Lobe-Fins
... into a tube dorsal to the notochord – Develops into the central nervous system: the brain and the spinal cord ...
... into a tube dorsal to the notochord – Develops into the central nervous system: the brain and the spinal cord ...
Special Senses
... The Fibrous Tunic Sclera White connective tissue layer Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” Cornea(many nerve ending,no blood vessels) ...
... The Fibrous Tunic Sclera White connective tissue layer Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” Cornea(many nerve ending,no blood vessels) ...
ST120 Respiratory System
... Pleural Cavity Pleura = covers the outer surface of lungs and the lining of the inner surface of the rib cage Parietal pleura lines the walls of the ...
... Pleural Cavity Pleura = covers the outer surface of lungs and the lining of the inner surface of the rib cage Parietal pleura lines the walls of the ...
Blood cells - LynClarkson
... within the plasma, a little like people would be suspended within a swimming pool. blood cell blood cell ...
... within the plasma, a little like people would be suspended within a swimming pool. blood cell blood cell ...
Organization of the Animal Body
... function are organized into tissues. Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate (specialize) into three fundamental embryonic tissues, called germ layers. From innermost to outermost layers, these are the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. These germ layers, in turn, differen ...
... function are organized into tissues. Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate (specialize) into three fundamental embryonic tissues, called germ layers. From innermost to outermost layers, these are the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. These germ layers, in turn, differen ...
Cells
... • Location: around hollow organs (intestine,bladder) • Function: involuntary contraction, to move food, fluid through tubes • Cells: smooth muscle cells • Special characteristics ...
... • Location: around hollow organs (intestine,bladder) • Function: involuntary contraction, to move food, fluid through tubes • Cells: smooth muscle cells • Special characteristics ...
ch2
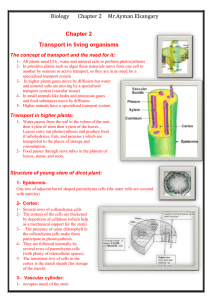
... 29- When cambium divides they give rise to secondary phloem ……….. and secondary xylem ………... 30- …………… is the internal part of the bundle which transports water and solutes 31- Xylem act a s a mechanical ……………. for the stem 32- ………… Consists of vessels, tracheids, parenchyma, pith and Medullary rays ...
... 29- When cambium divides they give rise to secondary phloem ……….. and secondary xylem ………... 30- …………… is the internal part of the bundle which transports water and solutes 31- Xylem act a s a mechanical ……………. for the stem 32- ………… Consists of vessels, tracheids, parenchyma, pith and Medullary rays ...
Cnidaria Kat Hunter Piper
... which serves as both the mouth and the anus. This opening is surrounded by tentacles and leads to an internal digestive cavity. ● Body plans: Radially symmetric ● They have three tissue layers, an outer protective epidermis, a middle layer called the mesoglea, and an inner layer called the gastroder ...
... which serves as both the mouth and the anus. This opening is surrounded by tentacles and leads to an internal digestive cavity. ● Body plans: Radially symmetric ● They have three tissue layers, an outer protective epidermis, a middle layer called the mesoglea, and an inner layer called the gastroder ...
Female Reproductive Cycle By Dr. Nand Lal Dhomeja
... • Breast size is determined primarily by heredity • Size also depends on the existing fat and glandular tissue • Breasts may exhibit cyclical changes, including increased swelling and tenderness prior to ...
... • Breast size is determined primarily by heredity • Size also depends on the existing fat and glandular tissue • Breasts may exhibit cyclical changes, including increased swelling and tenderness prior to ...
www.ourpgs.com
... reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. University of Cambridge International Examinations is part of t ...
... reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. University of Cambridge International Examinations is part of t ...
Neuroscience 9b – Vestibular Apparatus and Pathways
... nuclei supplying extraocular muscles. This results in the vestibulo-ocular reflex. When the head rotates to the left, the eyes rotate in compensation to the right with repositioning saccades to the left (used to maintain gaze on a target). Vestibular nystagmus is the involuntary movement of the eye ...
... nuclei supplying extraocular muscles. This results in the vestibulo-ocular reflex. When the head rotates to the left, the eyes rotate in compensation to the right with repositioning saccades to the left (used to maintain gaze on a target). Vestibular nystagmus is the involuntary movement of the eye ...
COURSE 120 ANAT. ( HISTOLOGY) ( I ) Basic Information Course
... Practical: 2 hours (Saturday, 2-4 pm.) (b) Group B: Lecture: 1 hour (Wednesday, 9-10 am.) Practical: 2 hours (Wednesday, 10- 12am.) Contact clock hours for female students: Lecture: 1 hour (Saturday, 9-10 am.) Practical: 2 hours (Saturday, 10-12 am.) ...
... Practical: 2 hours (Saturday, 2-4 pm.) (b) Group B: Lecture: 1 hour (Wednesday, 9-10 am.) Practical: 2 hours (Wednesday, 10- 12am.) Contact clock hours for female students: Lecture: 1 hour (Saturday, 9-10 am.) Practical: 2 hours (Saturday, 10-12 am.) ...
5. Tissue Organization
... epithelia that we will study in the lab. You will also be questioned about these tissues on the lecture exam, based on the information given below: Simple squamous epithelia are thin and delicate (Table 5.2a). The cells are shaped like fried eggs. This type of tissue forms the alveoli of the lungs a ...
... epithelia that we will study in the lab. You will also be questioned about these tissues on the lecture exam, based on the information given below: Simple squamous epithelia are thin and delicate (Table 5.2a). The cells are shaped like fried eggs. This type of tissue forms the alveoli of the lungs a ...
Blood cells - AIS IGCSE Science
... within the plasma, a little like people would be suspended within a swimming pool. blood cell blood cell ...
... within the plasma, a little like people would be suspended within a swimming pool. blood cell blood cell ...
An Introduction to Biology - Emory
... held opinions that opposed any concept of evolution in which species are permanent, are perfect, and do not evolve. In Judeo-Christian culture, the Old Testament account of creation fortified the idea that species were individually designed and permanent. In the 1700s, biology in Europe and America ...
... held opinions that opposed any concept of evolution in which species are permanent, are perfect, and do not evolve. In Judeo-Christian culture, the Old Testament account of creation fortified the idea that species were individually designed and permanent. In the 1700s, biology in Europe and America ...
CNS Embryology 2pptx (2)
... plates bend and form rhombic lips which join and form the cerebellar plate. • In a 12-week embryo, this plate shows a small midline vermis, and two lateral hemispheres. • A transverse fissure soon separates the nodule from vermis and lateral flocculus from hemispheres. • This flocculonodular lobe is ...
... plates bend and form rhombic lips which join and form the cerebellar plate. • In a 12-week embryo, this plate shows a small midline vermis, and two lateral hemispheres. • A transverse fissure soon separates the nodule from vermis and lateral flocculus from hemispheres. • This flocculonodular lobe is ...
Practice Exam 5
... c. it descends down an osmotic gradient, following the movement of water. d. the cells of the body create molecular attractions that pull the oxygen to them. e. oxygen diffuses from a higher to a lower pH. 35) What prompts a newborn baby to start to breathe? a. an increase in the concentration of ca ...
... c. it descends down an osmotic gradient, following the movement of water. d. the cells of the body create molecular attractions that pull the oxygen to them. e. oxygen diffuses from a higher to a lower pH. 35) What prompts a newborn baby to start to breathe? a. an increase in the concentration of ca ...
Sample Chapter
... The basement membrane provides structural support for the epithelium and also binds it to neighbouring structures. The cells of epithelial tissue form continuous sheets that serve as linings in different parts of the body. Epithelial tissue serves as membrane lining organs and helping to keep the bo ...
... The basement membrane provides structural support for the epithelium and also binds it to neighbouring structures. The cells of epithelial tissue form continuous sheets that serve as linings in different parts of the body. Epithelial tissue serves as membrane lining organs and helping to keep the bo ...
Body Systems
... ANATOMICAL POSITION – standing erect with face forward, arms at the side, palms forward ...
... ANATOMICAL POSITION – standing erect with face forward, arms at the side, palms forward ...
40. Respiratory system. Nose, larynx
... ciliated columnar epithelium Scattered goblet cells Underlying connective tissue lamina propria Mucous cells – secrete mucous Serous cells – secrete watery fluid with digestive enzymes, e.g. lysozyme ...
... ciliated columnar epithelium Scattered goblet cells Underlying connective tissue lamina propria Mucous cells – secrete mucous Serous cells – secrete watery fluid with digestive enzymes, e.g. lysozyme ...
Biology Paper - Acland Burghley School
... division to form two identical body cells State that mitosis occurs during growth or to produce replacement cells Compare the number of chromosomes in body cells and sex cells (gametes) Identify the reproductive organs as testes and ovaries State that meiosis is the type of cell division that f ...
... division to form two identical body cells State that mitosis occurs during growth or to produce replacement cells Compare the number of chromosomes in body cells and sex cells (gametes) Identify the reproductive organs as testes and ovaries State that meiosis is the type of cell division that f ...
LECTURE 11
... ectoderm – outer germ layer o develops into epidermis and nervous system endoderm – inner germ layer o develops into lining of digestive and respiratory systems animals with two germs layers are called diploblastic sometimes a third, middle layer forms mesoderm – middle germ layer o develops into in ...
... ectoderm – outer germ layer o develops into epidermis and nervous system endoderm – inner germ layer o develops into lining of digestive and respiratory systems animals with two germs layers are called diploblastic sometimes a third, middle layer forms mesoderm – middle germ layer o develops into in ...
The Smallest Unit of Life - Mona Shores Online Learning Center
... it's needed for life to exist. Plants use the process to make food; without it most life would desist. The process begins with plain water but not from the tap does it flow. Some water is made within leaf cells and some is sucked up from below. ...
... it's needed for life to exist. Plants use the process to make food; without it most life would desist. The process begins with plain water but not from the tap does it flow. Some water is made within leaf cells and some is sucked up from below. ...
STUDY GUIDE Human Anatomy Final Exam
... 228. The anterior roof of the mouth is formed by the: hard palate; the posterior roof: soft palate 229. Amylase is an enzyme found in: saliva; that digests: starch 230. The term for chewing is: mastication 231. The term for swallowing is: deglutition 232. The muscular tube that extends from the phar ...
... 228. The anterior roof of the mouth is formed by the: hard palate; the posterior roof: soft palate 229. Amylase is an enzyme found in: saliva; that digests: starch 230. The term for chewing is: mastication 231. The term for swallowing is: deglutition 232. The muscular tube that extends from the phar ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.