* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO101 Unit 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
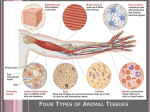
BIO102 Unit 1 Human organization Glossary adipose tissue a type of connective tissue that contains enlarged fibroblasts that store fat. This tissue is found beneath the skin, around the kidneys and on the surface of the heart. anterior toward or at the front of the body. The breastbone is anterior to the spine. bone connective tissue having a matrix of inorganic salts (mainly calcium salts) and protein fibers. The salts give bones rigidity and the fibers provide bones with elasticity and strength. blood type of connective tissue composed of a liquid matrix (plasma) containing inorganic and organic substances and formed elements (blood cells) cardiac muscles the type of muscle tissue only found in the heart cartilage a connective tissue in which cells lie within lacunae separated by a flexible matrix. cells the basic unit of living things. The structural and functional unit of a living thing. collagen fibers white protein fibers that gives connective tissue flexibility and strength. columnar column shaped cells of epithelial tissue that line the digestive tract and the oviducts. compact bone hard bone consisting cylindrical circular units called osteons with osteocytes (bone cells) located in spaces called lacunae arranged around a central canal which contains nerves and blood vessels. connective tissue a type of tissue characterized by cells separated by a matrix that often contains fibers. cuboidal cube shaped cells of epithelial tissue that line the kidney tubules. deep away from the body surface; more internal. The lungs are deep to the skin. dense fibrous connective tissue dense connective tissue that contains collagen fibers packed tightly together providing the strength that are found in tendons and ligaments. distal farther from the origin of a body part. The knee is distal to the thigh. dorsal towards the top of the body of an animal that walks on four legs. On the human body dorsal is towards the back of the body. elastic cartilage a type of cartilage that contains a abundance of elastic fibers making this cartilage more flexible. It is found in the outer ear. elastic fibers a yellow fiber that is composed a protein called elastin that is not as strong as collagen fibers but more elastic. endocrine glands that secrete their products directly into the blood stream. epithelial tissue a type of tissue that consists of tightly packed cells that forms a continuous layer or lining: lines internal cavities and covers the entire body. exocrine glands that secrete their products into ducts which lead directly to an organ or outside the body. fibrocartilage a type of cartilage that contains strong collagen fibers found in pads between vertebrae and in knee joints. frontal plane an imaginary cut the divides the body into dorsal and ventral protions. gland a cell or group of epithelial cells that are specialized to produce and secrete a substance. hyaline cartilage cartilage composed of very fine collagen fibers and a matrix having a milky appearance. inferior away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body. The navel is inferior to the chin. lateral away from the midline of the body. The arms are lateral to the chest. loose fibrous connective tissue loose connective tissue contain cells called fibroblasts which are scattered in a matrix containing both collagen and elastic fibers. This tissue allows for the expansion of lungs, arteries and the bladder. matrix unstructured semifluid substance that fills the spaces between cells in connective issues. medial toward or at the midline of the body. The heart is medial to the arm. muscular tissue a type of tissue that composed of fibers that can shorten resulting in the contraction of muscles and sometimes the movement of body parts. neuron nerve cell that consists of three parts: dendrites, cell body and axons. organism a living thing capable of performing the major requisites of life. organs combination of two or more different tissues performing a common function: heart, lung brain organ system group of related organs working together. platelets cell fragments of thrombocytes that are essential for blood clotting posterior toward or at the back of the body. The heart is posterior to the breastbone. proximal closer to the origin of the body part. The elbow is proximal to the wrist. pseudostratified epithelial tissue type of epithelial tissue that appears to be multilayered but is only composed of a single layer of cells. reticular connective tissue has a matrix composed of reticular fibers found in the lymph nodes, spleen and bone marrow. reticular fibers very thin types of collagen fibers that a highly branched that form delicate supporting networks sagittal plane an imaginary cut that divides the body into right and left portions. simple epithelial tissue type of epithelial tissue that is one cellular layer thick. skeletal muscles striated, involuntary muscle tissue that makes up those muscles that are attached to bones smooth muscles visceral or involuntary muscles of blood vessels, the digestive and respiratory systems. spongy bone type of bone that composed of thin plates that are filled with red bone marrow where blood cells are produced found at the ends of long bones. squamous flat type cells of epithelial tissue that lines the lungs, blood vessels and the skin.. stratified epithelial tissue type of epithelial tissue that is many layers thick. superficial toward or at the body surface (external). The skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles. superior toward the head end or upper part of a structure or body. The head is superior to the abdomen. transverse an imaginary cut that divides the body into upper and lower portions. tissues group of similar cells which perform a common function. In the human body there are four types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue. ventral on an animal that walks on four legs ventral is towards the bottom of the animal. On the human body ventral refers to the front of the body.