DNA REVIEW SHEET
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
Organism Genome (kb) Form
... chromatin fibre • Chromatin is formed by wrapping the DNA around complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different typ ...
... chromatin fibre • Chromatin is formed by wrapping the DNA around complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different typ ...
CH-13 Sect 1
... which is a small circular DNA molecule found naturally in some bacteria. The culture is treated with a(an) ______________, a compound that kills bacteria ...
... which is a small circular DNA molecule found naturally in some bacteria. The culture is treated with a(an) ______________, a compound that kills bacteria ...
Honors Biology Final Exam-‐Part 2-‐Semester 2
... 1. The process of cell division which produces cells identical to the original cell is: 2. The purpose of meiosis is to produce ____________ . 3. Body cells are 2n or ________________ . 4. Ga ...
... 1. The process of cell division which produces cells identical to the original cell is: 2. The purpose of meiosis is to produce ____________ . 3. Body cells are 2n or ________________ . 4. Ga ...
Bell work Objectives: DNA replication DNA Replication
... As we discussed in class, the DNA molecules consists of nitrogen base pairs. The order of the pairs determines the genetic code, which controls protein synthesis or the production of proteins. 6. What do we call a set of three nitrogen bases? ___________________ or ____________________ ...
... As we discussed in class, the DNA molecules consists of nitrogen base pairs. The order of the pairs determines the genetic code, which controls protein synthesis or the production of proteins. 6. What do we call a set of three nitrogen bases? ___________________ or ____________________ ...
Chapters Bacteria, viruses, prions
... Made of NUCLEIC ACID surrounded by PROTEIN COAT Tiny: smaller than ribosomes Can be double/single stranded Can have DNA/RNA Protein shell = CAPSID Some have ENVELOPES around capsid that aid in host infection BACTERIOPHAGES-viruses that infect bacteria Have no cellular machinery of their own Can only ...
... Made of NUCLEIC ACID surrounded by PROTEIN COAT Tiny: smaller than ribosomes Can be double/single stranded Can have DNA/RNA Protein shell = CAPSID Some have ENVELOPES around capsid that aid in host infection BACTERIOPHAGES-viruses that infect bacteria Have no cellular machinery of their own Can only ...
Dioxyribose Nucleic Acid
... that an organism needs to grow and function. DNA makes you who you are. ...
... that an organism needs to grow and function. DNA makes you who you are. ...
DNA as Videotape: Introductory Fact Sheet
... DNA is a tape--it's linear. • It carries information--genetic information. • The information is encoded. • The information has to be translated. • Cells translate the information on DNA. • The information on DNA makes traits.– genes • Cells can copy DNA. • DNA can be edited--for example, we can take ...
... DNA is a tape--it's linear. • It carries information--genetic information. • The information is encoded. • The information has to be translated. • Cells translate the information on DNA. • The information on DNA makes traits.– genes • Cells can copy DNA. • DNA can be edited--for example, we can take ...
Gene Q
... Questions 9 and 10 pertain to the following. Six independently derived mutants are recovered in Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound Z. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to compound Z. A summary of the ability of t ...
... Questions 9 and 10 pertain to the following. Six independently derived mutants are recovered in Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound Z. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to compound Z. A summary of the ability of t ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure ...
... Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure ...
DNA TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 11: (38) In DNA, which of
... Which of these molecules carries this code? A* DNA B ATP C Glucose D Lipid FALL 2005 – 11: 28 “Thymine—guanine—thymine—cytosine” describes — F nucleotides within an RNA strand G* a sequence of bases within a DNA section H points of DNA separation during protein synthesis J tRNA codons for specific a ...
... Which of these molecules carries this code? A* DNA B ATP C Glucose D Lipid FALL 2005 – 11: 28 “Thymine—guanine—thymine—cytosine” describes — F nucleotides within an RNA strand G* a sequence of bases within a DNA section H points of DNA separation during protein synthesis J tRNA codons for specific a ...
Biology Test Topics Chapters 11-12 Slideshows
... If the DNA of all organisms uses the same four bases (A, T, G, and C) then what accounts for the diversity of organisms? What is the process called by which DNA copies itself? What does it mean to say that DNA has “complimentary” strands? What does it mean to say that this process is “semi-conservat ...
... If the DNA of all organisms uses the same four bases (A, T, G, and C) then what accounts for the diversity of organisms? What is the process called by which DNA copies itself? What does it mean to say that DNA has “complimentary” strands? What does it mean to say that this process is “semi-conservat ...
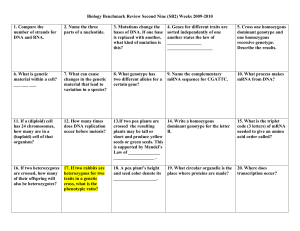
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel’s Law of ______________ __________________ . ...
... short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel’s Law of ______________ __________________ . ...
DNA WebQuest - Pearland ISD
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
Mutations
... • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an ...
... • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an ...
Name: DNA Stations Once Mendel`s work was rediscovered in the
... 10. What are three macromolecules Avery thought might hold the genetic information? ...
... 10. What are three macromolecules Avery thought might hold the genetic information? ...
PDF
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
... The DNA inside a cell is packaged very tightly into chromosomes. Within a human cell, 23 pairs of chromosomes fit in a structure that is one-tenth the width of a human hair, but if you unwound the chromosomes, the DNA would be six feet long. All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make ...
DNA: Structure and Function
... Famous Experiments from the 1940’s-1960’s that indicated DNA was the Molecule of Heredity • Griffith & Avery—DNA transformed nonvirulent bacteria to virulent bacteria • Hershey & Chase—DNA from viruses is injected to host bacteria cells, cells become ...
... Famous Experiments from the 1940’s-1960’s that indicated DNA was the Molecule of Heredity • Griffith & Avery—DNA transformed nonvirulent bacteria to virulent bacteria • Hershey & Chase—DNA from viruses is injected to host bacteria cells, cells become ...
Biology Name DNA Worksheet Period ______ Use your textbook to
... Explain why DNA replication is necessary for the continuation of life. ...
... Explain why DNA replication is necessary for the continuation of life. ...
Human Genomics - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... • To identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in human DNA. • To find where each gene is located • To determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA. • Store this information in databases. • Estimated time 15 years. (started in 1980) • Estimated cost US ...
... • To identify all the approximately 20,000-25,000 genes in human DNA. • To find where each gene is located • To determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA. • Store this information in databases. • Estimated time 15 years. (started in 1980) • Estimated cost US ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... DNA chains can be very long ! E. coli chromosome: 4.6x106 base pairs: 4.6x 106 x .34 nm = 1.5x106 nm = 1.5 mm ! Human DNA: 6x10-12 g/cell x 1/660 mol bp/g x 6.023x1023 bp/mol bp x 0.34x10-9 m/bp = 1.9 m ! Bacterial, viral DNA “chromosomes” are circles ! DNA in human chromosomes (and DNA of all euka ...
... DNA chains can be very long ! E. coli chromosome: 4.6x106 base pairs: 4.6x 106 x .34 nm = 1.5x106 nm = 1.5 mm ! Human DNA: 6x10-12 g/cell x 1/660 mol bp/g x 6.023x1023 bp/mol bp x 0.34x10-9 m/bp = 1.9 m ! Bacterial, viral DNA “chromosomes” are circles ! DNA in human chromosomes (and DNA of all euka ...
Worksheet for Biology 1107 Biological Molecules: Structure and
... 7. List the names of the four fatty acids found on page 3 of the biomolecules text. ...
... 7. List the names of the four fatty acids found on page 3 of the biomolecules text. ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.