Zoology - Cardinal Newman
... embryos have two cell layers… hydra and jellyfish….. they lack mesoderm. ...
... embryos have two cell layers… hydra and jellyfish….. they lack mesoderm. ...
Biology – Module 2 – Patterns in Nature
... Proteases begin the digestion of proteins. It has a thick strong muscular wall with a mucus lining to protect it from the acid inside. Churns the food by involuntary muscle contraction, mixing it with digestive juices. ...
... Proteases begin the digestion of proteins. It has a thick strong muscular wall with a mucus lining to protect it from the acid inside. Churns the food by involuntary muscle contraction, mixing it with digestive juices. ...
cnidaria powerpoint
... polyp life form. #11 shows the polyp undergoing asexual reproduction in the form of budding. The top of the polyp breaks off and goes on to form the medusa stage of the jellyfish’s life. (if this was an anemone the polyp would settle on the ocean floor and become a new polyp…. See picture of broodin ...
... polyp life form. #11 shows the polyp undergoing asexual reproduction in the form of budding. The top of the polyp breaks off and goes on to form the medusa stage of the jellyfish’s life. (if this was an anemone the polyp would settle on the ocean floor and become a new polyp…. See picture of broodin ...
Ch. 4 AP PP 2
... - found in the walls of blood vessels, around hollow organs (urinary bladder), in layers around respiratory, circulatory, digestive, and reproductive tracts - cells are small and slender, tapering to a point at each end; each has one nucleus - actin and myosin filaments are scattered, so there are n ...
... - found in the walls of blood vessels, around hollow organs (urinary bladder), in layers around respiratory, circulatory, digestive, and reproductive tracts - cells are small and slender, tapering to a point at each end; each has one nucleus - actin and myosin filaments are scattered, so there are n ...
B.Sc. questions - Nursing examinations in India
... The venous drainage of th intestines is mainly through a) Inferior Vena Cava b) Superior Vena Cava c) Portal Vein d) Gastroduodenal vein 2. The taste buds of the tongue are called a) Filiform Papillae b) Fungiform Papillae c) Vallate Papillae d) All of the above e) None of the above 3. The palatine ...
... The venous drainage of th intestines is mainly through a) Inferior Vena Cava b) Superior Vena Cava c) Portal Vein d) Gastroduodenal vein 2. The taste buds of the tongue are called a) Filiform Papillae b) Fungiform Papillae c) Vallate Papillae d) All of the above e) None of the above 3. The palatine ...
The inner ear The inner ear can be divided into
... of the basliar membrane and stretches from the apex to the base of the cochlea. Its receptor cells, which are called hair cells, are arranged in rows and they possess numerous hair like processes that extend into the endolymph of the cochlear duct. As sound vibrations pass through the inner ear, the ...
... of the basliar membrane and stretches from the apex to the base of the cochlea. Its receptor cells, which are called hair cells, are arranged in rows and they possess numerous hair like processes that extend into the endolymph of the cochlear duct. As sound vibrations pass through the inner ear, the ...
Animal Basics, Vertebrates, and Invertebrates
... • Eukaryotic cells with no cell wall or chloroplasts • Heterotrophs by ingestion (digest food inside their bodies) • Bodies are made of diploid cells (gametes are the only haploid cells) • Glucose stored as glycogen (a polysaccharide only found in animals) • Most are mobile at some point in their li ...
... • Eukaryotic cells with no cell wall or chloroplasts • Heterotrophs by ingestion (digest food inside their bodies) • Bodies are made of diploid cells (gametes are the only haploid cells) • Glucose stored as glycogen (a polysaccharide only found in animals) • Most are mobile at some point in their li ...
Laboratory Exercises
... In a Nonsmokers lungs, the cilia protrude from the cells that line the trachea and bronchioles sweep mucus and debris from the respiratory passageways. In a smokers lungs, the cilia are paralyzed or broken by cigarette smoke. Debris can reach the lungs and accumulate, blackening and clogging the del ...
... In a Nonsmokers lungs, the cilia protrude from the cells that line the trachea and bronchioles sweep mucus and debris from the respiratory passageways. In a smokers lungs, the cilia are paralyzed or broken by cigarette smoke. Debris can reach the lungs and accumulate, blackening and clogging the del ...
5 circulatorysystem - Teacher Geeks
... all the cells of your body alive. There are four components to the blood: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The plasma is mostly water and its function is to carry all the other components through the body. It is pale yellow and contains some sugar, protein, minerals and wast ...
... all the cells of your body alive. There are four components to the blood: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The plasma is mostly water and its function is to carry all the other components through the body. It is pale yellow and contains some sugar, protein, minerals and wast ...
2/22/17 Respiratory System
... Diaphragm relaxes and floor of thoracic cavity recoils elastically ...
... Diaphragm relaxes and floor of thoracic cavity recoils elastically ...
File - Study Guides
... 2. Closed circulatory system: a system where blood flows continuously through a network of blood vessels. Earthworms, some mollusks, and all vertebrates have this system. ...
... 2. Closed circulatory system: a system where blood flows continuously through a network of blood vessels. Earthworms, some mollusks, and all vertebrates have this system. ...
Document
... (internal and external) 2. set point - a normal value or range of values within which the condition has to remain for the body to work correctly 3. control center - set of cells or organ that a. compares input from receptors to the set point to see if there is a discrepancy b. if a discrepancy exist ...
... (internal and external) 2. set point - a normal value or range of values within which the condition has to remain for the body to work correctly 3. control center - set of cells or organ that a. compares input from receptors to the set point to see if there is a discrepancy b. if a discrepancy exist ...
Ch 4: Tissues
... Line hollow body cavities (ie. digestive organs) Open to the exterior Adapted for absorption or secretion ...
... Line hollow body cavities (ie. digestive organs) Open to the exterior Adapted for absorption or secretion ...
AP Circulatory
... • Cardiac output is adjusted by controls over rate and strength of heartbeat (nervous system) • Total resistance in vessels changes due to diameter changes (vasoconstriction and vasodilation) which is controlled by the nervous and endocrine system. • Baroreceptor response is main short-term control ...
... • Cardiac output is adjusted by controls over rate and strength of heartbeat (nervous system) • Total resistance in vessels changes due to diameter changes (vasoconstriction and vasodilation) which is controlled by the nervous and endocrine system. • Baroreceptor response is main short-term control ...
Cells→ Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems
... fresh oxygen (O2) from the air. When the blood reaches the lungs, part of the respiratory system, the blood is re-oxygenated. Your stomach, part of the digestive system, constantly interacts with your endocrine system and spreads hormones throughout your body. Examples of Systems It's easy to point ...
... fresh oxygen (O2) from the air. When the blood reaches the lungs, part of the respiratory system, the blood is re-oxygenated. Your stomach, part of the digestive system, constantly interacts with your endocrine system and spreads hormones throughout your body. Examples of Systems It's easy to point ...
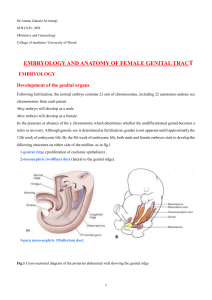
Dr.Amina Zakaria Al-tutunji M.B.Ch.B., MD. Obstetrics and
... 3-The Fallopian tubes (oviducts) Each tubeis about 10 cm long & extended outwards from the uterine cornu to end near the ovary. The tubes convey the ovum from the ovary towards the uterus & its the site of fertilization which provides oxygenation & nutrition for sperm, ovum and zygote. It is distigu ...
... 3-The Fallopian tubes (oviducts) Each tubeis about 10 cm long & extended outwards from the uterine cornu to end near the ovary. The tubes convey the ovum from the ovary towards the uterus & its the site of fertilization which provides oxygenation & nutrition for sperm, ovum and zygote. It is distigu ...
Chapter 6 - Juan Diego Academy
... connective tissue cells enlarge and differentiate into osteoblasts. Spongy bone tissue is produced in all directions by these osteoblasts in the membrane. Eventually, the periosteum is developed by outside cells of the membrane of the developing bone. Endochondral bones develop masses of hyaline car ...
... connective tissue cells enlarge and differentiate into osteoblasts. Spongy bone tissue is produced in all directions by these osteoblasts in the membrane. Eventually, the periosteum is developed by outside cells of the membrane of the developing bone. Endochondral bones develop masses of hyaline car ...
Organism with a type of coelom
... Organism with a type of coelom in which there is a body cavity with endoderm lining the outside body wall but not around the gut ...
... Organism with a type of coelom in which there is a body cavity with endoderm lining the outside body wall but not around the gut ...
Overview of the Four Basic Tissue Types
... of cells attached to one another to form an uninterrupted layer of cells that separates the underlying tissues from the outside world. ...
... of cells attached to one another to form an uninterrupted layer of cells that separates the underlying tissues from the outside world. ...
the autonomic nervous system
... of the CNS. • Within the cranial cavity the dura mater is intimately attached to the inside of the cranial bones and so fulfills the role of periosteum. – It also forms the falx cerebri, a median sickle-shaped fold that lies in the longitudinal fissure and partially separates the cerebral hemisphere ...
... of the CNS. • Within the cranial cavity the dura mater is intimately attached to the inside of the cranial bones and so fulfills the role of periosteum. – It also forms the falx cerebri, a median sickle-shaped fold that lies in the longitudinal fissure and partially separates the cerebral hemisphere ...
Homeostasis Practice Test Name: Date: 1. Which
... dust, and pollen are common causes. In some people, looking at a bright light can cause sneezing; this is known as the photic response. Sneezing usually begins when receptors in the interior of the nose are stimulated. A message is carried by a nerve to a reaction of the midbrain which in turn, stim ...
... dust, and pollen are common causes. In some people, looking at a bright light can cause sneezing; this is known as the photic response. Sneezing usually begins when receptors in the interior of the nose are stimulated. A message is carried by a nerve to a reaction of the midbrain which in turn, stim ...
Chapter 13
... bronchioles are the respiratory bronchioles, because some gas exchange occurs here. • The epithelial lining is simple cuboidal epithelium interspersed alveoli type cells called squamous pneumocytes. • Alveolar ducts originate from the respiratory bronchioles wherein the walls of the alveolar ducts a ...
... bronchioles are the respiratory bronchioles, because some gas exchange occurs here. • The epithelial lining is simple cuboidal epithelium interspersed alveoli type cells called squamous pneumocytes. • Alveolar ducts originate from the respiratory bronchioles wherein the walls of the alveolar ducts a ...
Cnidarians - carverbiology11
... Sponges rely on water being passed through its body cavity for respiration, circulation, and excretion Oxygen from the water diffuses into the cells of the sponge body, and ammonia and other wastes diffuse from the body into the water ...
... Sponges rely on water being passed through its body cavity for respiration, circulation, and excretion Oxygen from the water diffuses into the cells of the sponge body, and ammonia and other wastes diffuse from the body into the water ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.