Integumentary - WordPress.com
... The Largest Organ • Skin is 12-15% of body weight • 15-20 sq. ft ( 1.5-2.0 sq. meters) • Some organisms, such as insects, ...
... The Largest Organ • Skin is 12-15% of body weight • 15-20 sq. ft ( 1.5-2.0 sq. meters) • Some organisms, such as insects, ...
Baggie Cell Model - DNALC::Protocols
... There are about 25 trillion red blood cells in the human body. Red blood cells are unique in that they do not contain genetic material; they discard their nuclei soon after being made in the bone marrow. Red blood cells have a protein called hemoglobin that binds and carries oxygen to all of the oth ...
... There are about 25 trillion red blood cells in the human body. Red blood cells are unique in that they do not contain genetic material; they discard their nuclei soon after being made in the bone marrow. Red blood cells have a protein called hemoglobin that binds and carries oxygen to all of the oth ...
DIVERSITY NOTES
... E. Have a simple nervous system - Have a nerve net capable of sending signals F. Digestive system consists of a Gastrovascular cavity that only has one opening (food goes in and wastes go out the same opening) G. Have no defined respiratory system, but they perform gas exchange by diffusion – direct ...
... E. Have a simple nervous system - Have a nerve net capable of sending signals F. Digestive system consists of a Gastrovascular cavity that only has one opening (food goes in and wastes go out the same opening) G. Have no defined respiratory system, but they perform gas exchange by diffusion – direct ...
PowerPoint
... Epithelial and Connective Tissues • Classes of Tissues – Two classes—epithelial, connective – Muscle and Nervous Tissue (don’t fit in classes) ...
... Epithelial and Connective Tissues • Classes of Tissues – Two classes—epithelial, connective – Muscle and Nervous Tissue (don’t fit in classes) ...
33835_CellsBldgBlcks TG
... and fats), and use them to repair themselves and reproduce. All organisms are made up of cells; the simplest life forms are made up of only one cell. The vast majority of organisms are single-celled, while more complex life forms are multicellular. The individual cell is actually a system unto itsel ...
... and fats), and use them to repair themselves and reproduce. All organisms are made up of cells; the simplest life forms are made up of only one cell. The vast majority of organisms are single-celled, while more complex life forms are multicellular. The individual cell is actually a system unto itsel ...
Levels of Organization
... do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to normal view? 5. Why do you think a specimen placed under the microsco ...
... do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to normal view? 5. Why do you think a specimen placed under the microsco ...
Chapter 19: Blood
... • Peptide hormones made by endocrine organs Serum -liquid part of a blood sample: – in which dissolved fibrinogen has converted to solid fibrin ...
... • Peptide hormones made by endocrine organs Serum -liquid part of a blood sample: – in which dissolved fibrinogen has converted to solid fibrin ...
01-body cavities2008-02
... ,separating the pericardial cavity from the pleural cavities. The primordial mediastinum consists of a mass of mesenchym ( ...
... ,separating the pericardial cavity from the pleural cavities. The primordial mediastinum consists of a mass of mesenchym ( ...
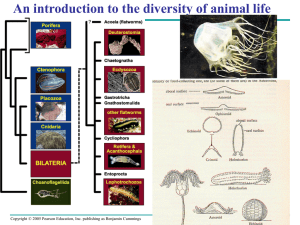
Animal Diversity Part I
... respiratory and reproductive tracts; the mesoderm layer, sandwiched between the other two, eventually gives rise to muscle, organs, and supportive tissues. Triploblastic animals, those possessing three tissue layers, are further classified by whether or not they have a body cavity called a coelom (p ...
... respiratory and reproductive tracts; the mesoderm layer, sandwiched between the other two, eventually gives rise to muscle, organs, and supportive tissues. Triploblastic animals, those possessing three tissue layers, are further classified by whether or not they have a body cavity called a coelom (p ...
Introduction to Planaria
... Planarians are predators and scavengers and eat live or dead animals using their muscular retractable pharynx which can extend out of the mouth opening on the ventral side up to half of their body length. The pharynx pins down the prey while enzymes secreted from the mouth soften the tissue. The dig ...
... Planarians are predators and scavengers and eat live or dead animals using their muscular retractable pharynx which can extend out of the mouth opening on the ventral side up to half of their body length. The pharynx pins down the prey while enzymes secreted from the mouth soften the tissue. The dig ...
Introduction to Planaria
... Planarians are predators and scavengers and eat live or dead animals using their muscular retractable pharynx which can extend out of the mouth opening on the ventral side up to half of their body length. The pharynx pins down the prey while enzymes secreted from the mouth soften the tissue. The dig ...
... Planarians are predators and scavengers and eat live or dead animals using their muscular retractable pharynx which can extend out of the mouth opening on the ventral side up to half of their body length. The pharynx pins down the prey while enzymes secreted from the mouth soften the tissue. The dig ...
Lecture 8 - Northern Arizona University
... a. Cells can be separated and develop into complete organisms. b. Vertebrate zygotes are like this. ...
... a. Cells can be separated and develop into complete organisms. b. Vertebrate zygotes are like this. ...
The differences between blood and tissue fluid and the formation of
... The diagram on the previous page shows the hydrostatic and osmotic pressures acting on a single capillary. At the venous end, the blood has lost its hydrostatic pressure. The combined effect of the hydrostatic pressure in the tissue fluid and the osmotic force of the plasma proteins are sufficient ...
... The diagram on the previous page shows the hydrostatic and osmotic pressures acting on a single capillary. At the venous end, the blood has lost its hydrostatic pressure. The combined effect of the hydrostatic pressure in the tissue fluid and the osmotic force of the plasma proteins are sufficient ...
Respiratory system
... • Consists of about 20 C-shaped hyaline cartilage pieces which are filled with smooth muscle and connective tissue between the ends. ...
... • Consists of about 20 C-shaped hyaline cartilage pieces which are filled with smooth muscle and connective tissue between the ends. ...
Science 8 Review Questions For Final Exam
... Eric Hamber Secondary – Learning Strategies Centre ...
... Eric Hamber Secondary – Learning Strategies Centre ...
video slide
... (‘Arthropod’ means jointed foot or limb). For many years these were treated as one huge phylum with three clear subphyla. More recently various lines of work, notably DNA analyses, suggest that the differences in these 3 subphyla are so great that they probably evolved the ‘armoured’ body form indep ...
... (‘Arthropod’ means jointed foot or limb). For many years these were treated as one huge phylum with three clear subphyla. More recently various lines of work, notably DNA analyses, suggest that the differences in these 3 subphyla are so great that they probably evolved the ‘armoured’ body form indep ...
Chapter 1 Basic science
... 2 Middle: very thick, spiral muscle fibres with blood vessels between 3 Inner: thin, oblique with condensation at each cornu and at the upper and lower end of the cervical canal — the internal and external os. Increase in size during pregnancy results mostly from hypertrophy of existing cells rather ...
... 2 Middle: very thick, spiral muscle fibres with blood vessels between 3 Inner: thin, oblique with condensation at each cornu and at the upper and lower end of the cervical canal — the internal and external os. Increase in size during pregnancy results mostly from hypertrophy of existing cells rather ...
from mesoderm - RuthenbergAP
... Cell Structure and Specialization • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes • Their cells lack cell walls • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have ...
... Cell Structure and Specialization • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes • Their cells lack cell walls • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have ...
A&P ch. 4 - Catherine Huff`s Site
... Secretions- specialized protein molecules that are produced in the RER, packaged by the golgi and discharged from the cell. Glands can be organized by factors: • Presence or absence of ducts ...
... Secretions- specialized protein molecules that are produced in the RER, packaged by the golgi and discharged from the cell. Glands can be organized by factors: • Presence or absence of ducts ...
Sperm - My Anatomy Mentor
... cells A (remains a stem cell) or B (goes on) When start to undergo meiosis are by definition called ...
... cells A (remains a stem cell) or B (goes on) When start to undergo meiosis are by definition called ...
Lab 6
... Muscle tissue is composed of long, excitable cells that are capable of contraction. Inside each cell, there are many microfilaments arranged in parallel. These microfilaments are of two types: actin and myosin. When a muscle cell contracts, these microfilaments slide past each other, and the muscle ...
... Muscle tissue is composed of long, excitable cells that are capable of contraction. Inside each cell, there are many microfilaments arranged in parallel. These microfilaments are of two types: actin and myosin. When a muscle cell contracts, these microfilaments slide past each other, and the muscle ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.