Biology II Chapter 5 Study Guide
... 5. ___________ law of thermodynamics (also called the law of conservation of energy), and energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another. (1st Law) 6. _______________ can be converted into mechanical energy. (Chemical energy) 7. _____ reactions are reactions th ...
... 5. ___________ law of thermodynamics (also called the law of conservation of energy), and energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another. (1st Law) 6. _______________ can be converted into mechanical energy. (Chemical energy) 7. _____ reactions are reactions th ...
Les 6b RNA Transcription and Translation
... A.A. allow the protein molecule to form its necessary structure Proteins have many structures/shapes ...
... A.A. allow the protein molecule to form its necessary structure Proteins have many structures/shapes ...
Biochemistry 462a - Proteins Extra Questions
... 5. The following question deals with the properties of amino acid sidechains buried in the hydrophobic interior of a protein. (A) Would the pKa of a buried lysine be higher or lower than the pKa of a surface Lys? (B) Would the strength of a buried hydrogen bond be stronger or weaker than a hydrogen ...
... 5. The following question deals with the properties of amino acid sidechains buried in the hydrophobic interior of a protein. (A) Would the pKa of a buried lysine be higher or lower than the pKa of a surface Lys? (B) Would the strength of a buried hydrogen bond be stronger or weaker than a hydrogen ...
Amino Acids, Proteins and Enzymes
... • ALL enantiomers are stereoisomers – Same formula, same chemical groups (COOH, NH3, etc.) but different spatial arrangement (like cis-trans) ...
... • ALL enantiomers are stereoisomers – Same formula, same chemical groups (COOH, NH3, etc.) but different spatial arrangement (like cis-trans) ...
Nucleotides
... • Linked by a 3′ → 5′ phosphodiester bond to form the “backbone” of RNA and DNA • RNAs are far less stable than DNA • Polynucleotides Are Directional Macromolecule – “5′- end” or the “3′- end” – the 5′- end is at the left ...
... • Linked by a 3′ → 5′ phosphodiester bond to form the “backbone” of RNA and DNA • RNAs are far less stable than DNA • Polynucleotides Are Directional Macromolecule – “5′- end” or the “3′- end” – the 5′- end is at the left ...
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
... including how easily substances react with one another. If the concentration of reactants increases, the rate of a chemical reaction (1) . When the temperature decreases, the speed of chemical reactions (2) . A (3) is a substance that increases the rate at which a chemical reaction proceeds without ...
... including how easily substances react with one another. If the concentration of reactants increases, the rate of a chemical reaction (1) . When the temperature decreases, the speed of chemical reactions (2) . A (3) is a substance that increases the rate at which a chemical reaction proceeds without ...
Notes - The University of Sydney
... base or acid. These solutions buffer best ± 1 pH unit either side of their pKa. The ratio of the acid and its conjugate base (or base and its conjugate acid) will determine the pH within this range. To work out the ratio of acid to base you employ the Henderson Hasselbalch equation (this equation us ...
... base or acid. These solutions buffer best ± 1 pH unit either side of their pKa. The ratio of the acid and its conjugate base (or base and its conjugate acid) will determine the pH within this range. To work out the ratio of acid to base you employ the Henderson Hasselbalch equation (this equation us ...
Gene expression PPT
... sites called promoters on DNA template strand. Transcription factor – Binds to promoter so that RNA polymerase can then bind Initiation – Other transcription factors bind, assembling a transcription initiation complex. – RNA polymerase begins to unwind DNA helix. ...
... sites called promoters on DNA template strand. Transcription factor – Binds to promoter so that RNA polymerase can then bind Initiation – Other transcription factors bind, assembling a transcription initiation complex. – RNA polymerase begins to unwind DNA helix. ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... Polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed to monosaccharides and then converted to glucose for glycolysis Proteins can be digested to amino acids, which are chemically altered and then used in the Krebs cycle Fats are broken up and fed into glycolysis and the Krebs cycle ...
... Polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed to monosaccharides and then converted to glucose for glycolysis Proteins can be digested to amino acids, which are chemically altered and then used in the Krebs cycle Fats are broken up and fed into glycolysis and the Krebs cycle ...
Protein Structure and Enzyme Function
... Student Background: Protein Structure and Enzyme Function Enzymes are nature’s ultimate multi-taskers. In our cells, they catalyze over 4,000 chemical reactions! They convert what we eat into cellular energy; they aid in cell communication and help regulate cellular processes. In the outside world, ...
... Student Background: Protein Structure and Enzyme Function Enzymes are nature’s ultimate multi-taskers. In our cells, they catalyze over 4,000 chemical reactions! They convert what we eat into cellular energy; they aid in cell communication and help regulate cellular processes. In the outside world, ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration.notebook
... Pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energyextracting reactions. Krebs Cycle occurs in mitochondrial matrix. Steps in the Krebs Cycle 1. Pyruvic acid from glycolsis enters the mitochondrion. 2. One Carbon from pyruvic acid becomes part of the molecule CO2, which wil ...
... Pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energyextracting reactions. Krebs Cycle occurs in mitochondrial matrix. Steps in the Krebs Cycle 1. Pyruvic acid from glycolsis enters the mitochondrion. 2. One Carbon from pyruvic acid becomes part of the molecule CO2, which wil ...
Translation - Phillipsburg School District
... • mRNA attaches to the ribosome (with the use of rRNA) • rRNA reads the mRNA in groups of 3 nucleotides called codons • Translation starts with a special codon – AUG—start codon—initiator ...
... • mRNA attaches to the ribosome (with the use of rRNA) • rRNA reads the mRNA in groups of 3 nucleotides called codons • Translation starts with a special codon – AUG—start codon—initiator ...
PracticeFinalSP2003
... bonds. Draw the polypeptide (short chain of amino acids) comprised by two alanine molecules and one glycine molecule in the order (ala)-(gly)-(ala). Draw a box around the peptide bonds in the molecule and mark with an asterisk any chiral carbons atoms. f) Digestion of proteins involves the ‘hydrolys ...
... bonds. Draw the polypeptide (short chain of amino acids) comprised by two alanine molecules and one glycine molecule in the order (ala)-(gly)-(ala). Draw a box around the peptide bonds in the molecule and mark with an asterisk any chiral carbons atoms. f) Digestion of proteins involves the ‘hydrolys ...
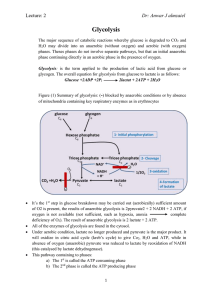
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... Each phase includes 5 reaction, therefore the pathway consist of ten reactions ...
... Each phase includes 5 reaction, therefore the pathway consist of ten reactions ...
Cellular Respiration
... of the cell and it has three parts associated with it: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain. ...
... of the cell and it has three parts associated with it: Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain. ...
complete week three vocabulary
... Activation Energy-‐ the energy requirement needed for reactants to undergo a chemical reaction Active Site-‐ the part of an enzyme where its substrate binds Aerobic Respiration-‐ respiration is a pathway ...
... Activation Energy-‐ the energy requirement needed for reactants to undergo a chemical reaction Active Site-‐ the part of an enzyme where its substrate binds Aerobic Respiration-‐ respiration is a pathway ...
Proteins - Many Structures, Many Functions
... bind to some other molecule. – For example, antibodies bind to particular foreign substances that fit their binding sites. – Enzyme recognize and bind to specific substrates, facilitating a chemical reaction. – Neurotransmitters pass signals from one cell to another by binding to receptor sites on p ...
... bind to some other molecule. – For example, antibodies bind to particular foreign substances that fit their binding sites. – Enzyme recognize and bind to specific substrates, facilitating a chemical reaction. – Neurotransmitters pass signals from one cell to another by binding to receptor sites on p ...
gil, virginia
... Carbon has a total of six electrons, with two in the first electron shell and four in the second shell. Having four valence electrons in a shell that holds eight, carbon has little tendency to gain or lose electrons and form ionic bonds; it would have to donate or accept for electrons to do so. Inst ...
... Carbon has a total of six electrons, with two in the first electron shell and four in the second shell. Having four valence electrons in a shell that holds eight, carbon has little tendency to gain or lose electrons and form ionic bonds; it would have to donate or accept for electrons to do so. Inst ...
Cellular Respiration
... Not all the H+ pumped out by the electrons shuttled by NADH and FADH2 are used to make ATP (they are used for other kinds of work). The ratio of NADH to ATP is wacky (10 H+ out for every one NADH, but we know what we don’t know. NADH from the cytosol made during glycolysis have issues. ...
... Not all the H+ pumped out by the electrons shuttled by NADH and FADH2 are used to make ATP (they are used for other kinds of work). The ratio of NADH to ATP is wacky (10 H+ out for every one NADH, but we know what we don’t know. NADH from the cytosol made during glycolysis have issues. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.