Kingdom Animalia - Evolution of Form and Function
... A triploblastic, probably vermiform organism with a complete digestive tract; coelom formed via enterocoely; radial, indeterminate cleavage, embryonic nervous system dorsal; embryonic circulatory system ventral. 10. For each of the following taxa, list the synapomorphies that set might them apart fr ...
... A triploblastic, probably vermiform organism with a complete digestive tract; coelom formed via enterocoely; radial, indeterminate cleavage, embryonic nervous system dorsal; embryonic circulatory system ventral. 10. For each of the following taxa, list the synapomorphies that set might them apart fr ...
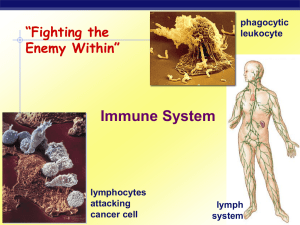
the lymphatic system and immunity
... called lymph capillaries. Lymph capillaries may occur singly or in extensive plexuses. They originate throughout the body, but not in avascular tissue, the central nervous system, splenic pulp, nor bone marrow. They are slightly larger and more permeable than blood capillaries. Lymph capillaries als ...
... called lymph capillaries. Lymph capillaries may occur singly or in extensive plexuses. They originate throughout the body, but not in avascular tissue, the central nervous system, splenic pulp, nor bone marrow. They are slightly larger and more permeable than blood capillaries. Lymph capillaries als ...
Sponges - A Coloring Worksheet
... for a sponge to reproduce asexually: budding, gemmules, and regeneration. Sponges can simply reproduce by budding, where a new sponge grows from older ones and eventually break off. Color the adult sponge pink and all the buds you can find red. Sponges can also reproduce by regeneration, where missi ...
... for a sponge to reproduce asexually: budding, gemmules, and regeneration. Sponges can simply reproduce by budding, where a new sponge grows from older ones and eventually break off. Color the adult sponge pink and all the buds you can find red. Sponges can also reproduce by regeneration, where missi ...
Taxonomy and Systematics: Seeking Order Amidst Diversity
... None of the following are unique to animals, but together distinguish animals from other organisms: Multicellular; heterotrophic; no cell walls; motile during some stage(s) in life A great diversity of body plans occur; some key features include: Organized federation of cells vs. cells in tissues Ti ...
... None of the following are unique to animals, but together distinguish animals from other organisms: Multicellular; heterotrophic; no cell walls; motile during some stage(s) in life A great diversity of body plans occur; some key features include: Organized federation of cells vs. cells in tissues Ti ...
Objectives
... above, the tissue looks like a sheet polygonal cells, much like a tile floor. 7. If you are having trouble distinguishing between two tissue types (say, transitional vs. stratified squamous), consider comparing them on two different microscopes placed along side of each other. Look at each one, goin ...
... above, the tissue looks like a sheet polygonal cells, much like a tile floor. 7. If you are having trouble distinguishing between two tissue types (say, transitional vs. stratified squamous), consider comparing them on two different microscopes placed along side of each other. Look at each one, goin ...
Objectives
... above, the tissue looks like a sheet polygonal cells, much like a tile floor. 7. If you are having trouble distinguishing between two tissue types (say, transitional vs. stratified squamous), consider comparing them on two different microscopes placed along side of each other. Look at each one, goin ...
... above, the tissue looks like a sheet polygonal cells, much like a tile floor. 7. If you are having trouble distinguishing between two tissue types (say, transitional vs. stratified squamous), consider comparing them on two different microscopes placed along side of each other. Look at each one, goin ...
AS 12-13 Cards 1-137_Layout 1
... contributes to each of these cavities. The ethmoid bone consists of four parts: a horizontal or cribriform plate, forming part of the base of the cranium; a perpendicular plate, constituting part of the nasal septum; and two lateral masses or labyrinths. • Cribriform plate: Contains many olfactory f ...
... contributes to each of these cavities. The ethmoid bone consists of four parts: a horizontal or cribriform plate, forming part of the base of the cranium; a perpendicular plate, constituting part of the nasal septum; and two lateral masses or labyrinths. • Cribriform plate: Contains many olfactory f ...
Chapter 10 1. When the adult of a descendant species resembles
... The oldest proglottids at the end of a tapeworm are filled with eggs, and are said to be adult. female. pregnant. mature. gravid. ...
... The oldest proglottids at the end of a tapeworm are filled with eggs, and are said to be adult. female. pregnant. mature. gravid. ...
Albert - Brookings School District
... The process of breathing is called respiration. First, air is taken into the lungs by the process of inhalation. A large sheet of muscle under the lungs called the diaphragm contracts, increasing the volume and decreasing the pressure in the lungs about 2 mm Hg. Additional chest muscles may assi ...
... The process of breathing is called respiration. First, air is taken into the lungs by the process of inhalation. A large sheet of muscle under the lungs called the diaphragm contracts, increasing the volume and decreasing the pressure in the lungs about 2 mm Hg. Additional chest muscles may assi ...
flatworms powerpoint
... a process called fission. The anterior and posterior ends hold a surface and the midsection constricts. This results in two new flatworms, one from the anterior end of the original flatworm and the other from the posterior end of the original flatworm. ...
... a process called fission. The anterior and posterior ends hold a surface and the midsection constricts. This results in two new flatworms, one from the anterior end of the original flatworm and the other from the posterior end of the original flatworm. ...
Phylum Porifera - Mr.Nolan`s Science Class`s
... ring of tentacles surrounds a central mouth stinging cells on the tentacles, cnidocytes, paralyse and capture prey first animals with a digestive system: gut has one opening serving as both mouth and anus gastrovascular cavity = simple digestive system with only one opening ...
... ring of tentacles surrounds a central mouth stinging cells on the tentacles, cnidocytes, paralyse and capture prey first animals with a digestive system: gut has one opening serving as both mouth and anus gastrovascular cavity = simple digestive system with only one opening ...
six key transitions in body plan
... approximate mirror images. • Bilateral symmetry is a body plan with distinct right and left halves that are mirror images. • The plan allows for specialization among body regions and more efficient movement. ...
... approximate mirror images. • Bilateral symmetry is a body plan with distinct right and left halves that are mirror images. • The plan allows for specialization among body regions and more efficient movement. ...
WikiJunior Biology - USP Theses Collection
... mitochondria - An organelle that makes power in a cell chloroplast - An organelle that makes sugar found in a plant or protist. ribosomes - An organelle that makes things called proteins. flagella - A tail on a cell that makes it swim. golgi body - An organelle which helps in secretion. ribosome - A ...
... mitochondria - An organelle that makes power in a cell chloroplast - An organelle that makes sugar found in a plant or protist. ribosomes - An organelle that makes things called proteins. flagella - A tail on a cell that makes it swim. golgi body - An organelle which helps in secretion. ribosome - A ...
Regents Biology - I Heart Science
... disadvantage use only after sick only good against bacteria ...
... disadvantage use only after sick only good against bacteria ...
Primary Sinus Surgery
... Infundibulum – funnel shaped area whereby the maxillary, ant ethmoid and frontal sinuses drains ...
... Infundibulum – funnel shaped area whereby the maxillary, ant ethmoid and frontal sinuses drains ...
1-Week 1-121
... Anatomy. Nevertheless, through this experience, we expect that you will acquire fundamental skills, reinforce and expand your knowledge, and develop personally and professionally. We hope that this experience drives you to learn more and experience more of what Anatomy has to offer. We wish you the ...
... Anatomy. Nevertheless, through this experience, we expect that you will acquire fundamental skills, reinforce and expand your knowledge, and develop personally and professionally. We hope that this experience drives you to learn more and experience more of what Anatomy has to offer. We wish you the ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... 49. Which of the following is a auditory receptor? A. Organ of corti B. Cristae ampullaris C. Utricle D. Saccule 50. Which of the following types of glial cells form myelin around the axons of the CNS? A. Oligondendrocytes B. Astrocytes form BBB C. Ependymal AKA: corcoid plexus what produces CFS ...
... 49. Which of the following is a auditory receptor? A. Organ of corti B. Cristae ampullaris C. Utricle D. Saccule 50. Which of the following types of glial cells form myelin around the axons of the CNS? A. Oligondendrocytes B. Astrocytes form BBB C. Ependymal AKA: corcoid plexus what produces CFS ...
Diseases of the endocrine system
... The word endocrine derives from the Greek words "endo," meaning within, and "crinis," meaning secrete. A group of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis. One example is the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal axis, which coordinates interactions among the hypothalamus ...
... The word endocrine derives from the Greek words "endo," meaning within, and "crinis," meaning secrete. A group of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis. One example is the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal axis, which coordinates interactions among the hypothalamus ...
Chapter 15 - Trematoda: Classification and Form and Function of
... • Young flukes which develop parthenogenetically in rediae and sporocysts • During their development, propagatory cells, derived from the original germ cell, give rise to the anlagen of the reproductive system of the adult fluke • Mouth is usually surrounded by an oral sucker • Mouth lead to the pha ...
... • Young flukes which develop parthenogenetically in rediae and sporocysts • During their development, propagatory cells, derived from the original germ cell, give rise to the anlagen of the reproductive system of the adult fluke • Mouth is usually surrounded by an oral sucker • Mouth lead to the pha ...
Chapter 28 Simple Invertebrates
... • They are animals but they completely lack symmetry (asymmetry) and are just a mass of specialized cells • Sort of like the sand-man in SpiderMan3- if you put the cells through a mesh sieve they would find each other and get back together again making a new sponge. ...
... • They are animals but they completely lack symmetry (asymmetry) and are just a mass of specialized cells • Sort of like the sand-man in SpiderMan3- if you put the cells through a mesh sieve they would find each other and get back together again making a new sponge. ...
Paraxial mesoderm
... embryological origin and mode of ossification. Describe the ossification of long bones. Describe the main steps for development of limbs. Differentiate muscles according to their embryological origin. ...
... embryological origin and mode of ossification. Describe the ossification of long bones. Describe the main steps for development of limbs. Differentiate muscles according to their embryological origin. ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.