Anatomy of a Soft Coral Polyp
... A polyp is a small marine invertebrate (spineless) animal. Some coral polyps are as small as the head of a pin and others can be as large as a foot in diameter, but the majority of them are small. A polyps' body has radial symmetry, which means that if a line were drawn any way through the middle of ...
... A polyp is a small marine invertebrate (spineless) animal. Some coral polyps are as small as the head of a pin and others can be as large as a foot in diameter, but the majority of them are small. A polyps' body has radial symmetry, which means that if a line were drawn any way through the middle of ...
PIGEON DISSECTION
... Human small intestine = about 22 feet long Human large intestine = 5 feet long Food can spend as long as 4 hours in the small intestine ...
... Human small intestine = about 22 feet long Human large intestine = 5 feet long Food can spend as long as 4 hours in the small intestine ...
because personal discovery is an important aspect
... epithelial – forms internal or external linings of organs and glands, specialized for lubrication, resisting abrasion, waterproofing, absorption, and/or secretion; rests on basement membrane; basal to apical or luminal polarity; one free surface; cellularity; specialized cell junctions including des ...
... epithelial – forms internal or external linings of organs and glands, specialized for lubrication, resisting abrasion, waterproofing, absorption, and/or secretion; rests on basement membrane; basal to apical or luminal polarity; one free surface; cellularity; specialized cell junctions including des ...
Phylum Cnidaria Characteristics
... 2. Diploblastic – meaning that they only have two tissue layers, ...
... 2. Diploblastic – meaning that they only have two tissue layers, ...
Cochlear labyrinth (pars auditiva labyrinthi)
... The columnar cells contact the basilar membrane with one end, while the other end is extended to form plates, which provide stability to the receptor cells of the organ of Corti. The columnar cells are assisted by the phalangeal cells, which also support the receptor cells. The receptor cells are ar ...
... The columnar cells contact the basilar membrane with one end, while the other end is extended to form plates, which provide stability to the receptor cells of the organ of Corti. The columnar cells are assisted by the phalangeal cells, which also support the receptor cells. The receptor cells are ar ...
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (I)
... The ectocervix (portio vaginalis) is lined by a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The superficial cells have intracytoplasmic glycogen (clear cytoplasm). The endocervical surface and the infoldings (glands) are lined by a simple columnar mucin-producing epithelium. The cytoplasm is lig ...
... The ectocervix (portio vaginalis) is lined by a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. The superficial cells have intracytoplasmic glycogen (clear cytoplasm). The endocervical surface and the infoldings (glands) are lined by a simple columnar mucin-producing epithelium. The cytoplasm is lig ...
1 - Corwith-Wesley-LuVerne High School
... i Stops blood flow ii Protect area from bacteria etc. d Granulation tissue forms pink tissue with many new capillaries e Phagocytes clean up debris f Surface epithelium begins to regenerate g Forms a scar F Developmental aspects of cells & tissue 1 Most cells continue to divide until puberty (except ...
... i Stops blood flow ii Protect area from bacteria etc. d Granulation tissue forms pink tissue with many new capillaries e Phagocytes clean up debris f Surface epithelium begins to regenerate g Forms a scar F Developmental aspects of cells & tissue 1 Most cells continue to divide until puberty (except ...
1 Chapter 4: The Tissue Level of Organization What are the four
... Bone Surface • Periosteum: – covers bone surfaces – fibrous layer – cellular layer ...
... Bone Surface • Periosteum: – covers bone surfaces – fibrous layer – cellular layer ...
Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Potato Osmosis
... A.1.1 formulate scientific question about observed relationships, ideas, problems, and/or issues, make predictions, and/or formulate hypotheses to focus inquiries or research A1.10 draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their ...
... A.1.1 formulate scientific question about observed relationships, ideas, problems, and/or issues, make predictions, and/or formulate hypotheses to focus inquiries or research A1.10 draw conclusions based on inquiry results and research findings, and justify their ...
Fungi have an mode of nutrition which requires the secretion of
... b. Cnidaria-radial symmetry, polyp and medusa body forms c. Platyhelminthes-flatworms, gastrovascular cavity, acoelomate d. Porifera-gastrovascular cavity, coelom present 66. Which of these statements is true of sponges? a. They have an open circulatory system. b. They are segmented animals. c. They ...
... b. Cnidaria-radial symmetry, polyp and medusa body forms c. Platyhelminthes-flatworms, gastrovascular cavity, acoelomate d. Porifera-gastrovascular cavity, coelom present 66. Which of these statements is true of sponges? a. They have an open circulatory system. b. They are segmented animals. c. They ...
The Living Cell - Discovery Education
... produced. (the organelle where cellular respiration takes place). 3. Network of passageways through which proteins move. 4. Organelle where proteins from the ER are sorted out, packaged, and shipped off. 5. Packets of digestive enzymes that fuse with food vacuoles. 6. The skin that encloses protopla ...
... produced. (the organelle where cellular respiration takes place). 3. Network of passageways through which proteins move. 4. Organelle where proteins from the ER are sorted out, packaged, and shipped off. 5. Packets of digestive enzymes that fuse with food vacuoles. 6. The skin that encloses protopla ...
Phylum Cnidaria (Coelenterata)
... (conditions unfavorable) » Zygotes remain dormant until conditions improve ...
... (conditions unfavorable) » Zygotes remain dormant until conditions improve ...
Ch 47 - Houston ISD
... and the inner cell mass of the blastocyst forms a flat disk of cells • As implantation is completed, gastrulation begins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... and the inner cell mass of the blastocyst forms a flat disk of cells • As implantation is completed, gastrulation begins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Lecture presentation
... and the inner cell mass of the blastocyst forms a flat disk of cells • As implantation is completed, gastrulation begins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... and the inner cell mass of the blastocyst forms a flat disk of cells • As implantation is completed, gastrulation begins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 9
... reactions are the result of a single cell responding to a stimulus. • Communication between cells may be possible, but we do not know for certain. ...
... reactions are the result of a single cell responding to a stimulus. • Communication between cells may be possible, but we do not know for certain. ...
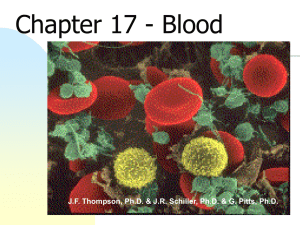
Chapter 17 - Blood - Anatomy and Physiology
... Normal component of inflammatory response to injuries and infections ...
... Normal component of inflammatory response to injuries and infections ...
Chapter 47 ppt
... and the inner cell mass of the blastocyst forms a flat disk of cells • As implantation is completed, gastrulation begins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... and the inner cell mass of the blastocyst forms a flat disk of cells • As implantation is completed, gastrulation begins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Physiology of Growth and Reproduction In Livestock
... released into a fluid vehicle such as blood plasma or lymph for transport. Bloodforming tissues include myeloid tissue of the bone marrow, and lymphatic tissues of the thymus gland, lymph nodes and spleen. Leukocytes (white blood cells) are produced in these sites, and are involved in immune respons ...
... released into a fluid vehicle such as blood plasma or lymph for transport. Bloodforming tissues include myeloid tissue of the bone marrow, and lymphatic tissues of the thymus gland, lymph nodes and spleen. Leukocytes (white blood cells) are produced in these sites, and are involved in immune respons ...
Lec 06 - Development of e
... phases: 1. Selection and induction of cells with embryogenic competence, 2. Development of these cells into embryos. ...
... phases: 1. Selection and induction of cells with embryogenic competence, 2. Development of these cells into embryos. ...
Integument
... •Aging, hormones, and the destructive effects of UV radiation permanently reduce the amount of elastin in the dermis, producing wrinkles and sagging skin. •The extensive distortion of the dermis that occurs over the abdomen during pregnancy or after a substantial weight gain can exceed the elastic ...
... •Aging, hormones, and the destructive effects of UV radiation permanently reduce the amount of elastin in the dermis, producing wrinkles and sagging skin. •The extensive distortion of the dermis that occurs over the abdomen during pregnancy or after a substantial weight gain can exceed the elastic ...
Development of the nervous system and sense organs I
... develops into impulse- conducting neuron. 5- The angioblasts develop also from the inner zone, but either remains attached to the inner limiting membrane or migrate and get attached to the outer limiting membrane. - The angioblasts that loose connection with the limiting membranes differentiate into ...
... develops into impulse- conducting neuron. 5- The angioblasts develop also from the inner zone, but either remains attached to the inner limiting membrane or migrate and get attached to the outer limiting membrane. - The angioblasts that loose connection with the limiting membranes differentiate into ...
Female Reproductive System
... the visceral peritoneum and hence called a serosa. • The myometrium is the thick middle layer, composed of three layers of smooth muscle, responsible for the powerful contractions during labor • The endometrium is a double epithelial layer, its inner basilar zone produces a new functional zone each ...
... the visceral peritoneum and hence called a serosa. • The myometrium is the thick middle layer, composed of three layers of smooth muscle, responsible for the powerful contractions during labor • The endometrium is a double epithelial layer, its inner basilar zone produces a new functional zone each ...
2- Lateral wall of cochlear duct
... impulse/second) in the nerve fibers leaving the crista. Movement of endolymph and cupula towards the ampulla causes ↑ in impulse rate, and movement away from ampulla causes ↓ in the impulse rate. This mechanism can be explained by considering rotation in a rotating chair about vertical axis, when t ...
... impulse/second) in the nerve fibers leaving the crista. Movement of endolymph and cupula towards the ampulla causes ↑ in impulse rate, and movement away from ampulla causes ↓ in the impulse rate. This mechanism can be explained by considering rotation in a rotating chair about vertical axis, when t ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
The Insect Gas Exchange System
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
... with chitin on the sides of its body. • The chitin give shape to the openings. • The spiracles can open and close by small ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.