Title - Iowa State University
... 7.) Molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains are ______. A. Heterophilic B. Enantomers C. Amphipathic D. Sugars 8.) An Enzyme speeds up an reaction by ___________ A. decrease activation energy of a reaction. B. increase the ΔG of a reaction C. decrease the Δ G of a reaction D. increa ...
... 7.) Molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains are ______. A. Heterophilic B. Enantomers C. Amphipathic D. Sugars 8.) An Enzyme speeds up an reaction by ___________ A. decrease activation energy of a reaction. B. increase the ΔG of a reaction C. decrease the Δ G of a reaction D. increa ...
a sample task
... amino acids in a polypeptide chain. For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in the diagram below. Each chain has its own set of amino acids, assembled in a particular order. For instance, the sequence of the A chain starts with glycine at the N-terminus ...
... amino acids in a polypeptide chain. For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in the diagram below. Each chain has its own set of amino acids, assembled in a particular order. For instance, the sequence of the A chain starts with glycine at the N-terminus ...
Topic Three Chemistry of Life - MrsGorukhomework
... 1. structural support – collagen, tendons, ligaments 2. transport of substances – hemoglobin 3. make up some hormones – insulin 4. receptor for hormones and other chemicals 5. defense of the body – antibodies 6. contractions of muscles – actin and myosin 7. enzymes for catalyzing reactions – A prote ...
... 1. structural support – collagen, tendons, ligaments 2. transport of substances – hemoglobin 3. make up some hormones – insulin 4. receptor for hormones and other chemicals 5. defense of the body – antibodies 6. contractions of muscles – actin and myosin 7. enzymes for catalyzing reactions – A prote ...
Amino acids - Zanichelli online
... Most are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Da. ...
... Most are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Da. ...
Pattern Matching: Organic Molecules
... maintains the level of the sugar glucose in your blood within a very narrow range. Glucose is the immediate source of energy for your cells. Sugars occur as ring structures. There are monosaccharides (single rings), disaccharides (double rings), and larger. In solution, single rings can dynamically ...
... maintains the level of the sugar glucose in your blood within a very narrow range. Glucose is the immediate source of energy for your cells. Sugars occur as ring structures. There are monosaccharides (single rings), disaccharides (double rings), and larger. In solution, single rings can dynamically ...
Bio160 ExIII Sp09
... e. the reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reactions are referred to as substrates 42. The substrate that is catalyzed by the enzyme we studied in our on-line enzyme lab is: a. glucose b. sucrose c. fructose d. invertase e. acarbose ...
... e. the reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reactions are referred to as substrates 42. The substrate that is catalyzed by the enzyme we studied in our on-line enzyme lab is: a. glucose b. sucrose c. fructose d. invertase e. acarbose ...
Characteristics all organisms share
... simple and complex carbohydrates? Name and give an example of each ...
... simple and complex carbohydrates? Name and give an example of each ...
macromolecules
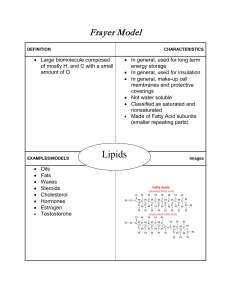
... Purpose – Cells use lipids for energy storage, insulation, and protective coverings Structure – Made mostly of carbon, hydrogen, a small amount of oxygen and fatty acids. Also are attached with single bonds and double bonds depending on the lipid Lipids usually have 2 hydrophilic heads and 2 hydroph ...
... Purpose – Cells use lipids for energy storage, insulation, and protective coverings Structure – Made mostly of carbon, hydrogen, a small amount of oxygen and fatty acids. Also are attached with single bonds and double bonds depending on the lipid Lipids usually have 2 hydrophilic heads and 2 hydroph ...
1. Sucrose is a disaccharide. It is formed from two
... Describe a biochemical test to find out if the solution collected from the apparatus contains (i) ...
... Describe a biochemical test to find out if the solution collected from the apparatus contains (i) ...
1 Name Chapter 3 Reading Guide Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and
... c. Explain the difference between your answer for the time of (A) and (B). Disulfide bridges are necessary for protein tertiary structure and must form before the enzyme active site can reappear, but there are other chemical interactions, such as hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, that o ...
... c. Explain the difference between your answer for the time of (A) and (B). Disulfide bridges are necessary for protein tertiary structure and must form before the enzyme active site can reappear, but there are other chemical interactions, such as hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, that o ...
How does DNA copy itself?
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
Organic Compound Notes
... Earth could have ________allowed the spontaneous formation of more complex (organic) molecules. ...
... Earth could have ________allowed the spontaneous formation of more complex (organic) molecules. ...
unit 2 - Biochem packet_hnrs
... Earth could have ________allowed the spontaneous formation of more complex (organic) molecules. ...
... Earth could have ________allowed the spontaneous formation of more complex (organic) molecules. ...
Macromolecules of the Human Body
... Chitin is one of many naturally occurring polymers. It is one of the most abundant natural materials in the world. Over time it is bio-degradable in the natural environment. Its breakdown may be catalyzed by enzymes called chitinases, secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, and produc ...
... Chitin is one of many naturally occurring polymers. It is one of the most abundant natural materials in the world. Over time it is bio-degradable in the natural environment. Its breakdown may be catalyzed by enzymes called chitinases, secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, and produc ...
CHAP Twenty-Five - Foothill College
... B) Hindered rotation and 1H NMR C) Sequencing via Selective Cleavage i) With aqueous acid at every peptide bond ii) Edman Degradation: N terminus iii) DNFB to identify N-terminus iv) Chymotripsin at C-terminus v) With cyanogen bromide BrCN at methionine C terminus vi) With chymotripsin at C end of p ...
... B) Hindered rotation and 1H NMR C) Sequencing via Selective Cleavage i) With aqueous acid at every peptide bond ii) Edman Degradation: N terminus iii) DNFB to identify N-terminus iv) Chymotripsin at C-terminus v) With cyanogen bromide BrCN at methionine C terminus vi) With chymotripsin at C end of p ...
BIOMG 3310: Principles of Biochemistry
... For example, Val, Ile, and Thr have a second methyl group branching out of the beta carbon, creating steric hindrance. ...
... For example, Val, Ile, and Thr have a second methyl group branching out of the beta carbon, creating steric hindrance. ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... Smaller units, monomers, join together to form polymers. The monomers in a polymer may be alike or different. ...
... Smaller units, monomers, join together to form polymers. The monomers in a polymer may be alike or different. ...
Proteins – where do they come from?
... • Plants make proteins by using materials made in photosynthesis ...
... • Plants make proteins by using materials made in photosynthesis ...
Chapter 3 Molecules
... carb- = coal (carboxyl group: a functional group in an organic molecule, consisting of an oxygen atom doublebonded to a carbon atom that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group) glyco- = sweet (glycogen: an extensively branched polysaccharide of many glucose monomers that serves as an energy-storage mole ...
... carb- = coal (carboxyl group: a functional group in an organic molecule, consisting of an oxygen atom doublebonded to a carbon atom that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group) glyco- = sweet (glycogen: an extensively branched polysaccharide of many glucose monomers that serves as an energy-storage mole ...
Core Topic 2: Molecular biology 21 hours Essential idea: Living
... Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
... Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
Biochemistry
... Acidic solutions contain higher concentration of H+ ions than pure water, then it will have pH values below seven Basic, or alkaline, solutions that contain lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure water, then it will have pH values above seven ...
... Acidic solutions contain higher concentration of H+ ions than pure water, then it will have pH values below seven Basic, or alkaline, solutions that contain lower concentrations of H+ ions than pure water, then it will have pH values above seven ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.