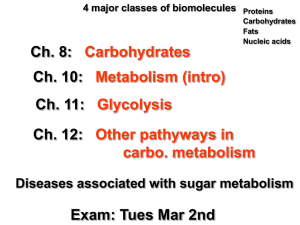
Organic Chemistry #2 Vocabulary Adhesion Cohesion Atom
... maximized, the active sites of the enzymes are all used adding more substrate does not increase the rate of reaction. ...
... maximized, the active sites of the enzymes are all used adding more substrate does not increase the rate of reaction. ...
Review 3
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
... (deoxy)ribonucleotides • Carbamoyl phosphate and urea • Pyruvate, oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate • PRPP ...
Organic Chemistry Chapters 2 and 3
... – Electrons are directly involved in the chemical reactions between atoms – An atom’s electrons vary in the amount of energy they possess • Electrons of an atom have potential energy because of their position in relation to the nucleus. – The more distant the electrons are from the nucleus the great ...
... – Electrons are directly involved in the chemical reactions between atoms – An atom’s electrons vary in the amount of energy they possess • Electrons of an atom have potential energy because of their position in relation to the nucleus. – The more distant the electrons are from the nucleus the great ...
Amino Acids 14.5 * 14.8
... Chain of hundreds or thousands of amino acids make up protein that serve many functions in living organisms. The order of chain length goes by peptide (shortest), polypeptide, proteins (longest). Polypeptides contain 30-50 amino acids ...
... Chain of hundreds or thousands of amino acids make up protein that serve many functions in living organisms. The order of chain length goes by peptide (shortest), polypeptide, proteins (longest). Polypeptides contain 30-50 amino acids ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... Conserved (the residue is generally similar, e.g. negatively charged) Not conserved (can be many different residues in different species) ...
... Conserved (the residue is generally similar, e.g. negatively charged) Not conserved (can be many different residues in different species) ...
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... NADH and FADH2 are from Krebs and glycolysis NADH and FADH2 release H to these reactions H is split into H+ and eThe e- move through the carriers to the biggest e- acceptor (moving down hill – releasing potential energy and increasing ...
... NADH and FADH2 are from Krebs and glycolysis NADH and FADH2 release H to these reactions H is split into H+ and eThe e- move through the carriers to the biggest e- acceptor (moving down hill – releasing potential energy and increasing ...
Title - Iowa State University
... Glycolysis requires Oxygen, which is termed ________ respiration. Glycolysis occurs in ___ steps or ___ phases. 3. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondrial matrix, where it is broken down to an ________ group, ___ CO2 group and ___ NADH molecule. 4. Next, the acetyl groups enter into the _____ cyc ...
... Glycolysis requires Oxygen, which is termed ________ respiration. Glycolysis occurs in ___ steps or ___ phases. 3. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondrial matrix, where it is broken down to an ________ group, ___ CO2 group and ___ NADH molecule. 4. Next, the acetyl groups enter into the _____ cyc ...
Synthesis of Fats, Proteins, and Carbohydrates Lab
... d. When a fat is made, 3 water molecules are also made (this is called a condensation reaction). Make the 3 water molecules by cutting out and gluing together the one H-H-H piece with three O-H pieces. Make sure to glue this piece onto the same sheet as the fat. e. Label your paper “Fat or Lipid” 3. ...
... d. When a fat is made, 3 water molecules are also made (this is called a condensation reaction). Make the 3 water molecules by cutting out and gluing together the one H-H-H piece with three O-H pieces. Make sure to glue this piece onto the same sheet as the fat. e. Label your paper “Fat or Lipid” 3. ...
Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) are not boring long polymers
... located within the core of the characteristic L‐shaped 3‐D structure of fully mature and functional tRNAs. Systematic presence or exclusion of a given modified nucleotide in the tRNA molecules belonging to thermophilic, mesophilic and psychrophilic organisms allows to str ...
... located within the core of the characteristic L‐shaped 3‐D structure of fully mature and functional tRNAs. Systematic presence or exclusion of a given modified nucleotide in the tRNA molecules belonging to thermophilic, mesophilic and psychrophilic organisms allows to str ...
L10v02-glycolysis and TCA
... Beta oxidation of fatty acids. Once inside the mitochondria, a fatty acid, which might have anywhere from 12 to 18 carbon molecules, are shortened by two carbons per cycle, always producing one molecule of acetyl‐CoA. The 12 carbon fatty acid could do this cycle six times. Each time the cycle oc ...
... Beta oxidation of fatty acids. Once inside the mitochondria, a fatty acid, which might have anywhere from 12 to 18 carbon molecules, are shortened by two carbons per cycle, always producing one molecule of acetyl‐CoA. The 12 carbon fatty acid could do this cycle six times. Each time the cycle oc ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Discuss the salient features of Crick and Watson model for the structure of DNA. ...
... Discuss the salient features of Crick and Watson model for the structure of DNA. ...
Reece9e_Lecture_C05
... Three of the four classes of macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids—form chain-like molecules called polymers. ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomer ...
... Three of the four classes of macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids—form chain-like molecules called polymers. ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomer ...
Slide 1
... • Linear polymer usually one reducing end (free anomeric carbon), one non-reducing end, and all internal monosaccharides are acetals that are not in equilibrium with open chains form. • Some polymers such as the disaccharide sucrose do not have a reducing end (both anomeric carbons are involved in t ...
... • Linear polymer usually one reducing end (free anomeric carbon), one non-reducing end, and all internal monosaccharides are acetals that are not in equilibrium with open chains form. • Some polymers such as the disaccharide sucrose do not have a reducing end (both anomeric carbons are involved in t ...
Cell Membrane
... reflects green light absorbs red and blue Light has many wavelengths Pigments are light absorbing molecules ...
... reflects green light absorbs red and blue Light has many wavelengths Pigments are light absorbing molecules ...
Chapter 3 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... •Most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers •A monomer is a single unit of a polymer like legos! • Four classes of life’s organic molecules are polymers – Carbohydrates (include sugars, starches etc) – Proteins – Nucleic acids – Lipids (fats) ...
... •Most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers •A monomer is a single unit of a polymer like legos! • Four classes of life’s organic molecules are polymers – Carbohydrates (include sugars, starches etc) – Proteins – Nucleic acids – Lipids (fats) ...
Nutrition and Metabolism
... Vitamins A vitamin is an organic compound needed in small quantities for normal metabolism that cannot be manufactured in the cells of the body. They are stored to a slight extent in all cells and to a major extent in the liver. ADEK are the fat soluble vitamins. There are extensive stores of A whic ...
... Vitamins A vitamin is an organic compound needed in small quantities for normal metabolism that cannot be manufactured in the cells of the body. They are stored to a slight extent in all cells and to a major extent in the liver. ADEK are the fat soluble vitamins. There are extensive stores of A whic ...
1) Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms: neutrons
... scale measures Hydrogen ions. 6) Describe the structures and functions of each of the four groups of macromolecules: Carbohydrates are what living things use as their MAIN source of energy; they range from simple to complex carbohydrates. Monosaccharides bond together to for polysaccharides. Cellulo ...
... scale measures Hydrogen ions. 6) Describe the structures and functions of each of the four groups of macromolecules: Carbohydrates are what living things use as their MAIN source of energy; they range from simple to complex carbohydrates. Monosaccharides bond together to for polysaccharides. Cellulo ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations
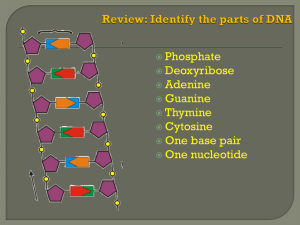
... Sugar is either DNA or RNA. Bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine (DNA), and uracil (RNA). Nucleotides link together to build nucleic acids. ...
... Sugar is either DNA or RNA. Bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine (DNA), and uracil (RNA). Nucleotides link together to build nucleic acids. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.