final-exam-tables-ba..
... are fairly close together, usually as a helix or pleated sheet. A protein’s tertiary structure describes the folding of a protein molecule due to other attractions within the molecule, often involving the variable (R) groups. A protein’s quaternary structure describes the bonding of two or more poly ...
... are fairly close together, usually as a helix or pleated sheet. A protein’s tertiary structure describes the folding of a protein molecule due to other attractions within the molecule, often involving the variable (R) groups. A protein’s quaternary structure describes the bonding of two or more poly ...
Biological Macromolecules and Lipids
... hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biol ...
... hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biol ...
Lecture 9
... In today’s lecture, we will take a brief look at the evolution of single cells. What’s a possible scenario for how life arose? This will be sort of a retroactive view, based on what we know about the molecules in cells; how might they have gotten together to generate “life”. ...
... In today’s lecture, we will take a brief look at the evolution of single cells. What’s a possible scenario for how life arose? This will be sort of a retroactive view, based on what we know about the molecules in cells; how might they have gotten together to generate “life”. ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... Phospholipids are amphipathic, the hydrocarbon tails are hydrophobic and cluster together to exclude water. The phosphate heads are hydrophilic and associate with the aqueous environment. ...
... Phospholipids are amphipathic, the hydrocarbon tails are hydrophobic and cluster together to exclude water. The phosphate heads are hydrophilic and associate with the aqueous environment. ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... 3. write and calculate equilibrium constant expression Organic & Biochemical Chemistry-(2) 1. proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are made up of repetitive combinations 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus ...
... 3. write and calculate equilibrium constant expression Organic & Biochemical Chemistry-(2) 1. proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are made up of repetitive combinations 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus ...
life.
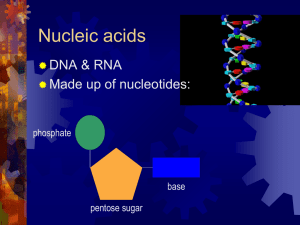
... What are the organic molecules that must have been present for early life to begin? • amino acids: to form proteins • sugars (which are a part of nucleotides) A nucleotide is three things: a nitrogenous base; a sugar; and a phosphate group. ...
... What are the organic molecules that must have been present for early life to begin? • amino acids: to form proteins • sugars (which are a part of nucleotides) A nucleotide is three things: a nitrogenous base; a sugar; and a phosphate group. ...
Biology Common Mid
... c. A set of three fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol. d. A sequence of nitrogenous bases attached to a sugar-phosphate backbone 14. What type of chemical reaction results in the breakdown of organic polymers into their monomers by addition of water? a. condensation b. hydrolysis c. ioniz ...
... c. A set of three fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol. d. A sequence of nitrogenous bases attached to a sugar-phosphate backbone 14. What type of chemical reaction results in the breakdown of organic polymers into their monomers by addition of water? a. condensation b. hydrolysis c. ioniz ...
tutorial on carbohydrates
... 8. What is the structural differences characterize starch, cellulose, and glycogen? 9. What shape do carbohydrate chains linked with α(1,4) glycosidic bonds generally have? 10. Determine the number of possible stereisomers in ribulose and sedoheptulose. ...
... 8. What is the structural differences characterize starch, cellulose, and glycogen? 9. What shape do carbohydrate chains linked with α(1,4) glycosidic bonds generally have? 10. Determine the number of possible stereisomers in ribulose and sedoheptulose. ...
File
... Part 4 of 5 Look at the diagram in this part of the investigation. Draw and label a diagram showing the interaction between the following terms/molecules: “ribosome”, “mRNA”, “tRNA”, “polypeptide” & “amino acid” ...
... Part 4 of 5 Look at the diagram in this part of the investigation. Draw and label a diagram showing the interaction between the following terms/molecules: “ribosome”, “mRNA”, “tRNA”, “polypeptide” & “amino acid” ...
Types of Organic compounds
... Types of Organic compounds Four major groups of organic compounds, necessary for life are: polymers monomers – Carbohydrates monosacchrides – Lipids fatty acids – Proteins amino acids – Nucleic acids nucleotides ...
... Types of Organic compounds Four major groups of organic compounds, necessary for life are: polymers monomers – Carbohydrates monosacchrides – Lipids fatty acids – Proteins amino acids – Nucleic acids nucleotides ...
ANSWERS BIOCHEMISTRY CARBOHYDRATES
... *Sodium palmitate and glycerol are formed. When an oil or fat is exposed to moist air for a long time , it develops an unpleasant smell and sour taste. This phenomenon is called rancidity. Hydrolytic rancidity can be prevented by refrigerating oils and fats. It is a process of removing impurities li ...
... *Sodium palmitate and glycerol are formed. When an oil or fat is exposed to moist air for a long time , it develops an unpleasant smell and sour taste. This phenomenon is called rancidity. Hydrolytic rancidity can be prevented by refrigerating oils and fats. It is a process of removing impurities li ...
Biological Molecules Review KEY
... the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken into smaller particles the process of breaking down large fat droplets into smaller fat droplets the loose association of amino acids in a polypeptide chain with each other, usually through H-bonds. e.g. alpha helix, beta pleated sheet the l ...
... the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken into smaller particles the process of breaking down large fat droplets into smaller fat droplets the loose association of amino acids in a polypeptide chain with each other, usually through H-bonds. e.g. alpha helix, beta pleated sheet the l ...
Additional Lab Exercise: Amino Acid Sequence in
... sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, messenger RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the formation of the final protein molecule. In DNA, a ...
... sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, messenger RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the formation of the final protein molecule. In DNA, a ...
Or Is It? Section 1: Characteristics of Living Things (pg 4-7)
... All living things are made of one or more cells. o A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life ...
... All living things are made of one or more cells. o A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life ...
Respiration
... • RESPIRATION a process where organic (food) molecules are oxidized & broken down to release E • Glycolysis is the 1o source of e- for the citric acid and etransport chain ...
... • RESPIRATION a process where organic (food) molecules are oxidized & broken down to release E • Glycolysis is the 1o source of e- for the citric acid and etransport chain ...
RESPIRATION
... Two types: Alcoholic Fermentation: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 2ATP (glucose) (ethanol) (carbon (Energy) dioxide) ...
... Two types: Alcoholic Fermentation: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + 2ATP (glucose) (ethanol) (carbon (Energy) dioxide) ...
Discussion Questions for Week 5: HWA Pages 167-177
... disadvantage. Explain why. 6. Phosphagens can be used to produce ATP as well. How does this mechanism work? 7. It is common belief that lactic acid causes muscle fatigue. Based on your reading, do you believe this to be true? 8. What other factors are mentioned that are believed to cause muscle fati ...
... disadvantage. Explain why. 6. Phosphagens can be used to produce ATP as well. How does this mechanism work? 7. It is common belief that lactic acid causes muscle fatigue. Based on your reading, do you believe this to be true? 8. What other factors are mentioned that are believed to cause muscle fati ...
FREE Sample Here
... Buffers are mechanisms that help keep pH within normal limits by taking up excess hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions. Maintaining pH within a narrow range is important to health. ...
... Buffers are mechanisms that help keep pH within normal limits by taking up excess hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions. Maintaining pH within a narrow range is important to health. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.