* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tissue Review
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Wound healing wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
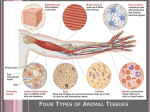
Tissue Review Development of Tissue: Endoderm becomes gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, endocrine glands and organs Mesoderm becomes bones, cartilage, blood, muscles Ectoderm becomes the nervous system and skin 4 types of human body tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Classifications of epithelial tissue Tissue type Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified columnar Stratified squamous Structure Single layer flat cells disc-shaped nuclei Single layer cube like cells large spherical nuclei Single layer of tall cells oval nuclei, many have cilia Location Lining of lymphatic & cardiovascular system Liver, surface of ovaries, duct linings of glands, lining of kidney tubules Non-ciliated – digestive tract, ciliated-bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus Single layer of cells w/different heights, nuclei seen at different levels Several layers of flat cells Lungs, nasal cavities, linings of reproductive system tubes Stratified cuboidal Several layers of cube like cells Stratified columnar Several layers of Transitional Several layers: basal cells cuboidal, surface cells dome-shaped Keratinized – skin, nonkeratinized-lining of esophagus, mouth, vagina Rare in body-sweat glands, mammary glands Rare- pharynx, male urethra, lining of some glandular ducts, salivary ducts Bladder, uterus, ureters, part of urethra Function Slick, friction reducing lining Makes insulin & glucagons in liver, secretion & absorption Moves substances through internal passageways, mucus secretion Secretion of mucus and propulsion of sex cells Protection of underlying areas subject to abrasion Secretion & absorption Secretion & absorption Stretches to permit distension Classification of connective tissue Tissue type Connective tissue proper-Loose: Areolar Structure Gel-like matrix w/all types of fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, wbc Matrix similar to areolar but w/closely packed adipocytes Location Widely distributed throughout the body Function Wraps around & cushions organs Under skin, around kidneys, within abdomen, breasts Tendons, ligaments & aponeuroses Connective tissue Cartilage-Hyaline Parallel collagen fibers w/ a few elastic fibers, major cell type is fibroblast Irregularly arranged collagen fibers with some elastic fibers, major cell type is fibroblast Jelly-like, chondrocytes in lacunae Reserves food stores, insulates against heat loss, supports & protects / nutrient needs of highly active organs Attaches bone to bone, muscle to bone, muscles to muscles Connective tissue Cartilage-Elastic Similar to hyaline but has more fibers External ear, epiglottis Connective tissue Cartilage-Fibrocartilage Matrix similar to hyaline but less firm w/thick collagen fibers Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint Connective tissue – Bone Hard, calcified matrix with collagen fibers, osteocytes are found in lacunae and are well vascularized Compact & spongy bones Connective tissue Blood Red (carry O2, CO2) and white cells (defense) in a fluid matrix (plasma) Contained within blood vessels Connective tissue proper-Loose: Adipose Connective tissue proper-Dense: Regular Connective tissue proper-Dense: Irregular Found in the dermis, submucosa of the digestive tract, and fibrous organ capsules Withstands tension in many directions providing structural strength Ends of long bones, nose, trachea, larynx Supports, reinforces, cushions, resists compression Maintains shape & structure while allowing flexibility Tensile (twisting) strength, absorbs compression shock Supports, protects, & provides levers for muscular action stores Ca, minerals, and fat, red marrow inside bones is the site of hematopoiesis Functions in the transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, and wastes Classification of Muscular Tissue Tissue type Muscle tissue - skeletal Muscle tissue - cardiac Muscle tissue - smooth Structure Long cylindrical cells that can stretch from knee to hip and have multiple nuclei intercalated disc = undulating double membrane separating adjacent cells in cardiac muscle fibers Location Muscles connecting bones Function Muscles contract and things move Heart Sheets of spindleshaped cells with central nuclei that have no striations Walls of hollow organs Propels blood as it contracts Intercalated discs support synchronized contraction of cardiac tissue Propels substances along internal passageways (i.e., peristalsis) Classification of Nervous Tissue Tissue type Nervous tissue Structure Branched neurons with long cellular processes and support cells Location Found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves Function Transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors (using ions)