* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 unit Chemistry-2
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
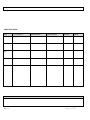
Grade: ___10____ Trigg County Public Schools Unit of Study Content Area: __Science________________ Course: _____Biology/Biology Pre AP_____________________ Bundle/Unit Title: __Chemistry of Life_______2______________________________________ Unit Synopsis This unit addresses the nature of matter, properties of water, carbon compounds, chemical reaction, and enzymes. Knowledge of Content Proposed Teaching Date 8/31/11 to 9/21/11 1|Page Standard Learning Targets A5 a. Identify subatomic particles and describe how they are arranged in atoms b. Describe the difference between ions and atoms and the importance of ions in biological processes c. Compare the types of bonding between atoms to form molecules d. Show how chemical reactions (e.g., photosynthesis, fermentation, cellular respiration) can be represented by chemical formulas e. Explain the difference between organic and inorganic compounds f. Explain the fundamental principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions g. Describe the general structure and function(s), including common functional groups, of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, carbohydrates, fatty 1. Students will identify subatomic particles and describe how they are arranged in atoms. 2. Students will describe the difference between ions and atoms and the importance of ions in biological processes. 3. Students will compare the types of bonding between atoms to form molecules. 4. Students will show how chemical reactions (e.g., photosynthesis, fermentation, cellular respiration) can be represented by chemical formulas. 5. Students will explain the difference between organic and inorganic compounds. 6. Students will explain the fundamental Target Level Student-Friendly “I Can…” Statements Critical Vocabulary I can identify subatomic particles and describe how they are arranged in atoms. I can describe the difference between ions and atoms and the importance of ions in biological processes. I can compare the types of bonding between atoms to form molecules. I can show how chemical reactions (e.g., photosynthesis, fermentation, cellular respiration) can be represented by chemical formulas. I can explain the difference between organic and inorganic compounds. Atom Catalyst Chemical Property Chemical Reaction Compound Covalent Bonding Electron Element Enzyme Intermolecular interactions, Ionic Bonding Isotope Matter Molecule Neutron Non-polar Nucleic Acid Periodic Table Polar Proton I can explain the fundamental principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. I can describe the general structure and Summer 2011 acids, glycerol, glycerides, lipids, amino acids, dipeptides, polypeptides, proteins, and nucleic acids h. Describe the function of enzymes, including how enzyme-substrate specificity works, in biochemical reactions i. Define and explain the unique properties of water that are essential to living organisms j. Explain how cells store energy temporarily as ATP 2|Page principles of the pH scale and the consequences of having the different concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions 7. Students will describe the general structure and function(s), including common functional groups, of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, carbohydrates, fatty acids, glycerol, glycerides, lipids, amino acids, dipeptides, polypeptides, proteins, and nucleic acids. 8. Students will describe the function of enzymes, including how enzymesubstrate specificity works, in biochemical reactions. 9. Students will define and explain the unique properties of water that are essential to living organisms. 10. Students will explain how cells store energy temporarily as ATP. function(s), including common functional groups, of monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, carbohydrates, fatty acids, glycerol, glycerides, lipids, amino acids, dipeptides, polypeptides, proteins, and nucleic acids. I can describe the function of enzymes, including how enzyme-substrate specificity works, in biochemical reactions. I can define and explain the unique properties of water that are essential to living organisms. I can explain how cells store energy temporarily as ATP. Summer 2011 CLASSROOM ASSESSMENT & REFLECTION Interim & End of Unit Common Assessments (Assessments & Rubrics Attached) Proposed Standards Assessment Method Interventions for Struggling Students Assessment (number only) Date Extensions for Proficient Students INSTRUCTIONAL RIGOR & STUDENT ENGAGEMENT/INSTRUCTIONAL RELEVANCE Resources: Essential Instructional Activities: 3|Page Summer 2011 Individual Teacher Activities: DAY # Day 1 “I CAN STATEMENTS….” Instructional Activities Formative Assessment Intervention Extension Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Ideas and Thoughts for Refinement 4|Page Summer 2011 5|Page Summer 2011