DNA functions worksheet
... 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for A. the sequence of amino acids in a protein B. the sequence of base pairs C. producing mutations D. making a recipe 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the structure of chromosomes? ...
... 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for A. the sequence of amino acids in a protein B. the sequence of base pairs C. producing mutations D. making a recipe 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the structure of chromosomes? ...
DNA REPLICATION HANDOUT
... 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while the other is 3’ to 5’. As you kno ...
... 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while the other is 3’ to 5’. As you kno ...
DNA Fingerprinting Notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... DNA replication protein synthesis genetic recombination ...
... DNA replication protein synthesis genetic recombination ...
Chapter 12 Review PPT
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
point of view that is personal rather than scientific
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
... The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(an) ____________________, in which two strands are wound around each other. double helix ...
Understanding DNA
... 2. Draw the cell and label the ff structures: a. cell membrane Note: Follow guidelines on b. chromosomes Making Diagrams ...
... 2. Draw the cell and label the ff structures: a. cell membrane Note: Follow guidelines on b. chromosomes Making Diagrams ...
Genetic Engineering
... Genetic Engineering the manipulation of living organisms for human use Chapter 13 ...
... Genetic Engineering the manipulation of living organisms for human use Chapter 13 ...
Webquest
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
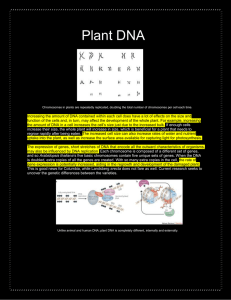
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... Chromosomes in plants are repeatedly replicated, doubling the total number of chromosomes per cell each time. ...
... Chromosomes in plants are repeatedly replicated, doubling the total number of chromosomes per cell each time. ...
Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
... psychological traits and was first identified in 1869. His structure, which was discovered by Francis Crick and James Watson in the middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: ...
... psychological traits and was first identified in 1869. His structure, which was discovered by Francis Crick and James Watson in the middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... the building blocks of DNA (and RNA) one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are tw ...
... the building blocks of DNA (and RNA) one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are tw ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... the building blocks of DNA (and RNA) one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are tw ...
... the building blocks of DNA (and RNA) one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are tw ...
Part I, for Exam 1: 1. Based on Chargaff`s rules, which of the
... 6. Describe qualitatively how the tm (melting temperature) for a double-stranded DNA depends upon its ...
... 6. Describe qualitatively how the tm (melting temperature) for a double-stranded DNA depends upon its ...
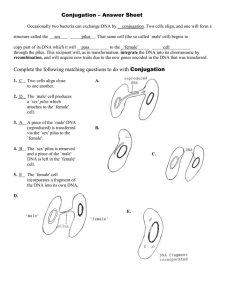
Conjugation Answer Sheet
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
genetics i - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... 11. (a) Name the enzyme that catalyzes the transcription of hnRNA. (b) Why does the hnRNA need to undergo changes? List the changes hnRNA undergoes and where in the cell such changes take place? 12. Name the different components present in deoxy-ribose nucleoside triphosphates. Give its two roles. 1 ...
... 11. (a) Name the enzyme that catalyzes the transcription of hnRNA. (b) Why does the hnRNA need to undergo changes? List the changes hnRNA undergoes and where in the cell such changes take place? 12. Name the different components present in deoxy-ribose nucleoside triphosphates. Give its two roles. 1 ...
Honors Biology
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
7529 DNA Sequencing - ACM
... Krusty Krab out of business. So, SpongeBob and his co-workers decided to switch to a brand new job. Their new startup is Krusty-Royan, a biological research institute whose main focus is on DNA sequencing. Their first customer is Sandy, the squirrel scientist, who has found the corpse of an alien fr ...
... Krusty Krab out of business. So, SpongeBob and his co-workers decided to switch to a brand new job. Their new startup is Krusty-Royan, a biological research institute whose main focus is on DNA sequencing. Their first customer is Sandy, the squirrel scientist, who has found the corpse of an alien fr ...
Questions - Humble ISD
... 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base is called ______ & includes _______ & _______ 7. a. Name the bond that holds the nucleotide together __________________ b. Name the bond between the nitrogen bases __________________ 8. What is DNA repl ...
... 5. A single-ringed N-base is called _____ & includes ________ & _______ 6. A double-ringed N-base is called ______ & includes _______ & _______ 7. a. Name the bond that holds the nucleotide together __________________ b. Name the bond between the nitrogen bases __________________ 8. What is DNA repl ...
jeopardy honors DNA
... into galactose and glucose in prokaryotes, and ____________ breaks lactose into glucose and galactose in eukaryotes. ...
... into galactose and glucose in prokaryotes, and ____________ breaks lactose into glucose and galactose in eukaryotes. ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.