File - Biology withMrs. Ellsworth
... 43. Do carbohydrates have polymers? Yes 44. If yes, what is the polymer of carboydrates called? polysaccharides 45. What main function do carbohydrates provide for living organisms? provides a quick energy source for living organisms Provides structure for plants 46. List 3 common carbohydrates: 1. ...
... 43. Do carbohydrates have polymers? Yes 44. If yes, what is the polymer of carboydrates called? polysaccharides 45. What main function do carbohydrates provide for living organisms? provides a quick energy source for living organisms Provides structure for plants 46. List 3 common carbohydrates: 1. ...
Study Guide for Chapter 3
... * take notes and make drawings in your notebook 3. Meet the following objectives: *Write them all out in your spiral bound science notebook Describe and draw the structure of a water molecule Explain how water’s polarity affects it’s ability to dissolve substances List 2 of water’s properties ...
... * take notes and make drawings in your notebook 3. Meet the following objectives: *Write them all out in your spiral bound science notebook Describe and draw the structure of a water molecule Explain how water’s polarity affects it’s ability to dissolve substances List 2 of water’s properties ...
Biology Chapter 2 Organic Molecules 9-26
... weaken bonds before breaking. Enzymes are proteins. Remember protein shape is important to function. Enzymes generally end in –ase and are named after the substrate they bind. ...
... weaken bonds before breaking. Enzymes are proteins. Remember protein shape is important to function. Enzymes generally end in –ase and are named after the substrate they bind. ...
Dna sequence and Cell Activity
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
ANSWERS - Unit 1 Review File
... What is the function of starch? Storage form of glucose in plants A starch molecule is a chain of what simple sugar units? glucose What is the function of glycogen? Storage form of glucose in animals What process splits polysaccharides into monosaccharides? hydrolysis The formation of a disaccharide ...
... What is the function of starch? Storage form of glucose in plants A starch molecule is a chain of what simple sugar units? glucose What is the function of glycogen? Storage form of glucose in animals What process splits polysaccharides into monosaccharides? hydrolysis The formation of a disaccharide ...
Biology Homework - Whitinsville Christian School
... 4. How are monomers, polymers, and macromolecules related to each other? ...
... 4. How are monomers, polymers, and macromolecules related to each other? ...
Amino acid metabolism III. Brake down of amino acids
... Purely ketogenic amino acids: can yield ketone bodies in the liver • leucine (Leu) very common in proteins • lysine (Lys) Glucogenic amino acids: can be converted to glucose and glycogen • alanine (Ala) • cysteine (Cys) • glycine (Gly) • serine (Ser) • asparagine (Asn) • aspartate (Asp) • methion ...
... Purely ketogenic amino acids: can yield ketone bodies in the liver • leucine (Leu) very common in proteins • lysine (Lys) Glucogenic amino acids: can be converted to glucose and glycogen • alanine (Ala) • cysteine (Cys) • glycine (Gly) • serine (Ser) • asparagine (Asn) • aspartate (Asp) • methion ...
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 07a Background
... http://www.pc.maricopa.edu/Biology/rcotter/BIO%20205/LessonBuilders/Chapter%2 01%20LB/molecules.jpg ...
... http://www.pc.maricopa.edu/Biology/rcotter/BIO%20205/LessonBuilders/Chapter%2 01%20LB/molecules.jpg ...
AP Chapter 5A WS - TJ
... 8. Double sugars are called List the monosaccharides that form each: a. Maltose b. Sucrose c. Lactose 9. Polymers of sugars form 10. Which forms of polysaccharide is best for each function: a. Strength of structure b. Storage and sugar release c. What biological theme is this addressing? ...
... 8. Double sugars are called List the monosaccharides that form each: a. Maltose b. Sucrose c. Lactose 9. Polymers of sugars form 10. Which forms of polysaccharide is best for each function: a. Strength of structure b. Storage and sugar release c. What biological theme is this addressing? ...
Study Guide-Carbon, monomers, polymers, amino acids, proteins
... -Is water added or removed in dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis? -How many monomers are there if given amount of water removed or added? -What bond forms between monomers? -In order for both dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis to proceed fast enough to be of value, what is needed? c. Structure ...
... -Is water added or removed in dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis? -How many monomers are there if given amount of water removed or added? -What bond forms between monomers? -In order for both dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis to proceed fast enough to be of value, what is needed? c. Structure ...
oxidation
... proteins 20 amino acids, carbohydrates glucose, fats glycerol and fatty acids Second stage: occurs in cytoplasm small organic units convert into simple units, Ex: sugars, fatty acids, glycerol, and amino acids are converted into acetyl unit of acetyl CoA; process does not require oxygen, yields ...
... proteins 20 amino acids, carbohydrates glucose, fats glycerol and fatty acids Second stage: occurs in cytoplasm small organic units convert into simple units, Ex: sugars, fatty acids, glycerol, and amino acids are converted into acetyl unit of acetyl CoA; process does not require oxygen, yields ...
Lipids - Cloudfront.net
... The “tail” end is scared of water and is given the name HYDROPHOBIC You will see why this is so important when we talk about ...
... The “tail” end is scared of water and is given the name HYDROPHOBIC You will see why this is so important when we talk about ...
What observations did Darwin make that lead him to the Theory of
... How are organisms ‘reservoirs’ of matter? 2. Explain electronegativity, polarity, covalent bonding, and hydrogen bonding in the context of water. How do these lead to cohesion and adhesion? 3. Discuss transpiration in plants, in the context of the properties of water. What factors influence the rate ...
... How are organisms ‘reservoirs’ of matter? 2. Explain electronegativity, polarity, covalent bonding, and hydrogen bonding in the context of water. How do these lead to cohesion and adhesion? 3. Discuss transpiration in plants, in the context of the properties of water. What factors influence the rate ...
Energy Production II - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... Only 5-10% of energy derived from oxidation of protein. Use of protein depends heavily on: 1. Energy balance (deficit = more PRO used) 2. CHO available (low = more PRO used) Amino acids derived from body protein can be used to produce: a. energy, via entry into TCA cycle b. glucose, via gluconeogene ...
... Only 5-10% of energy derived from oxidation of protein. Use of protein depends heavily on: 1. Energy balance (deficit = more PRO used) 2. CHO available (low = more PRO used) Amino acids derived from body protein can be used to produce: a. energy, via entry into TCA cycle b. glucose, via gluconeogene ...
Introduction to Biology
... 2- Carbohydrates are used for storing energy in living organisms’ bodies until they require it. 3- Carbohydrates are a basic component for some parts of the cell such as cellulose in the root of plant cells. Classification of carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are classified according to their molecular ...
... 2- Carbohydrates are used for storing energy in living organisms’ bodies until they require it. 3- Carbohydrates are a basic component for some parts of the cell such as cellulose in the root of plant cells. Classification of carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are classified according to their molecular ...
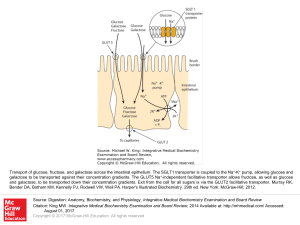
Slide ()
... Transport of glucose, fructose, and galactose across the intestinal epithelium. The SGLT1 transporter is coupled to the Na+-K+ pump, allowing glucose and galactose to be transported against their concentration gradients. The GLUT5 Na+-independent facilitative transporter allows fructose, as well as ...
... Transport of glucose, fructose, and galactose across the intestinal epithelium. The SGLT1 transporter is coupled to the Na+-K+ pump, allowing glucose and galactose to be transported against their concentration gradients. The GLUT5 Na+-independent facilitative transporter allows fructose, as well as ...
“Building” proteins!!
... The multi-coloured beads you have will be your amino acids and the much smaller single-coloured beads will be the bond joining the amino acids. You also have strings of different strength to use for different models. Among your materials you will find additional model making materials and tools such ...
... The multi-coloured beads you have will be your amino acids and the much smaller single-coloured beads will be the bond joining the amino acids. You also have strings of different strength to use for different models. Among your materials you will find additional model making materials and tools such ...
TABLE 3–1 Some Common Types of Enzymes
... catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule. catalyze polymerization reactions such as the synthesis of DNA and RNA. catalyze the addition of phosphate groups to molecules. Protein kinases are an important group of kinases that attach phosphate groups to proteins. catalyze the hydro ...
... catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule. catalyze polymerization reactions such as the synthesis of DNA and RNA. catalyze the addition of phosphate groups to molecules. Protein kinases are an important group of kinases that attach phosphate groups to proteins. catalyze the hydro ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... Obviously, proteins with different primary structures will have different secondary structures and thus different tertiary structures which will group into different quaternary structures ...
... Obviously, proteins with different primary structures will have different secondary structures and thus different tertiary structures which will group into different quaternary structures ...
Serine Proteases Teaching Exercises
... these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/glutamine, serine/threonine and histidine. Notice the distribution of polar amin ...
... these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/glutamine, serine/threonine and histidine. Notice the distribution of polar amin ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins Structure and Function
... The terms saturated, mono-unsaturated, and poly-unsaturated refer to the number of hydrogens attached to the hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acids as compared to the number of double bonds between carom atoms in the tail. Fats, which are mostly from animal sources, have all single bonds between the c ...
... The terms saturated, mono-unsaturated, and poly-unsaturated refer to the number of hydrogens attached to the hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acids as compared to the number of double bonds between carom atoms in the tail. Fats, which are mostly from animal sources, have all single bonds between the c ...
Chemical Foundations of Life The origin of life and organic
... Cellulose is probably the single most abundant organic molecule in the biosphere. It is the major structural material of which plants are made. Wood is largely cellulose while cotton and paper are almost pure cellulose. Like starch, cellulose is a polysaccharide with glucose as its monomer. However, ...
... Cellulose is probably the single most abundant organic molecule in the biosphere. It is the major structural material of which plants are made. Wood is largely cellulose while cotton and paper are almost pure cellulose. Like starch, cellulose is a polysaccharide with glucose as its monomer. However, ...
Examples - Cloudfront.net
... – Types of interactions (BETWEEN R GROUPS) • Positively charge R groups with negatively charged R-groups • Hydrophobic amino acids move toward the center to avoid water contact and opposite with hydrophilic amino acids. • polar R-groups form H-bonds with other polar Rgroups • R-group of the amino a ...
... – Types of interactions (BETWEEN R GROUPS) • Positively charge R groups with negatively charged R-groups • Hydrophobic amino acids move toward the center to avoid water contact and opposite with hydrophilic amino acids. • polar R-groups form H-bonds with other polar Rgroups • R-group of the amino a ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.