Practice Exam1
... A. binds in the central cavity in the T-form of hemoglobin. B. preferentially binds to deoxyhemoglobin and stabilizes it. C. is present in fetal red blood cells. D. None of the above E. All of the above 7. The configuration of most α-carbon atoms of amino acids linked in a peptide bond is A. cis B. ...
... A. binds in the central cavity in the T-form of hemoglobin. B. preferentially binds to deoxyhemoglobin and stabilizes it. C. is present in fetal red blood cells. D. None of the above E. All of the above 7. The configuration of most α-carbon atoms of amino acids linked in a peptide bond is A. cis B. ...
Biochemistry
... by the sharing of one or more electron pairs between two atoms Ionic bond - Chemical bonding resulting from the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or a group of atoms to another. ...
... by the sharing of one or more electron pairs between two atoms Ionic bond - Chemical bonding resulting from the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or a group of atoms to another. ...
Chemistry of the cell - University of Bristol
... RNA can not only carry information but also perform functions, similar to proteins: in the ribosome where the proteins are made it is the RNA which obviously joins the amino acids together. There are also “rybozymes” – species of RNA which can attack and destroy other RNAs. Nucleotides give rise to ...
... RNA can not only carry information but also perform functions, similar to proteins: in the ribosome where the proteins are made it is the RNA which obviously joins the amino acids together. There are also “rybozymes” – species of RNA which can attack and destroy other RNAs. Nucleotides give rise to ...
CH 3 RG 2014 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... 4. Study the following figure below and on the next page. See if you can understand why some R groups are nonpolar, some polar, and others electrically charged (acidic or basic). If you were given an R group, could you place it in the correct group? Work the R groups until you can see common element ...
... 4. Study the following figure below and on the next page. See if you can understand why some R groups are nonpolar, some polar, and others electrically charged (acidic or basic). If you were given an R group, could you place it in the correct group? Work the R groups until you can see common element ...
Introduction to Cells
... a hydroxyl group and the other provides a hydrogen and together these form water. Requires energy and is aided by enzymes. ...
... a hydroxyl group and the other provides a hydrogen and together these form water. Requires energy and is aided by enzymes. ...
No Slide Title
... towards, and fusing with, the plasma membrane. 11) In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, proteins always contain ________. nitrogen 12) A protein consists of sub-units called ____________ amino acids (of which there are about 20 types) joined together by peptide bonds to form polypeptides. 13) ...
... towards, and fusing with, the plasma membrane. 11) In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, proteins always contain ________. nitrogen 12) A protein consists of sub-units called ____________ amino acids (of which there are about 20 types) joined together by peptide bonds to form polypeptides. 13) ...
Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism
... Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 is able to synthesize fatty acids de novo from acetyl-CoA and incorporate them into phospholipids. This strain has an absolute requirement for several volatile acids for growth [1], utilizing isobutyrate and valerate for produ ...
... Text S3: Fatty acid synthesis and catabolism Fibrobacter succinogenes S85 is able to synthesize fatty acids de novo from acetyl-CoA and incorporate them into phospholipids. This strain has an absolute requirement for several volatile acids for growth [1], utilizing isobutyrate and valerate for produ ...
What is Health SCIENCE? - petlakhealthscience20
... • CORRECT AS CLASS – SELF-ASSESS – SUBMIT MARK ...
... • CORRECT AS CLASS – SELF-ASSESS – SUBMIT MARK ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthetic Pathways
... • A large excess of phosphate would drive the reaction to the right; that is, drive the hydrolysis of glycogen. • To provide an alternative pathway for the synthesis of glycogen, even in the presence of excess phosphate: ...
... • A large excess of phosphate would drive the reaction to the right; that is, drive the hydrolysis of glycogen. • To provide an alternative pathway for the synthesis of glycogen, even in the presence of excess phosphate: ...
Quiz 15
... 7. Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) t ...
... 7. Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) t ...
lec---10
... • Amino acids are joined together when a dehydration reaction removes a hydroxyl group from the carboxyl end of one amino acid and a hydrogen from the amino ...
... • Amino acids are joined together when a dehydration reaction removes a hydroxyl group from the carboxyl end of one amino acid and a hydrogen from the amino ...
2.3 Guided Notes
... b. Many carbon-based molecules are made of many small subunits bonded together. i. ________________________________ are the individual subunits. ii. ________________________________ are made of many monomers. ...
... b. Many carbon-based molecules are made of many small subunits bonded together. i. ________________________________ are the individual subunits. ii. ________________________________ are made of many monomers. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Some plant food-storage organs store small amounts of proteins in addition to large amounts of carbohydrates. Seeds usually contain proportionately larger amounts of proteins in addition to their complement of carbohydrates. ...
... Some plant food-storage organs store small amounts of proteins in addition to large amounts of carbohydrates. Seeds usually contain proportionately larger amounts of proteins in addition to their complement of carbohydrates. ...
Slide 1
... Phospholipids are structurally similar to fats and are an important component of all cells – For example, they are a major part of cell membranes, in which they cluster into a bilayer of phospholipids – The hydrophilic heads are in contact with the water of the environment and the internal part of ...
... Phospholipids are structurally similar to fats and are an important component of all cells – For example, they are a major part of cell membranes, in which they cluster into a bilayer of phospholipids – The hydrophilic heads are in contact with the water of the environment and the internal part of ...
Biochemistry of life
... Cholesterol is a steroid that is found in food and is also made in the body High levels of cholesterol can lead to hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) which can cause ...
... Cholesterol is a steroid that is found in food and is also made in the body High levels of cholesterol can lead to hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) which can cause ...
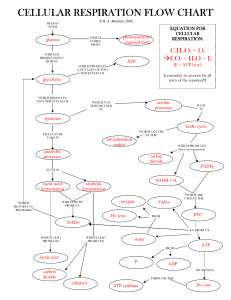
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to
... takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryoticcells. It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve since it is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth. The process does not use oxygen and is, ...
... takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryoticcells. It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve since it is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth. The process does not use oxygen and is, ...
(EXAMPLES: DNA and RNA) NUCLEIC ACIDS contain atoms of
... DNA and RNA have more structural & functional differences that will be discussed in later units. How many nucleotides are joined together to form this portion of a DNA molecule?_______________________ What is the cellular process (reaction) that combines monomers into polymers?______________________ ...
... DNA and RNA have more structural & functional differences that will be discussed in later units. How many nucleotides are joined together to form this portion of a DNA molecule?_______________________ What is the cellular process (reaction) that combines monomers into polymers?______________________ ...
Introduction Document
... atom and the N atom) and ψ (between the Cα atom and the other C atom) for the different amino acids would give exact structure. Very difficult problem. The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build ...
... atom and the N atom) and ψ (between the Cα atom and the other C atom) for the different amino acids would give exact structure. Very difficult problem. The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build ...
Organic Compounds Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test!~ 1
... 22. Which list consists of only polymers? A. sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids, lipids B. proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, amino acids C. proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, monosaccharides D. proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, polysaccharides 23. Cellulose differs from glycogen in that A. The monomers ...
... 22. Which list consists of only polymers? A. sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids, lipids B. proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, amino acids C. proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, monosaccharides D. proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, polysaccharides 23. Cellulose differs from glycogen in that A. The monomers ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Secondary = twisted and folded chain of amino acids. Tertiary = Chain is then twisted itself. Quaternary = The entire protein maintains a folded, twisted shape due to H-bonds and Van der Waals Forces. ...
... Secondary = twisted and folded chain of amino acids. Tertiary = Chain is then twisted itself. Quaternary = The entire protein maintains a folded, twisted shape due to H-bonds and Van der Waals Forces. ...
BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES
... A. It is important that the cell can control the rate of its reactions; otherwise, it would overproduce products. This would waste energy and raw materials B. COMPETITIVE INHIBITION 1. This is a type of regulation that occurs when a compound other than the substrate temporarily occupies the active s ...
... A. It is important that the cell can control the rate of its reactions; otherwise, it would overproduce products. This would waste energy and raw materials B. COMPETITIVE INHIBITION 1. This is a type of regulation that occurs when a compound other than the substrate temporarily occupies the active s ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.