lipids 1. Phospholipids-contain only 2 fatty acid tails. These are fou ...
2-2 Properties of Water
... glycogen. H. Plants store excess sugar as plant starch. I. Plants also make cellulose, a fiber that gives plants their strength and rigidity. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound found on the Earth. IV. Lipids A. Lipid – macromolecule made mainly from carbon, hydrogen, ...
... glycogen. H. Plants store excess sugar as plant starch. I. Plants also make cellulose, a fiber that gives plants their strength and rigidity. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound found on the Earth. IV. Lipids A. Lipid – macromolecule made mainly from carbon, hydrogen, ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Steps of Chaperonin 2 The cap attaches, causing the 3 ...
... Steps of Chaperonin 2 The cap attaches, causing the 3 ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... A space-filling model of lysozyme ...
... A space-filling model of lysozyme ...
Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
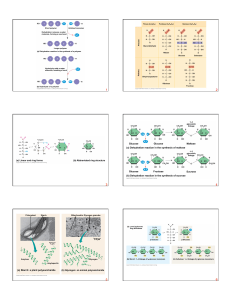
... a. Nucleotides – 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base b. Nucleic Acid – nucleotides joined by covalent bonds 1) Store and transmit genetic info a) RNA – Ribonucleic Acid b) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid 4. Proteins – made of C, H, O, N a. Amino Acids – 1) 20 different amino acids 2) a ...
... a. Nucleotides – 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base b. Nucleic Acid – nucleotides joined by covalent bonds 1) Store and transmit genetic info a) RNA – Ribonucleic Acid b) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid 4. Proteins – made of C, H, O, N a. Amino Acids – 1) 20 different amino acids 2) a ...
The Chemistry of Life
... – animals store glucose as glycogen in their livers – plants store glucose as starch – cellulose is the "roughage" or "fiber" needed for correct digestion. – cellulose cannot be digested by humans – cellulose in our diet promotes defecation and reduces colon cancer! ...
... – animals store glucose as glycogen in their livers – plants store glucose as starch – cellulose is the "roughage" or "fiber" needed for correct digestion. – cellulose cannot be digested by humans – cellulose in our diet promotes defecation and reduces colon cancer! ...
COVALENT BOND - hovanscience
... • Carbon makes up the basic structure, or “backbone,” of these compounds. • Each atom of carbon has four electrons in its outer energy level, which makes it possible for each carbon atom to form four bonds with other atoms. ...
... • Carbon makes up the basic structure, or “backbone,” of these compounds. • Each atom of carbon has four electrons in its outer energy level, which makes it possible for each carbon atom to form four bonds with other atoms. ...
Proteins Multiple choice Proteins can be classified as Polyesters
... b. Part of the structure of collagen is shown below. Draw a structural formula for an amino acid which could be obtained by hydrolysing this part of collagen. ...
... b. Part of the structure of collagen is shown below. Draw a structural formula for an amino acid which could be obtained by hydrolysing this part of collagen. ...
Spec for students digestion and metabolism
... AT skills covered by this practical activity: AT 2 and 8. Required practical 5: investigate the effect of pH on the rate of reaction of amylase enzyme. Students should use a continuous sampling technique to determine the time taken to completely digest a starch solution at a range of pH values. Iodi ...
... AT skills covered by this practical activity: AT 2 and 8. Required practical 5: investigate the effect of pH on the rate of reaction of amylase enzyme. Students should use a continuous sampling technique to determine the time taken to completely digest a starch solution at a range of pH values. Iodi ...
a) Water is a good solvent – all molecules in a living things are
... link with each other by the covalent bonds to form the chains of oligomers and polymers. The oligomers contain small number of monomers (from two to twenty), the polymers contain from hundreds to millions monomers in the chain. 2.1.2. The monomers for different types of polymers are: monosaccharides ...
... link with each other by the covalent bonds to form the chains of oligomers and polymers. The oligomers contain small number of monomers (from two to twenty), the polymers contain from hundreds to millions monomers in the chain. 2.1.2. The monomers for different types of polymers are: monosaccharides ...
food nutrients - Queensland Science Teachers
... Long-chain molecules made of amino acids Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and usually sulphur and phosphorus Used to repair and build body tissues, but can be used as a last source of energy Digestive enzymes break down proteins into amino acids There are over 30 amino acids. Plants can ma ...
... Long-chain molecules made of amino acids Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and usually sulphur and phosphorus Used to repair and build body tissues, but can be used as a last source of energy Digestive enzymes break down proteins into amino acids There are over 30 amino acids. Plants can ma ...
Elements Found in Living Things
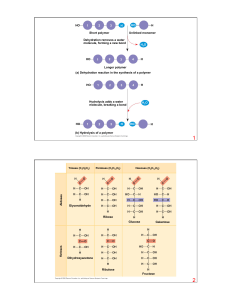
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different rati ...
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different rati ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, and proteins
... Both of the functional groups are covalently bonded to a central atom, called the alpha carbon Also bonded to the alpha carbon is a hydrogen atom and a chemical group symbolized by the letter R. R group is the variable part of an amino acid. R group structure determines the specific properties o ...
... Both of the functional groups are covalently bonded to a central atom, called the alpha carbon Also bonded to the alpha carbon is a hydrogen atom and a chemical group symbolized by the letter R. R group is the variable part of an amino acid. R group structure determines the specific properties o ...
Unit One Vocabulary
... there will be a quiz where you will be allowed to use your definitions. About midway through the unit you will be tested on your knowledge of this vocabulary. ...
... there will be a quiz where you will be allowed to use your definitions. About midway through the unit you will be tested on your knowledge of this vocabulary. ...
Biological Molecules - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 1. Many biological molecules are polymers A. ...
... 1. Many biological molecules are polymers A. ...
Biochemistry Notes
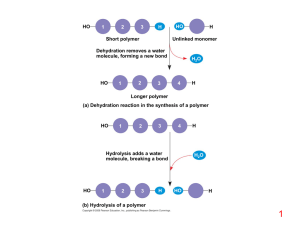
... 3. Monomers are joined in a condensation reaction that usually occurs between the –OH groups of two monomers. H2O is removed linking the two monomers with an oxygen ...
... 3. Monomers are joined in a condensation reaction that usually occurs between the –OH groups of two monomers. H2O is removed linking the two monomers with an oxygen ...
Note 1.3 Carbon Chemistry of Life
... Carbon has the ability to form the back-bone of large diverse molecules, because of the carbon’s ability to form bonds (four covalent bonds). These carbon chains (carbon skeletons) can form linear, ringed, and multi – branched molecules. Carbon has the ability to form four single covalent bonds, but ...
... Carbon has the ability to form the back-bone of large diverse molecules, because of the carbon’s ability to form bonds (four covalent bonds). These carbon chains (carbon skeletons) can form linear, ringed, and multi – branched molecules. Carbon has the ability to form four single covalent bonds, but ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... Functional groups and formation: Phosphate group Amino group Phosphodiester bond – occurs between phosphate group on one nucleotide and a hydroxyl group on the sugar of the next nucleotide in the strand (makes up the alternating sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA ...
... Functional groups and formation: Phosphate group Amino group Phosphodiester bond – occurs between phosphate group on one nucleotide and a hydroxyl group on the sugar of the next nucleotide in the strand (makes up the alternating sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA ...
Biomolecules - Good Earth School
... Nucleic Acids constitute an important class of biomolecules which are present in the nuclei of all living cells. They are biopolymers. The monomer present in them are called nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of three chemical constituents: a sugar, a nitrogen containing heterocyclic base and phospha ...
... Nucleic Acids constitute an important class of biomolecules which are present in the nuclei of all living cells. They are biopolymers. The monomer present in them are called nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of three chemical constituents: a sugar, a nitrogen containing heterocyclic base and phospha ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
... and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet of an animal B. Peptide bonds join amino acids 1. 2 amino acids form a dipeptide 2. Polypeptides are formed from more than 2 amino acids C. Proteins have 4 levels ...
... and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet of an animal B. Peptide bonds join amino acids 1. 2 amino acids form a dipeptide 2. Polypeptides are formed from more than 2 amino acids C. Proteins have 4 levels ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.