
Year 13 Winter Revision Guide
... enzyme inhibitors (competitive and non-competitive) Enzymes as biomarkers of disease: Some enzymes are only present or active during disease processes (e.g. white blood cells can release elastase during respiratory infections, hydrolysing the structural protein elastin within the lung leading to r ...
... enzyme inhibitors (competitive and non-competitive) Enzymes as biomarkers of disease: Some enzymes are only present or active during disease processes (e.g. white blood cells can release elastase during respiratory infections, hydrolysing the structural protein elastin within the lung leading to r ...
Lecture 6
... • During substrate-level phosphorylation, a high-energy from an intermediate in catabolism is added to ADP. ...
... • During substrate-level phosphorylation, a high-energy from an intermediate in catabolism is added to ADP. ...
Energy Metabolism and water vitamins
... ☻ Removes from circulation amino acids that are present in excess of need and converts them to p other amino acids ☻ Removes ammonia from the blood and converts it to urea to be sent to the kidneys for excretion ☻ Makes other nitrogen containing compounds the body needs – such as base used in DNA an ...
... ☻ Removes from circulation amino acids that are present in excess of need and converts them to p other amino acids ☻ Removes ammonia from the blood and converts it to urea to be sent to the kidneys for excretion ☻ Makes other nitrogen containing compounds the body needs – such as base used in DNA an ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... Called Lactic Acid fermentation in muscle cells (makes muscles tired) Called Alcoholic fermentation in yeast (produces ethanol) Nets only 2 ATP ...
... Called Lactic Acid fermentation in muscle cells (makes muscles tired) Called Alcoholic fermentation in yeast (produces ethanol) Nets only 2 ATP ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry
... Biochemicals • BIG molecules composed mostly of carbon. • Make up all living things! ...
... Biochemicals • BIG molecules composed mostly of carbon. • Make up all living things! ...
mb_ch03
... • Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. – A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. ...
... • Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. – A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. ...
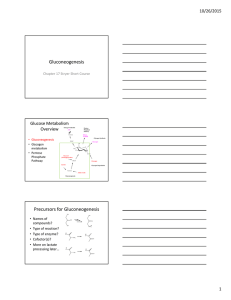
Gluconeogenesis Precursors for Gluconeogenesis
... – Costs ATP to make driving force for next reaction – First step in biosynthesis of glucose and many other molecules • Related to which amino acid? ...
... – Costs ATP to make driving force for next reaction – First step in biosynthesis of glucose and many other molecules • Related to which amino acid? ...
Ch 3 Notes
... • Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. – A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. ...
... • Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. – A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide. ...
3.the nature of proteins
... Every amino acid possesses an amino end and a carboxylic acid end There are twenty different naturally occurring amino acids Amino acids differ by virtue of the nature of their R groups Amino acids bond together forming peptide bonds When two amino acids bond during a condensation reaction ...
... Every amino acid possesses an amino end and a carboxylic acid end There are twenty different naturally occurring amino acids Amino acids differ by virtue of the nature of their R groups Amino acids bond together forming peptide bonds When two amino acids bond during a condensation reaction ...
2 unit Chemistry-2
... scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions 7. Students will describe the general structure and function(s), including common functional groups, of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, carbohydrates, fatty acids, glycerol, glycerides, ...
... scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions 7. Students will describe the general structure and function(s), including common functional groups, of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, carbohydrates, fatty acids, glycerol, glycerides, ...
Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions
... • Homolactic fermentation: Produces lactic acid only • Heterolactic fermentation: Produces lactic acid and other compounds ...
... • Homolactic fermentation: Produces lactic acid only • Heterolactic fermentation: Produces lactic acid and other compounds ...
Biochemistry with Elements of Chemistry - Collegium Medicum
... nonprotein amino acids(homocysteine, homoserine, ornithine, cytrulline, β-alanine, γ-aminobutyric acid, βaminoizobutyric acid) 5. The formation, structure and properties of the peptide bond. Some important peptides in the human organism (glutathione, peptide hormones, peptide antibiotics). The insul ...
... nonprotein amino acids(homocysteine, homoserine, ornithine, cytrulline, β-alanine, γ-aminobutyric acid, βaminoizobutyric acid) 5. The formation, structure and properties of the peptide bond. Some important peptides in the human organism (glutathione, peptide hormones, peptide antibiotics). The insul ...
Chapter 26 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Fats contain about 9 kcal/g • Carbohydrates and proteins, about 4 kcal/g – sugar and alcohol are “empty” calories -- few nutrients ...
... • Fats contain about 9 kcal/g • Carbohydrates and proteins, about 4 kcal/g – sugar and alcohol are “empty” calories -- few nutrients ...
Amino Acids and Proteins: →Protein Functions: enzymes, transport
... 4) Reactions of amino acids: The side chains exhibit specific chemical reactivities, depending on the nature of the functional group (see figure 4.8). It is the characteristic behavior of the side chain that governs the reactivity of amino acids incorporated into proteins. Polymerization of Amino Ac ...
... 4) Reactions of amino acids: The side chains exhibit specific chemical reactivities, depending on the nature of the functional group (see figure 4.8). It is the characteristic behavior of the side chain that governs the reactivity of amino acids incorporated into proteins. Polymerization of Amino Ac ...
Biology_1_&_2_files/2 Biochemistry ACADEMIC
... major source of energy for many organisms, including humans. ...
... major source of energy for many organisms, including humans. ...
Assaying
... Major interfering agents: Detergents, nucleic acids, particulates, lipid droplets Highly susceptible to contamination by buffers, biological materials and salts Protein amino acid composition is extremely important, thus the choice of a standard is very difficult, especially for purified proteins Ab ...
... Major interfering agents: Detergents, nucleic acids, particulates, lipid droplets Highly susceptible to contamination by buffers, biological materials and salts Protein amino acid composition is extremely important, thus the choice of a standard is very difficult, especially for purified proteins Ab ...
Name - Phillips Scientific Methods
... This is called the ___________________________ gradient. Click this link. 8. What passes through the proton channel? ____________________ 9. Is this by diffusion or active transport? __________________ 10. What is produced by this special protein channel as H+ ions continue to pass through it? _____ ...
... This is called the ___________________________ gradient. Click this link. 8. What passes through the proton channel? ____________________ 9. Is this by diffusion or active transport? __________________ 10. What is produced by this special protein channel as H+ ions continue to pass through it? _____ ...
Exam Review 2 10/2/16
... A. The Y-shaped region where the DNA is split into two separate strands for coding B. Growing as DNA replication proceeds because synthesis is bidirectional C. The location at which the replication process begins D. Present only in bacterial cells and not in eukaryotes 45. Reverse transcriptase is c ...
... A. The Y-shaped region where the DNA is split into two separate strands for coding B. Growing as DNA replication proceeds because synthesis is bidirectional C. The location at which the replication process begins D. Present only in bacterial cells and not in eukaryotes 45. Reverse transcriptase is c ...
Paper - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... (B) catalyses a rate-limiting reaction in porphyrin biosynthesis (C) requires the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate (D) all of the above 36. The catabolism of heme : (A) occurs in the cells of the reticuloendothelial system (B) involves the oxidative cleavage of the porphyrin ring (C) results in the libe ...
... (B) catalyses a rate-limiting reaction in porphyrin biosynthesis (C) requires the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate (D) all of the above 36. The catabolism of heme : (A) occurs in the cells of the reticuloendothelial system (B) involves the oxidative cleavage of the porphyrin ring (C) results in the libe ...
CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 1 Human Cells
... I can explain how DNA probes with fluorescent labels are used in identifying disease and in showing relationships between individuals e.g. paternity testing, and this can be carried out multiple times with microarrays. I can describe the difference between anabolic and catabolic processes, and expla ...
... I can explain how DNA probes with fluorescent labels are used in identifying disease and in showing relationships between individuals e.g. paternity testing, and this can be carried out multiple times with microarrays. I can describe the difference between anabolic and catabolic processes, and expla ...
Jeopardy - Montville.net
... Have their own genome; don’t have enzymes, ribosomes, or ATP; have external protein shells called capsids; infect only specific cells; have two life cycles (lysic and lysogenic); are smaller than bacteria ...
... Have their own genome; don’t have enzymes, ribosomes, or ATP; have external protein shells called capsids; infect only specific cells; have two life cycles (lysic and lysogenic); are smaller than bacteria ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.






















![Biochemistry 2 [1203253] intended learning outcomes DNA, RNA](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002558734_1-17434e4debf95f3be87a42da9306bb2f-300x300.png)