Outline
... – a substance in food that is used by the body to promote normal growth, maintenance, and repair ...
... – a substance in food that is used by the body to promote normal growth, maintenance, and repair ...
Organic Molecules Notes
... A deficiency of amino acids may adversely affect hair growth. There are twenty common amino acids: alanine, arginine, aspargine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, serine, threonine, tryptophan, tyro ...
... A deficiency of amino acids may adversely affect hair growth. There are twenty common amino acids: alanine, arginine, aspargine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, serine, threonine, tryptophan, tyro ...
Organic Molecule Cut-Outs
... 4. Glue the “monomers” and “polymers” labels under the appropriate structures. 5. Glue the “Importance” box on the paper and write the importance of proteins (from your notes). 6. Glue the title “Proteins” in an appropriate place. 7. Repeat steps 2–7 for Carbohydrates, except you’ll have a glucose c ...
... 4. Glue the “monomers” and “polymers” labels under the appropriate structures. 5. Glue the “Importance” box on the paper and write the importance of proteins (from your notes). 6. Glue the title “Proteins” in an appropriate place. 7. Repeat steps 2–7 for Carbohydrates, except you’ll have a glucose c ...
Chapter 4 - Open Yale Courses
... shape is the tertiary structure, and the formation of a complex with other polypeptide chains is the quaternary structure. • All the information necessary for a protein to fold properly into its tertiary structure is contained in the primary amino acid sequence. • Non-covalent interactions such as h ...
... shape is the tertiary structure, and the formation of a complex with other polypeptide chains is the quaternary structure. • All the information necessary for a protein to fold properly into its tertiary structure is contained in the primary amino acid sequence. • Non-covalent interactions such as h ...
Ch - Humble ISD
... Catabolism – chemical rxns (usually Hydrolysis reactions) Break down larger food molecules into smaller chem. units; release energy ...
... Catabolism – chemical rxns (usually Hydrolysis reactions) Break down larger food molecules into smaller chem. units; release energy ...
Protein Synthesis
... beads and pipe cleaners. When you have your protein completed, have your teacher check it. If there are any errors, please go back and find your mistakes. 8. Did you have any “mutations” during the process? ____________ ...
... beads and pipe cleaners. When you have your protein completed, have your teacher check it. If there are any errors, please go back and find your mistakes. 8. Did you have any “mutations” during the process? ____________ ...
File - Biology withMrs. Ellsworth
... Indicate which number is neutral. Indicate the acid range. Indicate the base range. Indicate which side is more concentrated with OH- and Indicate which side is more concentrated with H+. ...
... Indicate which number is neutral. Indicate the acid range. Indicate the base range. Indicate which side is more concentrated with OH- and Indicate which side is more concentrated with H+. ...
Lecture 5: The Chemistry of Life III
... • Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods • Chitin also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi ...
... • Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods • Chitin also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi ...
Packet 2 - Organic Chemistry
... _______________ breaks down carbohydrates like glucose for use in cellular respiration Cellular respiration is the process through which the body generates energy, or ________ Starch and cellulose are polysaccharides comprised of long chains of ___________. ...
... _______________ breaks down carbohydrates like glucose for use in cellular respiration Cellular respiration is the process through which the body generates energy, or ________ Starch and cellulose are polysaccharides comprised of long chains of ___________. ...
Features of Life and the Cell
... Two additional properties of water: 5. Capillary Action - the ability to move upward against gravity. Due to the combined properties of adhesion and ...
... Two additional properties of water: 5. Capillary Action - the ability to move upward against gravity. Due to the combined properties of adhesion and ...
Molecular Biology and Chemistry - Systems Biology Research Group
... within the cell, and cell recognition; it also provides a passage way for certain molecules and a stable site for binding and catalysis of enzymes [7]. The components that give the membrane its architecture and uid characteristics are the phospholipid bilayers. The phospholipid bilayer that makes u ...
... within the cell, and cell recognition; it also provides a passage way for certain molecules and a stable site for binding and catalysis of enzymes [7]. The components that give the membrane its architecture and uid characteristics are the phospholipid bilayers. The phospholipid bilayer that makes u ...
Document
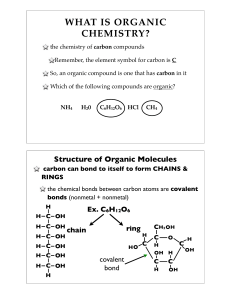
... WHAT IS BIOCHEMISTRY? the chemistry of LIFE Remember, the elements found in all living things include Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHNOPS) Thus, biochemistry involves carbon compounds. ...
... WHAT IS BIOCHEMISTRY? the chemistry of LIFE Remember, the elements found in all living things include Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHNOPS) Thus, biochemistry involves carbon compounds. ...
Proteins
... Carbs can be single sugar units or polymers which are composed of three or more subunits Single sugar units, like glucose, have a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Carbs can also be classified according to the number of sugar units they contain ...
... Carbs can be single sugar units or polymers which are composed of three or more subunits Single sugar units, like glucose, have a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Carbs can also be classified according to the number of sugar units they contain ...
Slide 1
... with some differences: • RNA molecule is single-stranded (rather than double stranded in DNA) • Uracil instead of Thymine. So in RNA Adenine binds with Uracil ...
... with some differences: • RNA molecule is single-stranded (rather than double stranded in DNA) • Uracil instead of Thymine. So in RNA Adenine binds with Uracil ...
Document
... glycerol and fatty acids. The types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids (cholesterol). ...
... glycerol and fatty acids. The types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids (cholesterol). ...
Chapter 2.3: Carbon Compounds
... 1. Breaking and forming chemical bonds requires energy release or absorption 2. Reactions that release energy can occur ...
... 1. Breaking and forming chemical bonds requires energy release or absorption 2. Reactions that release energy can occur ...
Microbial Metabolism Lipids and Proteins - ASAB-NUST
... • Some bacteria and fungi particularly pathogenic, food spoilage, and soil microorganisms can use proteins as their source of carbon and energy. • They secrete protease enzymes that hydrolyze proteins and polypeptides to amino acids, which are transported into the cell and catabolized ...
... • Some bacteria and fungi particularly pathogenic, food spoilage, and soil microorganisms can use proteins as their source of carbon and energy. • They secrete protease enzymes that hydrolyze proteins and polypeptides to amino acids, which are transported into the cell and catabolized ...
CHM 112
... A polysaccharide has a molar mass of about 400 g/mol and is soluble in water while a triglyceride with the same molar mass is highly insoluble. Explain why. Lipids have large, non-polar hydrocarbon sections which are not attracted to water. Carbohydrates have multiple hydroxyl groups that form hydro ...
... A polysaccharide has a molar mass of about 400 g/mol and is soluble in water while a triglyceride with the same molar mass is highly insoluble. Explain why. Lipids have large, non-polar hydrocarbon sections which are not attracted to water. Carbohydrates have multiple hydroxyl groups that form hydro ...
Protein Synthesis Drawing
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.