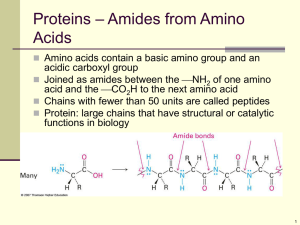
Proteins…
... Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
... Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
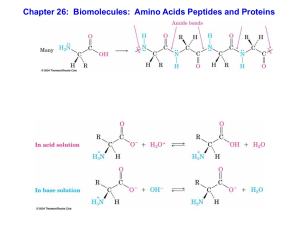
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... enantiomers are required for any protein or peptide synthesis Resolution of racemic mixtures is inherently inefficient since at least half the material is discarded An efficient alternative is enantioselective synthesis Chiral metal catalysts are popular tools More recently using enzymes to do non-n ...
... enantiomers are required for any protein or peptide synthesis Resolution of racemic mixtures is inherently inefficient since at least half the material is discarded An efficient alternative is enantioselective synthesis Chiral metal catalysts are popular tools More recently using enzymes to do non-n ...
CHAPTERS 2 & 3 Continued
... Phospholipids are important lipids • Phospholipids are structurally similar to fats and are an important component of all cells – For example, they are a major part of cell membranes, in which they cluster into a bilayer of phospholipids – The hydrophilic heads are in contact with the water of the ...
... Phospholipids are important lipids • Phospholipids are structurally similar to fats and are an important component of all cells – For example, they are a major part of cell membranes, in which they cluster into a bilayer of phospholipids – The hydrophilic heads are in contact with the water of the ...
BIOMOLECULES-L2 students
... and Doritos “fat free”?? Olestra is a synthetic fat - it is very big and bulky. Because it is so bulky, the fat-digesting enzymes in our intestines cannot break it down...and it passes through unchanged. ...
... and Doritos “fat free”?? Olestra is a synthetic fat - it is very big and bulky. Because it is so bulky, the fat-digesting enzymes in our intestines cannot break it down...and it passes through unchanged. ...
Overview of Energy and Metabolism
... Metabolism is the ability to acquire and use energy from the environment. Metabolic processes are all the chemical reactions that occur in cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Two Kinds of Metabolic Reactions: 1. Catabolism = breakdown of large molecules into simple ones to produce energy. (re ...
... Metabolism is the ability to acquire and use energy from the environment. Metabolic processes are all the chemical reactions that occur in cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Two Kinds of Metabolic Reactions: 1. Catabolism = breakdown of large molecules into simple ones to produce energy. (re ...
project III
... Project III CS 626 Due Thursday May 1, 03 In this project we shall consider the folding of a two-dimensional “protein”. The “protein” is embedded in a two dimensional square lattice with a constant spacing a . “Amino acids” are placed in the lattice points. A lattice point can be either empty or occ ...
... Project III CS 626 Due Thursday May 1, 03 In this project we shall consider the folding of a two-dimensional “protein”. The “protein” is embedded in a two dimensional square lattice with a constant spacing a . “Amino acids” are placed in the lattice points. A lattice point can be either empty or occ ...
Organic Compounds
... Lipids store excess energy in the body. Animals tend to store lipids as fats, while plants store lipids as oils. When an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can obtain energy by breaking down lipids. ...
... Lipids store excess energy in the body. Animals tend to store lipids as fats, while plants store lipids as oils. When an organism has used up most of its carbohydrates, it can obtain energy by breaking down lipids. ...
Document
... is liberated, and H atoms removed are ultimately delivered to molecular oxygen, forming water. Some energy released is used to form ATP. Catabolic reactions Anabolic reactions © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... is liberated, and H atoms removed are ultimately delivered to molecular oxygen, forming water. Some energy released is used to form ATP. Catabolic reactions Anabolic reactions © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
proteins
... Strings are finite sequences over an alphabet S (also called sequences) DNA (characters: nucleotides) S = {A,C,G,T} RNA (characters: nucleotides) S = {A,C,G,U} Proteins (characters: peptides) S = {A,C,D,E,F,. . . ,W,Y} ...
... Strings are finite sequences over an alphabet S (also called sequences) DNA (characters: nucleotides) S = {A,C,G,T} RNA (characters: nucleotides) S = {A,C,G,U} Proteins (characters: peptides) S = {A,C,D,E,F,. . . ,W,Y} ...
fat-soluble
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
Chapter 25 - FacultyWeb
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
... NADH produced by glycolysis in skeletal muscle fibers leads to production of two ATP molecules in mitochondria, but NADH produced by glycolysis in cardiac muscle cells leads to production of three ATP molecules. Why? ...
Chapter 8 Summary
... (NAD+, FAD, and NADP+) and reduced (NADH + H+, FADH2, and NADPH + H+) forms. Enzymes involved in metabolic pathways are regulated primarily by hormones. The hormone insulin promotes energy storage, whereas the hormone glucagon promotes energy mobilization. The hormones cortisol and epinephrine also ...
... (NAD+, FAD, and NADP+) and reduced (NADH + H+, FADH2, and NADPH + H+) forms. Enzymes involved in metabolic pathways are regulated primarily by hormones. The hormone insulin promotes energy storage, whereas the hormone glucagon promotes energy mobilization. The hormones cortisol and epinephrine also ...
Quiz:1
... 7. The non-polar amino acids such as iso-leucine, leucine, valine, alanine, phenyl alanine are soluble in water but when they are present in a peptide (joined together by amide bond), the peptide is insoluble in water. Why? 8. What will be the net charge on a poly-lysine peptide at neutral pH and at ...
... 7. The non-polar amino acids such as iso-leucine, leucine, valine, alanine, phenyl alanine are soluble in water but when they are present in a peptide (joined together by amide bond), the peptide is insoluble in water. Why? 8. What will be the net charge on a poly-lysine peptide at neutral pH and at ...
Carbon Macromolecules
... • Include Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) and Polysaccharides (Complex Sugars) • Glucose, sucrose, fructose, and cellulose. ...
... • Include Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) and Polysaccharides (Complex Sugars) • Glucose, sucrose, fructose, and cellulose. ...
PowerPoint - Garnet Valley School District
... Examples: Organic Compounds: Compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Examples: ...
... Examples: Organic Compounds: Compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Examples: ...
Question 2: Multiple-Choice Standard: Chemistry of Life
... Standard: Chemistry of Life - B 1.2 Ovalbumin is a protein found in eggs. Which of the following best describes the molecular structure of ovalbumin? A. a group of six carbon atoms joined in a ring B. a chain of amino acids folded and twisted into a molecule C. a set of three fatty acids attached to ...
... Standard: Chemistry of Life - B 1.2 Ovalbumin is a protein found in eggs. Which of the following best describes the molecular structure of ovalbumin? A. a group of six carbon atoms joined in a ring B. a chain of amino acids folded and twisted into a molecule C. a set of three fatty acids attached to ...
Name
... 1. What is a monomer? 2. How can you tell if a molecule is organic or inorganic? 3. What are the four categories of organic macromolecules? 4. Which three atoms are found in all of the organic macromolecules? 5. Explain dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. 6. Draw the following molecules: ...
... 1. What is a monomer? 2. How can you tell if a molecule is organic or inorganic? 3. What are the four categories of organic macromolecules? 4. Which three atoms are found in all of the organic macromolecules? 5. Explain dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. 6. Draw the following molecules: ...
Name Due date ______ Strive for a 5 – AP Biology Review Unit 1
... 20. A student added a strong acid to a beaker containing a solution with a functional protein. After adding the acid, the protein no longer functioned. Explain how adding the acid altered the protein’s structure and function. Be sure to include the following terms in your answer: protons, 3D structu ...
... 20. A student added a strong acid to a beaker containing a solution with a functional protein. After adding the acid, the protein no longer functioned. Explain how adding the acid altered the protein’s structure and function. Be sure to include the following terms in your answer: protons, 3D structu ...
Honors
... Molecules • All compounds are either organic or inorganic. • Organic compounds are made of carbon. • This is NOT the same organic from the food store or farmers market. ...
... Molecules • All compounds are either organic or inorganic. • Organic compounds are made of carbon. • This is NOT the same organic from the food store or farmers market. ...
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
... Contains an imidazole ring that is partially protonated in neutral solution Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24 ...
... Contains an imidazole ring that is partially protonated in neutral solution Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24 ...
Document
... Q: Enzymes must function properly for organisms to stay alive and healthy. What determines the enzyme’s function? _______________________ Q: What factors can cause an enzyme’s shape to change, thus affecting its function? ...
... Q: Enzymes must function properly for organisms to stay alive and healthy. What determines the enzyme’s function? _______________________ Q: What factors can cause an enzyme’s shape to change, thus affecting its function? ...
Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
... 2 or more amino acids can be joined together by the reaction of the amino group (NH2) of one amino acid and the carboxyl group (COOH) of another The bond formed is a chain and is called a ...
... 2 or more amino acids can be joined together by the reaction of the amino group (NH2) of one amino acid and the carboxyl group (COOH) of another The bond formed is a chain and is called a ...
“Are we really what we eat?” “Where does the `stuff` that makes us
... -Glycogen: stored in liver and muscle cells, and is a secondary long-term energy storage (animals) ...
... -Glycogen: stored in liver and muscle cells, and is a secondary long-term energy storage (animals) ...
Chemical Foundations
... Organic Compounds - contain carbon - 4 major families o Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, and Proteins Macromolecules ...
... Organic Compounds - contain carbon - 4 major families o Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, and Proteins Macromolecules ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.