chapter_3_presentation
... capillaries. It is here that gases are exchanged. Oxygen and carbon dioxide pass back and forth between the air in the alveoli (respiratory system) and the blood in the capillaries (circulatory system). Oxygen passes from the alveoli into the capillaries by dif fusion. The air in your alveoli ha ...
... capillaries. It is here that gases are exchanged. Oxygen and carbon dioxide pass back and forth between the air in the alveoli (respiratory system) and the blood in the capillaries (circulatory system). Oxygen passes from the alveoli into the capillaries by dif fusion. The air in your alveoli ha ...
Nasty Cnidarians Book assignment
... closer look and find thousands of tiny polyps attached to a calcium carbonate skeleton. These polyps have tentacles lined with nematocysts and a gastrovascular cavity. This organism is also diploblastic and contains mesenteries lined with cnidocytes. In addition to the microscopic cnidocytes you obs ...
... closer look and find thousands of tiny polyps attached to a calcium carbonate skeleton. These polyps have tentacles lined with nematocysts and a gastrovascular cavity. This organism is also diploblastic and contains mesenteries lined with cnidocytes. In addition to the microscopic cnidocytes you obs ...
Nasty Cnidarias - CherylannHayes
... closer look and find thousands of tiny polyps attached to a calcium carbonate skeleton. These polyps have tentacles lined with nematocysts and a gastrovascular cavity. This organism is also diploblastic and contains mesenteries lined with cnidocytes. In addition to the microscopic cnidocytes you obs ...
... closer look and find thousands of tiny polyps attached to a calcium carbonate skeleton. These polyps have tentacles lined with nematocysts and a gastrovascular cavity. This organism is also diploblastic and contains mesenteries lined with cnidocytes. In addition to the microscopic cnidocytes you obs ...
BIOL0601 Module 4 Assignment 4 (M4A)
... binds with the substrate and the antibody has a zone which is capable of recognizing an antigen. The enzyme is regenerated after it has accomplished the transformation of substrate to product and can undergo many such cycles. The antibody is destroyed along with the antigen to which it has attached. ...
... binds with the substrate and the antibody has a zone which is capable of recognizing an antigen. The enzyme is regenerated after it has accomplished the transformation of substrate to product and can undergo many such cycles. The antibody is destroyed along with the antigen to which it has attached. ...
Cause. - Cleveland Clinic
... are shown. The endothelial cells that line the rest of the inner wall of the blood vessel are not shown.) Note that the endothelial cells fit snugly together. There are “tight junctions” between them. ...
... are shown. The endothelial cells that line the rest of the inner wall of the blood vessel are not shown.) Note that the endothelial cells fit snugly together. There are “tight junctions” between them. ...
Chapter 20 Unifying Concept of Animal Structure and Function
... - senses stimuli. - rapidly transmits information. 神經元 Neurons carry signals by conducting electrical impulses. 樹突 Dendrites 細胞本體 ...
... - senses stimuli. - rapidly transmits information. 神經元 Neurons carry signals by conducting electrical impulses. 樹突 Dendrites 細胞本體 ...
Parazoa-Eumetazoa dichotomy
... openings designate a digestive tract • A body cavity is a fluid filled space separating the digestive tract from the outer body wall • Animals without a cavity between the digestive tract and the outer body wall are called ACOELOMATES ...
... openings designate a digestive tract • A body cavity is a fluid filled space separating the digestive tract from the outer body wall • Animals without a cavity between the digestive tract and the outer body wall are called ACOELOMATES ...
4 Histology - Orange Coast College
... Some epithelia are richly innervated to detect changes in the environment at that body or organ surface. Most nervous tissue is in the underlying connective tissue. ...
... Some epithelia are richly innervated to detect changes in the environment at that body or organ surface. Most nervous tissue is in the underlying connective tissue. ...
1 CLASS 1X BIOLOGY PLANT TISSUES Definition of tissue Tissues
... Straw coloured fluid similar to blood in composition but devoid of RBC’S and proteins. ...
... Straw coloured fluid similar to blood in composition but devoid of RBC’S and proteins. ...
File
... 1. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Cardiac muscle tissue contracts to help the heart pump blood throughout the body. The heart is an organ in the cardiovascular system. Describe how this system helps perform maintenance for organisms, such as humans. ...
... 1. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Cardiac muscle tissue contracts to help the heart pump blood throughout the body. The heart is an organ in the cardiovascular system. Describe how this system helps perform maintenance for organisms, such as humans. ...
from the Early Cretaceous in China
... Remark. It is indubitable to classify this species into the family Saldidae based on the combination of characters: compound eyes large, rostrum long, posterior margin of pronotum concave, hemelytra with costal fracture and medial fracture, membrane with few cells. The new genus has six cells on its ...
... Remark. It is indubitable to classify this species into the family Saldidae based on the combination of characters: compound eyes large, rostrum long, posterior margin of pronotum concave, hemelytra with costal fracture and medial fracture, membrane with few cells. The new genus has six cells on its ...
08. female genital system
... They are formed from the proliferating surface epithelium. They penetrate the mesenchyme but they still close to the surface epithelium. ...
... They are formed from the proliferating surface epithelium. They penetrate the mesenchyme but they still close to the surface epithelium. ...
BIO101 Unit 4
... are produced found at the ends of long bones. squamous flat type cells of epithelial tissue that lines the lungs, blood vessels and the skin.. stratified epithelial tissue type of epithelial tissue that is many layers thick. superficial toward or at the body surface (external). The skin is superfici ...
... are produced found at the ends of long bones. squamous flat type cells of epithelial tissue that lines the lungs, blood vessels and the skin.. stratified epithelial tissue type of epithelial tissue that is many layers thick. superficial toward or at the body surface (external). The skin is superfici ...
What is an animal?
... and anus in deuterostomes – Some cells on the surface of the embryo may migrate into the blastopore to form a new cavity called the archenteron or “primitive gut” – As a result of this cell movement, a threelayered embryo called a gastrula is formed Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishin ...
... and anus in deuterostomes – Some cells on the surface of the embryo may migrate into the blastopore to form a new cavity called the archenteron or “primitive gut” – As a result of this cell movement, a threelayered embryo called a gastrula is formed Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishin ...
File - Science with Ms. Friess
... strong and made up of cartilage This is so that the change in air pressure when we breathe doesn’t cause the tube to collapse ...
... strong and made up of cartilage This is so that the change in air pressure when we breathe doesn’t cause the tube to collapse ...
Cnidarians - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... • Drifting and of the medusoid body form • Size can range from 12 mm to 2 m across (Cyanea arctica is over 40 m long!) • They have no head, skeleton, or special organs for breathing or excreting • Scyphozoa have a more developed nervous system than other cnidarians; a nerve ring circling the edge of ...
... • Drifting and of the medusoid body form • Size can range from 12 mm to 2 m across (Cyanea arctica is over 40 m long!) • They have no head, skeleton, or special organs for breathing or excreting • Scyphozoa have a more developed nervous system than other cnidarians; a nerve ring circling the edge of ...
Kingdom Animalia
... movement of water is produced by the beating of the flagella of collar cells, or choanocytes, in the flagellated chambers, or radial canals. The choanocytes capture and digest food particles brought in by the water cur rents with the aid of collar-like structures surrounding their flagella. ...
... movement of water is produced by the beating of the flagella of collar cells, or choanocytes, in the flagellated chambers, or radial canals. The choanocytes capture and digest food particles brought in by the water cur rents with the aid of collar-like structures surrounding their flagella. ...
Slide 1
... lens, moves lens for focusing Choroid coatprovides blood supply, pigments absorb extra light Anterior of eye filled with aqueous humor. Lens-Transparent, lies behind iris, largely composed of lens fibers, elastic, held in place by suspensory ligaments of ciliary body ...
... lens, moves lens for focusing Choroid coatprovides blood supply, pigments absorb extra light Anterior of eye filled with aqueous humor. Lens-Transparent, lies behind iris, largely composed of lens fibers, elastic, held in place by suspensory ligaments of ciliary body ...
HEART - Wikispaces
... • The spaces between the ribs are known as intercostal spaces; they contain the intercostal muscles, nerves, and arteries. ...
... • The spaces between the ribs are known as intercostal spaces; they contain the intercostal muscles, nerves, and arteries. ...
Performance Benchmark N
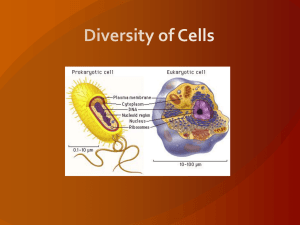
... Multicellular organisms exhibit many levels of organization starting with cells. Cells are differentiated, meaning that not all cells are identical within an organism. Each cell has the same genetic code (DNA) but not all genes are active within a cell. For example, a skin cell has a different struc ...
... Multicellular organisms exhibit many levels of organization starting with cells. Cells are differentiated, meaning that not all cells are identical within an organism. Each cell has the same genetic code (DNA) but not all genes are active within a cell. For example, a skin cell has a different struc ...
Anatomy & Physiology Mid Term Review
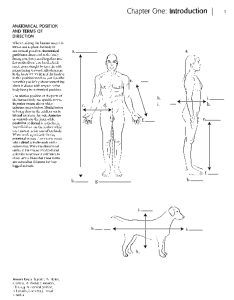
... directional terms have the same meaning (in humans): superior and caudal inferior and cranial inferior and cephalad anterior and ventral anterior and dorsal ...
... directional terms have the same meaning (in humans): superior and caudal inferior and cranial inferior and cephalad anterior and ventral anterior and dorsal ...
Grade 6 Life Posttest
... ____ 12. Many animals have skeletons that provide support so that they can remain upright. In contrast, plants cells depend on a cellular structure for support. What structure provides support for a plant cell? A. nucleus B. cell wall C. chloroplast D. cell membrane ____ 13. Which statement correctl ...
... ____ 12. Many animals have skeletons that provide support so that they can remain upright. In contrast, plants cells depend on a cellular structure for support. What structure provides support for a plant cell? A. nucleus B. cell wall C. chloroplast D. cell membrane ____ 13. Which statement correctl ...
Grade 6 Life Posttest
... ____ 12. Many animals have skeletons that provide support so that they can remain upright. In contrast, plants cells depend on a cellular structure for support. What structure provides support for a plant cell? A. nucleus B. cell wall C. chloroplast D. cell membrane ____ 13. Which statement correctl ...
... ____ 12. Many animals have skeletons that provide support so that they can remain upright. In contrast, plants cells depend on a cellular structure for support. What structure provides support for a plant cell? A. nucleus B. cell wall C. chloroplast D. cell membrane ____ 13. Which statement correctl ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.