Unit 1 - Body Chemistry Notes
... – long branching chains of linked simple sugars – Includes glycogen in animals, and starch & cellulose in plants – Interesting tidbit: glucose needed for muscle contraction is usually stored as glycogen ...
... – long branching chains of linked simple sugars – Includes glycogen in animals, and starch & cellulose in plants – Interesting tidbit: glucose needed for muscle contraction is usually stored as glycogen ...
Electrons
... carbohydrate, lipid, protein, nucleic acids 2. Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds carbohydrates – energy lipids – store energy proteins – form tissue nucleic acids – transmit hereditary information ...
... carbohydrate, lipid, protein, nucleic acids 2. Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds carbohydrates – energy lipids – store energy proteins – form tissue nucleic acids – transmit hereditary information ...
This exam has 8 pages, including this one.
... a) at pH values within one pH unit of its pKa. b) at pH values within two pH units of its pKa c) at pH values within three pH units of its pKa. d) at any pH value. 3. If the φ and ψ angles of each peptide unit in a protein are both known, the following will also be determined: a) complete secondary ...
... a) at pH values within one pH unit of its pKa. b) at pH values within two pH units of its pKa c) at pH values within three pH units of its pKa. d) at any pH value. 3. If the φ and ψ angles of each peptide unit in a protein are both known, the following will also be determined: a) complete secondary ...
Relationship between mutation and resistance to fluoroquinolones
... The development of single cells to a functional organ and finally a complete organism is an amazing interplay of numerous factors. Since their identification, a class of proteins called basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins has been found to be involved in various developmental processes. Generally ...
... The development of single cells to a functional organ and finally a complete organism is an amazing interplay of numerous factors. Since their identification, a class of proteins called basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins has been found to be involved in various developmental processes. Generally ...
Document
... Takes place in liver and kidney Synthesis of glucose or glycogen from non carbohydrates like pyruvate, lactate glucogenic amino acids, glycerol and propionic acid Pathway involves steps of TCA cycle and reversal of glycolysis The irreversible steps of glycolysis are catalysed by Hexokinase P ...
... Takes place in liver and kidney Synthesis of glucose or glycogen from non carbohydrates like pyruvate, lactate glucogenic amino acids, glycerol and propionic acid Pathway involves steps of TCA cycle and reversal of glycolysis The irreversible steps of glycolysis are catalysed by Hexokinase P ...
File
... 7. chemical 8. to run all of the chemical reactions in the body; are biological catalysts; are proteins (CHON); decrease the activation energy; speed up chemical reactions; can be re-used 9. what the enzyme attaches to (like a lock and key) 10. an enzyme that starts the chemical reactions by lowerin ...
... 7. chemical 8. to run all of the chemical reactions in the body; are biological catalysts; are proteins (CHON); decrease the activation energy; speed up chemical reactions; can be re-used 9. what the enzyme attaches to (like a lock and key) 10. an enzyme that starts the chemical reactions by lowerin ...
final exam review f12 answers
... The energy it takes to start a chemical reaction 31. What is an enzyme? How does it act as a catalyst? A protein that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 32. The cell membrane is sometimes described as a fluid mosaic because of the large molecules that move around on its surfa ...
... The energy it takes to start a chemical reaction 31. What is an enzyme? How does it act as a catalyst? A protein that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy 32. The cell membrane is sometimes described as a fluid mosaic because of the large molecules that move around on its surfa ...
C h e m g u id e –... AMINO ACIDS: ACID-BASE BEHAVIOUR
... electrophoresis. Describe how you would carry out simple electrophoresis on a solution containing one of these ions. e) The final result of the electrophoresis you have described will probably be a spot on a piece of paper. How does this spot give you information about the charge on the ion? Illustr ...
... electrophoresis. Describe how you would carry out simple electrophoresis on a solution containing one of these ions. e) The final result of the electrophoresis you have described will probably be a spot on a piece of paper. How does this spot give you information about the charge on the ion? Illustr ...
lecture1
... They are not the reverse of each other They are independently regulated They often take place in different locations in the cells (compartmentalization β-oxidation-mutochondria syn of fatty acids – cytosol. Cellular regulation of metabolic pathways Metabolic pathways can be linear, e.g. glycolysis o ...
... They are not the reverse of each other They are independently regulated They often take place in different locations in the cells (compartmentalization β-oxidation-mutochondria syn of fatty acids – cytosol. Cellular regulation of metabolic pathways Metabolic pathways can be linear, e.g. glycolysis o ...
Chapter 2 Biochemistry Goux Guided Notes
... - Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. - Living things store extra sugar as complex carbohydrates known as _____starches______________ - Single sugar molecules are also called ______monosaccharides______ - The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are kn ...
... - Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. - Living things store extra sugar as complex carbohydrates known as _____starches______________ - Single sugar molecules are also called ______monosaccharides______ - The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides are kn ...
Chapter 3 – The Molecules of Cells
... break bonds • Enzymes are specialized proteins that speed up the chemical reactions in cells • Enzymes are extremely important – without them, many reactions cannot take place. If you lack lactase, you cannot hydrolyze the bond in lactose ...
... break bonds • Enzymes are specialized proteins that speed up the chemical reactions in cells • Enzymes are extremely important – without them, many reactions cannot take place. If you lack lactase, you cannot hydrolyze the bond in lactose ...
Power Point Presentation
... positioning reactive compounds in order to control the precise location at which chemical reactions take place. This general approach should allow the construction of large atomically precise objects by a sequence of precisely controlled chemical reactions, building objects molecule by molecule. An ...
... positioning reactive compounds in order to control the precise location at which chemical reactions take place. This general approach should allow the construction of large atomically precise objects by a sequence of precisely controlled chemical reactions, building objects molecule by molecule. An ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter #4
... dehydration synthesis. A by-product of dehydration synthesis is water. The process of splitting two molecule by adding water is called hydrolysis. Hydrolysis occurs during digestion. ...
... dehydration synthesis. A by-product of dehydration synthesis is water. The process of splitting two molecule by adding water is called hydrolysis. Hydrolysis occurs during digestion. ...
Minilab 11-1
... ffif, complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA baies risted in the column marked DNA Base Sequence. Use the letters A, U, C, or G. ffi ldentify the. process responsibre by writing its name on the arrow in column A. ffiB complete column D by writing the correct ant ...
... ffif, complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA baies risted in the column marked DNA Base Sequence. Use the letters A, U, C, or G. ffi ldentify the. process responsibre by writing its name on the arrow in column A. ffiB complete column D by writing the correct ant ...
Transcription - smithlhhsb121
... The replication of DNA takes place in S phase of interphase However, DNA is also used during G1 to assemble proteins This process is broken down into two distinct segments: transcription and translation The entire human genome is found in every cell, but only a portion is activated This portion has ...
... The replication of DNA takes place in S phase of interphase However, DNA is also used during G1 to assemble proteins This process is broken down into two distinct segments: transcription and translation The entire human genome is found in every cell, but only a portion is activated This portion has ...
BIOLOGY FACTS THE STUDENT ABSOLUTELY - Mr-Paullers-wiki
... • Monosaccharides - glucose, fructose simple sugars CsHi20s ⋅ Form disaccharides by condensation (lose water when making larger molecules) ⋅ Glucose is blood sugar and is made by plants • Polysaccharides - complex chains of glucose ⋅ Starch - storage in plants ⋅ Glycogen - storage in animals, later ...
... • Monosaccharides - glucose, fructose simple sugars CsHi20s ⋅ Form disaccharides by condensation (lose water when making larger molecules) ⋅ Glucose is blood sugar and is made by plants • Polysaccharides - complex chains of glucose ⋅ Starch - storage in plants ⋅ Glycogen - storage in animals, later ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... and redox reactions, explain why this is true. Fats have lots of hydrogen-carbon bonds, and each of these store energy. Ex: fats have more bonds that can be oxidized compared to carbs. - The figure to the right (figure is from POGIL packet) outlines the process of cellular respiration. Glucose and o ...
... and redox reactions, explain why this is true. Fats have lots of hydrogen-carbon bonds, and each of these store energy. Ex: fats have more bonds that can be oxidized compared to carbs. - The figure to the right (figure is from POGIL packet) outlines the process of cellular respiration. Glucose and o ...
Energy in cells
... inside living cells which releases energy to drive the metabolic activities that take place in cells Aerobic respiration – takes place in the presence of oxygen ...
... inside living cells which releases energy to drive the metabolic activities that take place in cells Aerobic respiration – takes place in the presence of oxygen ...
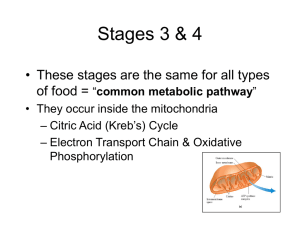
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... Series of electron carriers Each carrier exists in oxidized or reduced form High energy electrons pass down the electron transport chain in a series of redox reactions These reactions are coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). They lose energy as they pass along the chain ...
... Series of electron carriers Each carrier exists in oxidized or reduced form High energy electrons pass down the electron transport chain in a series of redox reactions These reactions are coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). They lose energy as they pass along the chain ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The creation of a concentration gradient of H+ ions across the inner membrane. This involves active pumping of H+s. • The H+s then diffuse down their concentration gradient through an ATP Synthase enzyme that produces ATP • Process produces about 32 ATP ...
... • The creation of a concentration gradient of H+ ions across the inner membrane. This involves active pumping of H+s. • The H+s then diffuse down their concentration gradient through an ATP Synthase enzyme that produces ATP • Process produces about 32 ATP ...
Electron Transport Chain
... When the cells of the body do not have enough oxygen to perform the duties requires (ie. During ...
... When the cells of the body do not have enough oxygen to perform the duties requires (ie. During ...
Learning Objectives Chapter 2 Biochem [10-30
... triacylglycerols; remnants cleared from the body by the liver VLDL: synthesized in the liver; remnants cleared by the liver, or they form low-density lipoprotein (LDL) which is cleared by the liver or by peripheral cells. When they pass through blood vessels in adipose tissue, triacylglycerols are d ...
... triacylglycerols; remnants cleared from the body by the liver VLDL: synthesized in the liver; remnants cleared by the liver, or they form low-density lipoprotein (LDL) which is cleared by the liver or by peripheral cells. When they pass through blood vessels in adipose tissue, triacylglycerols are d ...
Macromolecules webquest answer key
... Overview and Learning Objectives. Students start with images of living organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals. They "zoom" into cells and tissues to discover. Distance Learning Object: Biology Labs. Designer: Alan Peterka Instructor: Keith Hench. Explanation: Biology labs for non-majors. The ...
... Overview and Learning Objectives. Students start with images of living organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals. They "zoom" into cells and tissues to discover. Distance Learning Object: Biology Labs. Designer: Alan Peterka Instructor: Keith Hench. Explanation: Biology labs for non-majors. The ...
Document
... • Cats are specifically adapted for a high protein, low carb diet. They depend on gluconeogenesis as a major source of energy. Cat’s are limited in their ability to conserve protein due to continuous protein catabolism. • Metabolism of excess amino acids increases liver and kidney overload. ...
... • Cats are specifically adapted for a high protein, low carb diet. They depend on gluconeogenesis as a major source of energy. Cat’s are limited in their ability to conserve protein due to continuous protein catabolism. • Metabolism of excess amino acids increases liver and kidney overload. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.