Document
... high temperatures. However, the abiodic formation of amino acids requires NH3 • NH3 was not stable in the Archean atmosphere ...
... high temperatures. However, the abiodic formation of amino acids requires NH3 • NH3 was not stable in the Archean atmosphere ...
Homework #4: VERSION 2.1
... Don’t forget 2 – the hard copy you hand in during class should only have the last four digits of your PID # as an identifier. ...
... Don’t forget 2 – the hard copy you hand in during class should only have the last four digits of your PID # as an identifier. ...
Name: ____ ______ Unit 4: Living Things Metabolize Section A
... Review Questions: How do you know that a chemical reaction has taken place? Identify the two parts of a chemical reaction. Relate energy changes to chemical reactions (in other words, when is energy gained and when is energy lost?) How are enzymes activated? ...
... Review Questions: How do you know that a chemical reaction has taken place? Identify the two parts of a chemical reaction. Relate energy changes to chemical reactions (in other words, when is energy gained and when is energy lost?) How are enzymes activated? ...
Lecture 13
... • A molecule of glucose (6 carbons) is split into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3 carbons). This is an oxidation event. ...
... • A molecule of glucose (6 carbons) is split into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3 carbons). This is an oxidation event. ...
Introduction, ppt file - Cheriton School of Computer Science
... the molecule. In addition, other noncovalent interactions including electrostatic and van der Waals will enable the protein once folded to be slightly more stable than not. When oil, a nonpolar, hydrophobic molecule, is placed into water, they push ...
... the molecule. In addition, other noncovalent interactions including electrostatic and van der Waals will enable the protein once folded to be slightly more stable than not. When oil, a nonpolar, hydrophobic molecule, is placed into water, they push ...
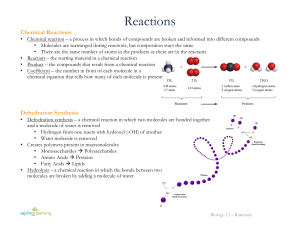
Reactions
... • Usually end with the suffix “-ase” and its name comes from the substrate • Have optimal temperatures and pH to maintain normal functioning • Enzymes lower the activation energy of the reaction • Activation energy – the minimum amount of energy needed to cause a chemical reaction to occur • Without ...
... • Usually end with the suffix “-ase” and its name comes from the substrate • Have optimal temperatures and pH to maintain normal functioning • Enzymes lower the activation energy of the reaction • Activation energy – the minimum amount of energy needed to cause a chemical reaction to occur • Without ...
chapter 24
... When we don’t have enough carbohydrates to meet our energy needs, the body will break down stored fats. However, the breakdown of large amounts of fat will cause acetyl-CoA molecules to accumulate in the liver. These molecules will combine to form ketone bodies through the ...
... When we don’t have enough carbohydrates to meet our energy needs, the body will break down stored fats. However, the breakdown of large amounts of fat will cause acetyl-CoA molecules to accumulate in the liver. These molecules will combine to form ketone bodies through the ...
Section 3 - Carbon Compounds
... called amino acids. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group (–NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (–COOH) on the other end. Figure 2–16 shows one reason why proteins are among the most diverse macromolecules. More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. All amino acids are identica ...
... called amino acids. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group (–NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (–COOH) on the other end. Figure 2–16 shows one reason why proteins are among the most diverse macromolecules. More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. All amino acids are identica ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. – Monosaccharides are simple sugars. – Polysaccharides include starches, cellulose, and glycogen. ...
... Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. – Monosaccharides are simple sugars. – Polysaccharides include starches, cellulose, and glycogen. ...
Amino acids
... A. Glucose, a six-membered ring monosaccharide. B. Fructose, a five-membered ring monosaccharide. C. Sucrose, a disaccharide containing glucose and fructose. D. Molecular representation of starch illustrating the alpha-glycosidic linkages joining monosaccharides to form the polysaccharide structure ...
... A. Glucose, a six-membered ring monosaccharide. B. Fructose, a five-membered ring monosaccharide. C. Sucrose, a disaccharide containing glucose and fructose. D. Molecular representation of starch illustrating the alpha-glycosidic linkages joining monosaccharides to form the polysaccharide structure ...
Amino acids catabolism
... The conversion of serine to glycine involves one-C unit from serine to an acceptor This is catalyzed by serine hydroxymethylase, with pyridoxal phosphate as coenzyme The acceptor is tetrahydropholate (derivative of folic acid) – its structure has 3 parts: a subtituted pteridine ring, p-aminobenzoic ...
... The conversion of serine to glycine involves one-C unit from serine to an acceptor This is catalyzed by serine hydroxymethylase, with pyridoxal phosphate as coenzyme The acceptor is tetrahydropholate (derivative of folic acid) – its structure has 3 parts: a subtituted pteridine ring, p-aminobenzoic ...
Test Review Unit 1
... 10) What is asexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parent)? 11) What is sexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parents)? 12) What is the cell theory? ...
... 10) What is asexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parent)? 11) What is sexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parents)? 12) What is the cell theory? ...
Protein Synthesis Facts
... Each one of your somatic cells (all cells in the body that are not sexcells) has 46 DNA molecules. Each of your sex-cells has 23 DNA molecules. It takes a cell just a few hours for a cell to copy all of its DNA This replication is achieved with very few errors (only about one per billion nucleotides ...
... Each one of your somatic cells (all cells in the body that are not sexcells) has 46 DNA molecules. Each of your sex-cells has 23 DNA molecules. It takes a cell just a few hours for a cell to copy all of its DNA This replication is achieved with very few errors (only about one per billion nucleotides ...
Biochem BIG IDEAS - Canvas by Instructure
... 1. Carbon moves from the environment to organisms where it is used to build carbohydrates, proteins, lipids or nucleic acids. Carbon is used in storage compounds and cell formation in all organisms. 2. Nitrogen moves from the environment to organisms where it is used in building proteins and nucleic ...
... 1. Carbon moves from the environment to organisms where it is used to build carbohydrates, proteins, lipids or nucleic acids. Carbon is used in storage compounds and cell formation in all organisms. 2. Nitrogen moves from the environment to organisms where it is used in building proteins and nucleic ...
Ch 9 Practice Q word
... Practice questions Ch 9 STUDY NOTES AND TEXTBOOK BEFORE ATTEMPTING THESE. This is NOT COMPREHENSIVE (does not contain all the information you need to study for the exam. Consult note and textbook) ...
... Practice questions Ch 9 STUDY NOTES AND TEXTBOOK BEFORE ATTEMPTING THESE. This is NOT COMPREHENSIVE (does not contain all the information you need to study for the exam. Consult note and textbook) ...
CH 9 PowerPoint
... nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups: with one nucleotide containing an adenosine ring, and the other containing nicotinamide. In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is therefore found in two forms in cells: NAD+ ...
... nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups: with one nucleotide containing an adenosine ring, and the other containing nicotinamide. In metabolism, NAD+ is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is therefore found in two forms in cells: NAD+ ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
final-exam-backup
... Ribosomes attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum make proteins that are designed to be exported from the cell. The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other substances through the cell. The ER membranes are also made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. As ...
... Ribosomes attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum make proteins that are designed to be exported from the cell. The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other substances through the cell. The ER membranes are also made of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. As ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. – Monosaccharides are simple sugars. – Polysaccharides include starches, cellulose, and glycogen. ...
... Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. • Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. – Monosaccharides are simple sugars. – Polysaccharides include starches, cellulose, and glycogen. ...
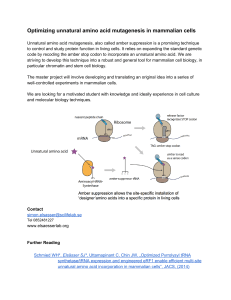
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.