Chapter 42 - The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation
... muscle contraction causes bones to move – Muscle fibers (cells) are multinucleated – Contract by means of myofibrils, which contain ordered actin and myosin filaments ...
... muscle contraction causes bones to move – Muscle fibers (cells) are multinucleated – Contract by means of myofibrils, which contain ordered actin and myosin filaments ...
Organogenesis Of The Gastrointestinal Tract.
... Gut tube consists of three layers. --inner epithelium(1) derived from endoderm forms the different functional cells of the mucosa of the GI-tract. --the hepatocytes of the liver and secretory cells of pancreas. --the middle layer(2) of mesoderm forms the stroma, supporting cells and the striated and ...
... Gut tube consists of three layers. --inner epithelium(1) derived from endoderm forms the different functional cells of the mucosa of the GI-tract. --the hepatocytes of the liver and secretory cells of pancreas. --the middle layer(2) of mesoderm forms the stroma, supporting cells and the striated and ...
What is photorespiration?
... into a three-carbon piece and a two-carbon piece in a process called photorespiration. Unlike normal cellular respiration in the mitochondria, this process produces no ATP, nor additional organic molecules. Note: Oxygen can poison a plant by inhibiting the Calvin cycle. Rice, wheat and soybeans are ...
... into a three-carbon piece and a two-carbon piece in a process called photorespiration. Unlike normal cellular respiration in the mitochondria, this process produces no ATP, nor additional organic molecules. Note: Oxygen can poison a plant by inhibiting the Calvin cycle. Rice, wheat and soybeans are ...
Block 2 Unit 1 Objectives
... b. The cells in the stratum basale are arranged in a single layer and are cuboidal to columnar in shape. It is this layer in which mitosis is primarily occurring. Small bundles of keratin, called tonofilaments or cytokeratin, first appear in this layer. These cells have desmosomes to attach to each ...
... b. The cells in the stratum basale are arranged in a single layer and are cuboidal to columnar in shape. It is this layer in which mitosis is primarily occurring. Small bundles of keratin, called tonofilaments or cytokeratin, first appear in this layer. These cells have desmosomes to attach to each ...
Document
... Other types of connective tissue include blood, lymph, and tissue fluid (collectively considered vascular tissue), composed of distinctive cells in a watery ground substance, the plasma. Vascular tissue lacks fibers under normal conditions. Cartilage is a semirigid form of connective tissue with close ...
... Other types of connective tissue include blood, lymph, and tissue fluid (collectively considered vascular tissue), composed of distinctive cells in a watery ground substance, the plasma. Vascular tissue lacks fibers under normal conditions. Cartilage is a semirigid form of connective tissue with close ...
Slajd 1 - Naslovnica - Web Stomatološkog fakulteta
... Anatomy employs two chief methods of study - the systemic and topographic.In the former the body is regarded as consisting of systems and organs. The divisions of systemic anatomy are: ...
... Anatomy employs two chief methods of study - the systemic and topographic.In the former the body is regarded as consisting of systems and organs. The divisions of systemic anatomy are: ...
Chapter 15 - Trematoda: Classification and Form and Function of
... The egg of trematodes is not an ovum, but the developing embryo enclosed by a shell (capsule) In some cases, the egg contains a fully developed miracidium Most embryos develop when outside the body of the host (in the environment) In order for the embryo to develop there must be water or considerabl ...
... The egg of trematodes is not an ovum, but the developing embryo enclosed by a shell (capsule) In some cases, the egg contains a fully developed miracidium Most embryos develop when outside the body of the host (in the environment) In order for the embryo to develop there must be water or considerabl ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • forms internal ring around front of eye • ciliary processes – radiating folds • ciliary muscles – contract and relax to move lens ...
... • forms internal ring around front of eye • ciliary processes – radiating folds • ciliary muscles – contract and relax to move lens ...
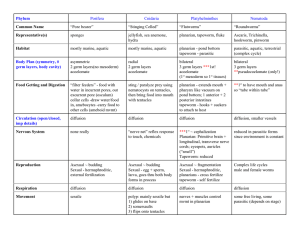
Phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Common
... then bring food into mouth with tentacles ...
... then bring food into mouth with tentacles ...
Introduction to Biomechanics for engineering students
... pattern is as follows: blood returns through the veins to the right atrium of the heart; from there it is pumped by one of the pumping functions trough the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery, and then into the lungs. From the lungs it returns through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium of ...
... pattern is as follows: blood returns through the veins to the right atrium of the heart; from there it is pumped by one of the pumping functions trough the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery, and then into the lungs. From the lungs it returns through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium of ...
Lesson 24
... Any substance added to increase the bulk of the body of the organism is also due to the activity of the cells. • Reproduction: No matter how an organism reproduces, whether sexually or asexually, it is again the cells that carry out the process. The male sperm is a cell and so is the female egg. Whe ...
... Any substance added to increase the bulk of the body of the organism is also due to the activity of the cells. • Reproduction: No matter how an organism reproduces, whether sexually or asexually, it is again the cells that carry out the process. The male sperm is a cell and so is the female egg. Whe ...
On the Growth in Length of the Prog Embryo.
... whilst the continuation of the cavity produced by an overgrowth is the direct effect of the secondary centre of growth, producing the elongation of the animal. The splitting process in the frog corresponds in results to the invagination process of Amphioxus, while the overgrowth of certain parts of ...
... whilst the continuation of the cavity produced by an overgrowth is the direct effect of the secondary centre of growth, producing the elongation of the animal. The splitting process in the frog corresponds in results to the invagination process of Amphioxus, while the overgrowth of certain parts of ...
Chapter 3 : The Remarkable Body
... -Blood travels within arteries, veins, and capillaries, as well as within the heart’s chambers -circulating within these vessels is the plasma of the blood -Lymph -the fluid that moves form the blood stream into tissue spaces and then travels in its own vessels -which eventually drain back into the ...
... -Blood travels within arteries, veins, and capillaries, as well as within the heart’s chambers -circulating within these vessels is the plasma of the blood -Lymph -the fluid that moves form the blood stream into tissue spaces and then travels in its own vessels -which eventually drain back into the ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION (define)
... 2. List at least 4 specific functions of white blood cells (how they help fight infections). ...
... 2. List at least 4 specific functions of white blood cells (how they help fight infections). ...
Gi tract embryology 1
... The amnion encloses the body stalk and the yolk sac with their blood vessels to form the tubular umbilical cord ...
... The amnion encloses the body stalk and the yolk sac with their blood vessels to form the tubular umbilical cord ...
Introduction to Biomechanics for engineering students
... phosphor) and further, the red blood cells are produced and stored in the red bone marrow within the long skeletal bones. To provide locomotion the skeletal bones are joined together through the joints that have a very low friction due to the cartilage covered contact layer and a lubrication system. ...
... phosphor) and further, the red blood cells are produced and stored in the red bone marrow within the long skeletal bones. To provide locomotion the skeletal bones are joined together through the joints that have a very low friction due to the cartilage covered contact layer and a lubrication system. ...
Chapter 4: The Tissue Level of Organization
... – Covers exposed surfaces – Lines internal passageways – Forms glands ...
... – Covers exposed surfaces – Lines internal passageways – Forms glands ...
SENSES OF HEARING AND BALANCE: THE EAR (cont.)
... • Scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm): ring-shaped venous sinus found deep within the anterior portion of the sclera at its junction with the cornea ...
... • Scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm): ring-shaped venous sinus found deep within the anterior portion of the sclera at its junction with the cornea ...
10-4
... Adult Stem Cells For years, biologists have suspected that adult organisms might also contain some types of stem cells. Cells in the blood and skin, for example, have a limited life span and must be constantly replaced. This suggests that the body contains pools of stem cells from which new skin and ...
... Adult Stem Cells For years, biologists have suspected that adult organisms might also contain some types of stem cells. Cells in the blood and skin, for example, have a limited life span and must be constantly replaced. This suggests that the body contains pools of stem cells from which new skin and ...
Tissue: The Living Fabric
... Histology: study of tissues Types of Tissues: 1. Epithelium (covering) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) ...
... Histology: study of tissues Types of Tissues: 1. Epithelium (covering) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) ...
Histology and Integument
... function: absorption and secretion body locations: found in large ducts in most exocrine glands and in some parts of male urethra structure: two or more layers of cells; cells at apical surface are cuboidal £ basement membrane £ apical surface £ basal surface function: protection and secretion bo ...
... function: absorption and secretion body locations: found in large ducts in most exocrine glands and in some parts of male urethra structure: two or more layers of cells; cells at apical surface are cuboidal £ basement membrane £ apical surface £ basal surface function: protection and secretion bo ...
Histology and Integument
... structure: two or more layers of cells; cells at the apical surface are columnar £ basement membrane £ basal surface £ apical surface function: protection and secretion body locations: ciliated form lines most of the respiratory tract; nonciliated form is rare and lines the epididymis and part of ...
... structure: two or more layers of cells; cells at the apical surface are columnar £ basement membrane £ basal surface £ apical surface function: protection and secretion body locations: ciliated form lines most of the respiratory tract; nonciliated form is rare and lines the epididymis and part of ...
Working with Hydra
... contract. The gastrodermis is specialized by region, as shown by the distribution of cells and the changes in nutritivemuscular cell form. Mucous gland cells are abundant near the Hydra’s mouth, and enzymatic gland cells secrete enzymes for extracellular food digestion. The column contains gastroder ...
... contract. The gastrodermis is specialized by region, as shown by the distribution of cells and the changes in nutritivemuscular cell form. Mucous gland cells are abundant near the Hydra’s mouth, and enzymatic gland cells secrete enzymes for extracellular food digestion. The column contains gastroder ...
Auditory analyzer
... sound vibrations. However, insects have described specific auditory organs, they may be located in different parts of the body and consist of a thin stretched membrane which separates the outside air from the ear cavity. On the inside of the membrane are auditory receptor cells. With these bodies, s ...
... sound vibrations. However, insects have described specific auditory organs, they may be located in different parts of the body and consist of a thin stretched membrane which separates the outside air from the ear cavity. On the inside of the membrane are auditory receptor cells. With these bodies, s ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.