Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 2
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
Bulletin 1 - DNA: The Cookbook of Life - ctahr
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
Evolution process by which species change over time
... DNA Evidence of Evolution • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic ...
... DNA Evidence of Evolution • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic ...
glossary of technical terms
... The field of science and engineering relating to the adaptation of living organisms or biological processes to industrial and commercial applications. ...
... The field of science and engineering relating to the adaptation of living organisms or biological processes to industrial and commercial applications. ...
Pierce chapter 10
... • Binds to certain DNA sequences; bends DNA – Facilitates binding of transcription proteins; activates genes for male traits ...
... • Binds to certain DNA sequences; bends DNA – Facilitates binding of transcription proteins; activates genes for male traits ...
Review Questions - effinghamschools.com
... What is NOT true of DNA a) It is located in the nucleus b) It delivers information for making proteins to the ribosome. c) It provides instructions for controling cell activities d) It is found in all living organisms e) All of these are true ...
... What is NOT true of DNA a) It is located in the nucleus b) It delivers information for making proteins to the ribosome. c) It provides instructions for controling cell activities d) It is found in all living organisms e) All of these are true ...
2015 Chaffey College Poster
... different traits and look different. The sequence targeted in this case is the common gene on the DNA of all fish which codes for the 16S ribosome and this is called “mitochondrial targeHng”. T ...
... different traits and look different. The sequence targeted in this case is the common gene on the DNA of all fish which codes for the 16S ribosome and this is called “mitochondrial targeHng”. T ...
Document
... Erwin Chargaff showed that the percentages of adenine and thymine are almost always equal in DNA. The percentages of guanine and cytosine are also almost equal. Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray diffraction studies revealed the double-helix structure of DNA. James Watson and Francis Crick built a model that ...
... Erwin Chargaff showed that the percentages of adenine and thymine are almost always equal in DNA. The percentages of guanine and cytosine are also almost equal. Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray diffraction studies revealed the double-helix structure of DNA. James Watson and Francis Crick built a model that ...
What are the potential benefits to knowing more - B
... 1.What are the potential benefits to knowing more about your genetic predisposition to disease? 2.What are the possible negatives to knowing? ...
... 1.What are the potential benefits to knowing more about your genetic predisposition to disease? 2.What are the possible negatives to knowing? ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
... (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
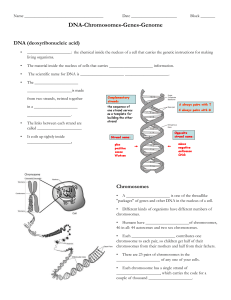
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Document
... Structure of DNA Using Rosalind Franklin’s data, two scientists: James Watson (USA) Francis Crick (GBR) Proposed that DNA was a double-helix. Watson & Crick along with Maurice Wilkins jointly received the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for their work. ...
... Structure of DNA Using Rosalind Franklin’s data, two scientists: James Watson (USA) Francis Crick (GBR) Proposed that DNA was a double-helix. Watson & Crick along with Maurice Wilkins jointly received the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for their work. ...
chapter 19_updates
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
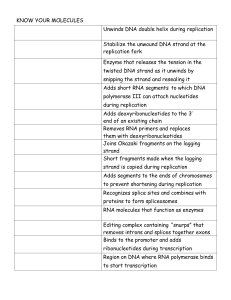
Know your molecules organizer
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
Revisiting Genetics
... They are guanine (G), cytosine, thymine, adenine) RNA = ribonucleic acid similar to DNA except it has a uracil nucleotide rather than a thymine. ...
... They are guanine (G), cytosine, thymine, adenine) RNA = ribonucleic acid similar to DNA except it has a uracil nucleotide rather than a thymine. ...
Modern Genetics
... The structure of DNA was discovered in the 1950’s by James Watson and Francis Crick. According to Watson and Crick, DNA molecules are shaped like a twisted ladder. The twisted ladder structure is called a double helix. ...
... The structure of DNA was discovered in the 1950’s by James Watson and Francis Crick. According to Watson and Crick, DNA molecules are shaped like a twisted ladder. The twisted ladder structure is called a double helix. ...
GENETICS
... • If the DNA in one cell were stretched out into one line it would be 3 meter long. • To fit into the cell the DNA is packaged into compact units called chromosomes. • To fit all of the DNA into chromosomes the DNA is first twisted into a double helix then further twisted around protein molecules. • ...
... • If the DNA in one cell were stretched out into one line it would be 3 meter long. • To fit into the cell the DNA is packaged into compact units called chromosomes. • To fit all of the DNA into chromosomes the DNA is first twisted into a double helix then further twisted around protein molecules. • ...
Document
... 12. List two examples of things proteins help determine about you. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... 12. List two examples of things proteins help determine about you. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
DIR RD 4C-2
... 12. List two examples of things proteins help determine about you. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... 12. List two examples of things proteins help determine about you. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis Test Study Guide THERE WILL BE 21
... mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUCG. 15. What would the sequence of DNA be from which the mRNA strand CUCAAGUGCUUC was made? 16. The original DNA sequence below undergoes the following chang ...
... mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUCG. 15. What would the sequence of DNA be from which the mRNA strand CUCAAGUGCUUC was made? 16. The original DNA sequence below undergoes the following chang ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.