Unit Study Guide
... What is the role of DNA Helicase in the processes of replication and transcription? What is made at the end of transcription? Why does transcription have to take place; in other words, why is mRNA made? What is the role of the enzyme RNA polymerase in the process of transcription? Where does the mRN ...
... What is the role of DNA Helicase in the processes of replication and transcription? What is made at the end of transcription? Why does transcription have to take place; in other words, why is mRNA made? What is the role of the enzyme RNA polymerase in the process of transcription? Where does the mRN ...
DNA Extraction KEY
... 1. The DNA extraction buffer is made up of detergent and salt. Why is there detergent in the buffer? Break down the cell walls/ membranes. 2. What is the purpose of the salt found in extraction buffer? adds positive charge and neutralizes the negative charge of the DNA that is a result of the phosph ...
... 1. The DNA extraction buffer is made up of detergent and salt. Why is there detergent in the buffer? Break down the cell walls/ membranes. 2. What is the purpose of the salt found in extraction buffer? adds positive charge and neutralizes the negative charge of the DNA that is a result of the phosph ...
Exam Review 2B -- Rodermel
... 6. Explain the end replication problem and why not all DNA have this problem: ...
... 6. Explain the end replication problem and why not all DNA have this problem: ...
Genetics Introduction:
... o Watson and Crick discovered 3D structure of DNA o Molecular structure of DNA is double helix comprised of a linear sequence of paired nucleotide bases and a sugar phosphate backbone o Nucleotides= building blocks= phosphate + sugar (5C deoxyribose) + base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) o 2 ...
... o Watson and Crick discovered 3D structure of DNA o Molecular structure of DNA is double helix comprised of a linear sequence of paired nucleotide bases and a sugar phosphate backbone o Nucleotides= building blocks= phosphate + sugar (5C deoxyribose) + base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) o 2 ...
Chapter 9 DNA: The Genetic Material
... How did Watson & Crick figure it out? They used information from other scientists! Wilkins & Franklin used X-ray diffraction. ...
... How did Watson & Crick figure it out? They used information from other scientists! Wilkins & Franklin used X-ray diffraction. ...
Cribado genético del cáncer colorrectal mediante el estudio del
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
NAME CH11 In class assignment Due 2/18/14 Across 1. Initials of
... 2) When a restriction enzyme cuts a piece of DNA, portions of the ends are single stranded. Another term for these single stranded sections is: a) “single ends” b) “lonely ends” c) “sticky ends” d) “fragmented ends” 3) In order to produce a transgenic animal, DNA must be injected into the __________ ...
... 2) When a restriction enzyme cuts a piece of DNA, portions of the ends are single stranded. Another term for these single stranded sections is: a) “single ends” b) “lonely ends” c) “sticky ends” d) “fragmented ends” 3) In order to produce a transgenic animal, DNA must be injected into the __________ ...
Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls for aCGH and Microarray
... ParagonDx controls are of the highest standard for industry. DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
... ParagonDx controls are of the highest standard for industry. DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
... • Inbreeding- continued breeding of ind. with similar characteristics. – Ex- different dog breeds – Can be dangerous due to increased chance for genetic defects. ...
2 - Blue Valley Schools
... nitrogenous base five-carbon sugar adenine guanine cytosine Erwin Chargaff Rosalind Franklin x-ray diffraction 2 nm 0.34 nm James Watson Francis Crick double strand DNA replication hydrogen bonds base pair sugar phosphate backbone semiconservative DNA ligase DNA repair Chapter 12 protein synthesis t ...
... nitrogenous base five-carbon sugar adenine guanine cytosine Erwin Chargaff Rosalind Franklin x-ray diffraction 2 nm 0.34 nm James Watson Francis Crick double strand DNA replication hydrogen bonds base pair sugar phosphate backbone semiconservative DNA ligase DNA repair Chapter 12 protein synthesis t ...
Bell Ringer
... Genes in cells are made of DNA, which is a complex molecule. The structure of a DNA molecule contains the information that a cell needs to carry out all of its functions. In a way, DNA is like the cell’s encyclopedia. Suppose that you go to the library to do research for a science project. You find ...
... Genes in cells are made of DNA, which is a complex molecule. The structure of a DNA molecule contains the information that a cell needs to carry out all of its functions. In a way, DNA is like the cell’s encyclopedia. Suppose that you go to the library to do research for a science project. You find ...
Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two
... 2. Draw and label a diagram of translation showing a ribosome, mRNA, tRNA, and a polypeptide chain with at least 3 amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Questions 1. How are DNA and RNA different? 2. How does your genotype determine your phenotype (include DNA, RNA & protein)? 3. Use the following DN ...
... 2. Draw and label a diagram of translation showing a ribosome, mRNA, tRNA, and a polypeptide chain with at least 3 amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Questions 1. How are DNA and RNA different? 2. How does your genotype determine your phenotype (include DNA, RNA & protein)? 3. Use the following DN ...
Cell Cycle SG
... 14. The bases are always added from the ____________ direction to form the new DNA strands. 15. What makes a DNA molecule antiparallel? List all the differences between the leading & lagging strands. Strand How It is Built 16. leading strand 17. lagging strand 18. Label the following drawing of the ...
... 14. The bases are always added from the ____________ direction to form the new DNA strands. 15. What makes a DNA molecule antiparallel? List all the differences between the leading & lagging strands. Strand How It is Built 16. leading strand 17. lagging strand 18. Label the following drawing of the ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passedon to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mature organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring' ...
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passedon to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mature organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring' ...
Research Questions
... 1. How does a gene become a protein ? DNA creates mRNA to send to ribosomes through transcription , then ribosomes read the mRNA and convert the three nitrogen bases into an amino acid. Which then are fixed together , more complex ...
... 1. How does a gene become a protein ? DNA creates mRNA to send to ribosomes through transcription , then ribosomes read the mRNA and convert the three nitrogen bases into an amino acid. Which then are fixed together , more complex ...
Study Guide Ch
... 31. 3 base code of nitrogen bases is called a ____________________________________. 32. (T/F) 1 codon codes for 3 amino acid. 33. Condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes is called ___________________________________. 34. _____________________________________ is the tip of a euka ...
... 31. 3 base code of nitrogen bases is called a ____________________________________. 32. (T/F) 1 codon codes for 3 amino acid. 33. Condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes is called ___________________________________. 34. _____________________________________ is the tip of a euka ...
Intro to Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab
... Where have you heard of genes before? What do genes have to do with DNA? Gene = Segments of DNA that control the production of protein ...
... Where have you heard of genes before? What do genes have to do with DNA? Gene = Segments of DNA that control the production of protein ...
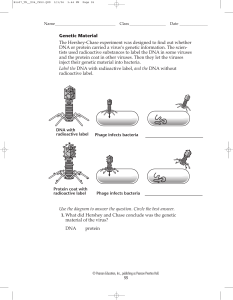
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> protein -> trait ...
... What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> protein -> trait ...
They are the offspring of these two people They are the
... Every organism exhibits one or more of the traits of their grandparents. Your description could involve; via the people who married into the family, by the expression of a recessive trait, via mutation. The children share more traits with parents than the grandchildren share. The children share more ...
... Every organism exhibits one or more of the traits of their grandparents. Your description could involve; via the people who married into the family, by the expression of a recessive trait, via mutation. The children share more traits with parents than the grandchildren share. The children share more ...
Multiple choice questions
... Hydrogen bonds are covalent bonds stabilize the DNA double helix stabilize protein structures form between two electronegative atoms form between adenin and guanine have a bond energy of 20-30 kcal mol-1 ...
... Hydrogen bonds are covalent bonds stabilize the DNA double helix stabilize protein structures form between two electronegative atoms form between adenin and guanine have a bond energy of 20-30 kcal mol-1 ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between proteins are due to the amino acids they contain. DNA is a sequence of bases and each set of three bases ...
... genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between proteins are due to the amino acids they contain. DNA is a sequence of bases and each set of three bases ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.