K CHAPTER 2: BODY TISSUES AND MEMBRANES At the end of
... study of tissues. 1.1. Embryonic tissue Approximately 13 or 14 days after fertilization, the cells that give rise to the new individual, called embryonic stem cells form a slightly elongated disk consisting of two layers called the ectoderm and the endoderm. Cells of ectoderm then migrate between th ...
... study of tissues. 1.1. Embryonic tissue Approximately 13 or 14 days after fertilization, the cells that give rise to the new individual, called embryonic stem cells form a slightly elongated disk consisting of two layers called the ectoderm and the endoderm. Cells of ectoderm then migrate between th ...
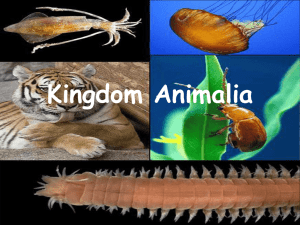
Kingdom Animalia
... rise to muscles, circulatory, reproductive and excretory systems • Ectoderm (outermost germ layer): gives rise to sensory organs, nerves, integumentary system (skin, hair, nails, etc.) ...
... rise to muscles, circulatory, reproductive and excretory systems • Ectoderm (outermost germ layer): gives rise to sensory organs, nerves, integumentary system (skin, hair, nails, etc.) ...
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... Within these specialized structures oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between air and blood. Each alveoli wall usually lies between two neighbouring alveoli and is called an inter-alveolar septum. An alveolar septum consists of two thin squamous epithelial layers between which lie capill ...
... Within these specialized structures oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between air and blood. Each alveoli wall usually lies between two neighbouring alveoli and is called an inter-alveolar septum. An alveolar septum consists of two thin squamous epithelial layers between which lie capill ...
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... Within these specialized structures oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between air and blood. Each alveoli wall usually lies between two neighbouring alveoli and is called an inter-alveolar septum. An alveolar septum consists of two thin squamous epithelial layers between which lie capill ...
... Within these specialized structures oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between air and blood. Each alveoli wall usually lies between two neighbouring alveoli and is called an inter-alveolar septum. An alveolar septum consists of two thin squamous epithelial layers between which lie capill ...
The Digestive System:
... A muscular sac that mechanically processes food into chyme. Produces gastric juice that contains pepsin and HCl Begins the chemical digestion of proteins. Produces a protective layer of mucus, so it does not digest itself. o Small Intestine: The pancreas, liver, and gall bladder excrete in ...
... A muscular sac that mechanically processes food into chyme. Produces gastric juice that contains pepsin and HCl Begins the chemical digestion of proteins. Produces a protective layer of mucus, so it does not digest itself. o Small Intestine: The pancreas, liver, and gall bladder excrete in ...
invertebrate survey lab
... and relatively few setae (hairs) compared to polychaetes (most live in soil or fresh water). • Leeches: external parasites that suck the blood and body fluids of their host. • Polychaetes: marine annelids that have paired, ...
... and relatively few setae (hairs) compared to polychaetes (most live in soil or fresh water). • Leeches: external parasites that suck the blood and body fluids of their host. • Polychaetes: marine annelids that have paired, ...
File
... Sac with a central digestive compartment Single opening serving as both mouth and anus Ring of tentacles on oral surface ...
... Sac with a central digestive compartment Single opening serving as both mouth and anus Ring of tentacles on oral surface ...
PEDIATRIC ASTHMA - Ravenwood-PA
... • The trachea and bronchi form the tracheobronchial tree. • The trachea branches into the right and left main stem bronchi known as the carina. • The right and left main stem bronchi divide to become the lobar bronchi, then segmental bronchi, then terminal bronchioles. • Beyond the terminal bronchio ...
... • The trachea and bronchi form the tracheobronchial tree. • The trachea branches into the right and left main stem bronchi known as the carina. • The right and left main stem bronchi divide to become the lobar bronchi, then segmental bronchi, then terminal bronchioles. • Beyond the terminal bronchio ...
Uterus
... Ampulla, Isthmus and Intramural (Interstitium) part Fertilization of the ovum takes place in the ampulla. Blood supply is by the ovarian artery ...
... Ampulla, Isthmus and Intramural (Interstitium) part Fertilization of the ovum takes place in the ampulla. Blood supply is by the ovarian artery ...
living environment
... (1) Both are involved in asexual reproduction. (2) Both occur only in reproductive cells. (3) The number of chromosomes is reduced by half. (4) DNA replication occurs before the division of the nucleus. ...
... (1) Both are involved in asexual reproduction. (2) Both occur only in reproductive cells. (3) The number of chromosomes is reduced by half. (4) DNA replication occurs before the division of the nucleus. ...
Proifera
... A coelom is a fluid filled body cavity that is usually in the middle germ layer or mesoderm. The coelom allows the internal organs to develop independently of the body wall. ...
... A coelom is a fluid filled body cavity that is usually in the middle germ layer or mesoderm. The coelom allows the internal organs to develop independently of the body wall. ...
Kingdom Animalia: Phyla Porifera and Cnidaria
... The basic body plan of the cnidarians is a sac-like structure, with a gastrovascular cavity. The gastrovascular cavity has a single opening which serves as both mouth and anus; it is often surrounded by tentacles. The body wall has an external cell layer, the epidermis; an internal cell layer, the g ...
... The basic body plan of the cnidarians is a sac-like structure, with a gastrovascular cavity. The gastrovascular cavity has a single opening which serves as both mouth and anus; it is often surrounded by tentacles. The body wall has an external cell layer, the epidermis; an internal cell layer, the g ...
neural control and coordination
... divides the cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed as the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The hemispheres are connected by a tract of nerve fibres called corpus callosum. The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called cerebral cortex and is thrown into prom ...
... divides the cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed as the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The hemispheres are connected by a tract of nerve fibres called corpus callosum. The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called cerebral cortex and is thrown into prom ...
Unit 11 Invertebrates
... cortex controls and coordinates body movements and senses; medula oblongata helps monitor and maintain other body systems ...
... cortex controls and coordinates body movements and senses; medula oblongata helps monitor and maintain other body systems ...
Scanned Document
... The balloon is a semi-permeable membrane and the molecules of helium are small enough to slowly pass through. Explain in detail, why the volume of the balloon decreases. As the volume of helium decreases there is less and less pressure being applied to the balloon from the inside. This results in th ...
... The balloon is a semi-permeable membrane and the molecules of helium are small enough to slowly pass through. Explain in detail, why the volume of the balloon decreases. As the volume of helium decreases there is less and less pressure being applied to the balloon from the inside. This results in th ...
The Human Body: An Orientation
... • Early prophase—chromatin threads condense into chromosomes • Chromosomes are made up of two threads called chromatids (sister chromatids) • Chromatids are held together by the centromere • Centriole pairs separate from one another • The mitotic spindle forms ...
... • Early prophase—chromatin threads condense into chromosomes • Chromosomes are made up of two threads called chromatids (sister chromatids) • Chromatids are held together by the centromere • Centriole pairs separate from one another • The mitotic spindle forms ...
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
... Water evaporates from the surface of the leaves, through the open stomata. As this water evaporates, water is pulled up through the xylem to take its place. This constant moving of water through the xylem from the roots to the leaves is known as the transpiration stream. Water moves into the roots f ...
... Water evaporates from the surface of the leaves, through the open stomata. As this water evaporates, water is pulled up through the xylem to take its place. This constant moving of water through the xylem from the roots to the leaves is known as the transpiration stream. Water moves into the roots f ...
Entodermal derivatives: formation of the gut, liver, and pancreas
... arises from a region just caudal to septum transversum that has been ...
... arises from a region just caudal to septum transversum that has been ...
Respiratory System Guided Notes
... A. The two lungs are different in shape and size. The left lung has only ______ lobes to give heart some room while the right lung has _______ lobes. B. The lungs weigh about _________________. C. The _________________ pleura line the thoracic cavity wall while the __________pleura line the external ...
... A. The two lungs are different in shape and size. The left lung has only ______ lobes to give heart some room while the right lung has _______ lobes. B. The lungs weigh about _________________. C. The _________________ pleura line the thoracic cavity wall while the __________pleura line the external ...
Respiratory Notes -- Anatomy
... A. The two lungs are different in shape and size. The left lung has only ______ lobes to give heart some room while the right lung has _______ lobes. B. The lungs weigh about _________________. C. The _________________ pleura line the thoracic cavity wall while the __________pleura line the external ...
... A. The two lungs are different in shape and size. The left lung has only ______ lobes to give heart some room while the right lung has _______ lobes. B. The lungs weigh about _________________. C. The _________________ pleura line the thoracic cavity wall while the __________pleura line the external ...
ears - berlinanatomy
... - the canal directs sound waves to the middle ear 3. Tympanic membrane (tympanum)- closes the inner end of the auditory canal - also called eardrum - because it is S shaped, you cannot see the tympanic membrane without a special instrument ...
... - the canal directs sound waves to the middle ear 3. Tympanic membrane (tympanum)- closes the inner end of the auditory canal - also called eardrum - because it is S shaped, you cannot see the tympanic membrane without a special instrument ...
Lab Exer 9 Anatomy of the Respiratory System
... The epiglottis a flap of elastic cartilage, attached to the superior border of the thyroid cartilage, covers the glottis during swallowing to prevent drawing in by suction (aspiration) of liquids and solids into the breathing system. At the inferior end of the larynx is the cricoid cartilage. Trache ...
... The epiglottis a flap of elastic cartilage, attached to the superior border of the thyroid cartilage, covers the glottis during swallowing to prevent drawing in by suction (aspiration) of liquids and solids into the breathing system. At the inferior end of the larynx is the cricoid cartilage. Trache ...
File
... Cnidarians have a nerve network that covers their entire body. They have radial symmetry and can move in any one direction quickly. It is theorized that the he nerve net feels the same stimulus all over their body at once equally. Some jellyfish have eyes and eight sensory centers along their margin ...
... Cnidarians have a nerve network that covers their entire body. They have radial symmetry and can move in any one direction quickly. It is theorized that the he nerve net feels the same stimulus all over their body at once equally. Some jellyfish have eyes and eight sensory centers along their margin ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.