CHAPTER 2 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Animals, like plants, absorb
... Animals, like plants, absorb their food in fluid form. In order that solid food shall become fluid, preparatory to being taken into the blood stream, it must un dergo certain mechanical and chemical changes. The parts of the body set aside for this purpose are known as the di gestive or alimentary ...
... Animals, like plants, absorb their food in fluid form. In order that solid food shall become fluid, preparatory to being taken into the blood stream, it must un dergo certain mechanical and chemical changes. The parts of the body set aside for this purpose are known as the di gestive or alimentary ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes
... Type of fission in which the worm divides into two fragments without prior differentiation of new parts. Transverse cleavage just posterior to the pharynx divides the worm into an anterior, nearly normal, worm with head, mouth, pharynx and most of the gut, and an incomplete, headless posterior mas ...
... Type of fission in which the worm divides into two fragments without prior differentiation of new parts. Transverse cleavage just posterior to the pharynx divides the worm into an anterior, nearly normal, worm with head, mouth, pharynx and most of the gut, and an incomplete, headless posterior mas ...
Bio2Unit1-7.14.15 - Grainger County Schools
... CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through communication and transport. 3216.1.2Conduct an experiment or simulation to demonstrate the movement of molecules through diffusion, facilitate ...
... CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through communication and transport. 3216.1.2Conduct an experiment or simulation to demonstrate the movement of molecules through diffusion, facilitate ...
Tissues
... Most of the tissues they contain are living. Another difference between animals and plants is in the pattern of growth. The growth in plants is limited to certain regions, while this is not so in animals. There are some tissues in plants that divide throughout their life. These tissues are localised ...
... Most of the tissues they contain are living. Another difference between animals and plants is in the pattern of growth. The growth in plants is limited to certain regions, while this is not so in animals. There are some tissues in plants that divide throughout their life. These tissues are localised ...
as a PDF
... Evolutionary loss of tails of ascidian tadpoles contrasts with the conservatism of the vertebrate ‘pharyngula’ stage. Similarities among vertebrate pharyngulas was an inspiration for von Baer’s and Haeckel’s laws on evolutionary conservatism of early stages in development. The conservatism of the ph ...
... Evolutionary loss of tails of ascidian tadpoles contrasts with the conservatism of the vertebrate ‘pharyngula’ stage. Similarities among vertebrate pharyngulas was an inspiration for von Baer’s and Haeckel’s laws on evolutionary conservatism of early stages in development. The conservatism of the ph ...
Chapter 13 - Angelo State University
... layers: ectoderm and endoderm; mesoderm may be derived from ectoderm. There is an internal body cavity: the gastrovascular cavity. Extracellular digestion occurs in the gastrovascular cavity; gastrodermal cells accomplish cellular digestion. ...
... layers: ectoderm and endoderm; mesoderm may be derived from ectoderm. There is an internal body cavity: the gastrovascular cavity. Extracellular digestion occurs in the gastrovascular cavity; gastrodermal cells accomplish cellular digestion. ...
Development anatomy of the respiratory organ
... directed more laterally than • In the next division step, which the somewhat larger one on occurs at the end of the embryonic period, the the right that - parallel to segments of the individual the esophagus - is directed pulmonary lobes arise. more caudally. ...
... directed more laterally than • In the next division step, which the somewhat larger one on occurs at the end of the embryonic period, the the right that - parallel to segments of the individual the esophagus - is directed pulmonary lobes arise. more caudally. ...
tissues - Linn-Benton Community College
... Cells closely packed form continuous sheets Little space between cells Polarity (apical vs. basal) Supported by connective tissue Avascular but innervated Exception = glandular tissue is vascular ...
... Cells closely packed form continuous sheets Little space between cells Polarity (apical vs. basal) Supported by connective tissue Avascular but innervated Exception = glandular tissue is vascular ...
Embryology Respiratory System د.ايناس فاضل كاظم
... gas exchange) until after birth. The respiratory tract, diaphragm and lungs do form early in embryonic development. The respiratory tract is divided anatomically into 2 main parts: 1. upper respiratory tract, consisting of the nose, nasal cavity and the pharynx 2. lower respiratory tract consisting ...
... gas exchange) until after birth. The respiratory tract, diaphragm and lungs do form early in embryonic development. The respiratory tract is divided anatomically into 2 main parts: 1. upper respiratory tract, consisting of the nose, nasal cavity and the pharynx 2. lower respiratory tract consisting ...
Chapter 25: What is an animal?
... known as an embryo. Recall that an embryo is an organism at an early stage of growth and development. The two cells that result from cleavage then divide to form four cells and so on, until a cell-covered, fluid-filled ball called a blastula (BLAS chuh luh) is formed. In some animals, such as a lanc ...
... known as an embryo. Recall that an embryo is an organism at an early stage of growth and development. The two cells that result from cleavage then divide to form four cells and so on, until a cell-covered, fluid-filled ball called a blastula (BLAS chuh luh) is formed. In some animals, such as a lanc ...
2- Vascular and muscular coat:
... ANATOMY LAB 1 This sheet can be read after the lab handout , it's just a main points plus extra note ...
... ANATOMY LAB 1 This sheet can be read after the lab handout , it's just a main points plus extra note ...
Document
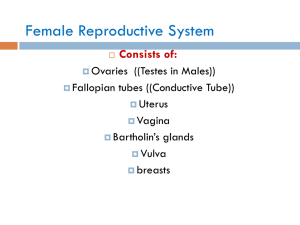
... cells called the germinal epithelium • Embedded in the ovary cortex are ovarian follicles • Each follicle consists of an immature egg called an oocyte • Cells around the oocyte are called: • Follicle cells (one cell layer thick) • Granulosa cells (when more than one layer is present) Copyright © 200 ...
... cells called the germinal epithelium • Embedded in the ovary cortex are ovarian follicles • Each follicle consists of an immature egg called an oocyte • Cells around the oocyte are called: • Follicle cells (one cell layer thick) • Granulosa cells (when more than one layer is present) Copyright © 200 ...
PAROTID GLANDS - Chennai City Branch Of ASI
... glands lying largely below the external acoustic meatus between mandible and sternocleidomastoid muscle and it also projects forwards on the surface of masseter ...
... glands lying largely below the external acoustic meatus between mandible and sternocleidomastoid muscle and it also projects forwards on the surface of masseter ...
The Nose
... ethmoid , the frontal bone , the nasal bone & the nasal cartilages . The lateral wall is marked by three projections called the superior , meddle , inferior nasal conchae . the area below each concha is referred to as ameatus . The spheno- ethmoidal recess is a small area of the nose that lies above ...
... ethmoid , the frontal bone , the nasal bone & the nasal cartilages . The lateral wall is marked by three projections called the superior , meddle , inferior nasal conchae . the area below each concha is referred to as ameatus . The spheno- ethmoidal recess is a small area of the nose that lies above ...
Prenatal Development Timeline
... Early pregnancy factor (EPF) Activation of the genome Blastomeres begin rapidly dividing ...
... Early pregnancy factor (EPF) Activation of the genome Blastomeres begin rapidly dividing ...
Placenta and Extraembryonic Membranes
... the sixth week, when blood-forming activity transfers to intraembryonic sites, especially the liver. As the tubular gut forms, the attachment site of the yolk stalk becomes progressively less prominent, until by 6 weeks it has effectively lost contact with the gut. In a small percentage of adults, t ...
... the sixth week, when blood-forming activity transfers to intraembryonic sites, especially the liver. As the tubular gut forms, the attachment site of the yolk stalk becomes progressively less prominent, until by 6 weeks it has effectively lost contact with the gut. In a small percentage of adults, t ...
Anatomy handout
... The excretory system is concerned with the removal of the waste products of metabolism, which consist of carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen-containing substances. The organs of excretion are the gills, spleen, liver, and kidney. The gills, as mentioned previously, are concerned with the interchan ...
... The excretory system is concerned with the removal of the waste products of metabolism, which consist of carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen-containing substances. The organs of excretion are the gills, spleen, liver, and kidney. The gills, as mentioned previously, are concerned with the interchan ...
Gustatory and Olfactory Systems - Dr. Costanzo
... Individual taste buds are made up of specialized epithelial cells (approximately 40-50 cells per bud) which form a barrel-shaped structure. At the surface of each taste bud is a small fluid-filled opening in the epithelium called the taste pore. It is through this pore that chemical stimuli reach t ...
... Individual taste buds are made up of specialized epithelial cells (approximately 40-50 cells per bud) which form a barrel-shaped structure. At the surface of each taste bud is a small fluid-filled opening in the epithelium called the taste pore. It is through this pore that chemical stimuli reach t ...
iv) What kind of variation is shown by Tay-Sachs
... 6. Give the name of two plants that can be used in medicines and the diseases they can treat. 7. Describe how a sugary plant can be used to make a fuel. 8a) Why are we having to look at better ways of growing food plants? b) What is the name of the method used to increase the yield of crop plants? c ...
... 6. Give the name of two plants that can be used in medicines and the diseases they can treat. 7. Describe how a sugary plant can be used to make a fuel. 8a) Why are we having to look at better ways of growing food plants? b) What is the name of the method used to increase the yield of crop plants? c ...
Schwannoma - Rackcdn.com
... of which served as the basis for the analysis of our cases – Lesion location: They concluded, in congruence with other published case reports, that these lesions occurred mostly in the nasal cavity or within the ethmoid air cells – Lesion configuration: They concluded that lesions arising from the s ...
... of which served as the basis for the analysis of our cases – Lesion location: They concluded, in congruence with other published case reports, that these lesions occurred mostly in the nasal cavity or within the ethmoid air cells – Lesion configuration: They concluded that lesions arising from the s ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.