* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Science with Ms. Friess
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
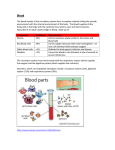
Cells Osmosis + Diffusion Respiratory 10 Digestive Circulatory System Grab Bag 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 Cells Osmosis + Diffusion -10 A Cell Membrane is a thin outer layer surrounding a cell and can be described as: • A) Impermeable • B) Selectively-Permeable • C) Permeable to everything Cells Osmosis + Diffusion -10 A) Selectively-Permeable Also Know as Semi-Permeable • This means that the membrane is able to let certain wanted substances in to the cell (nutrients, water, and oxygen) and block other substances from coming in to the cell. Cells Osmosis + Diffusion -20 • Choose 3 Cell Organelles from the following list, describe, and explain the function » Nucleus Golgi » Cytoplasm Lysosome » Mitochondria Vacuole » Ribosome » Endoplasmic Reticulum Cells Osmosis + Diffusion - 20 Cells Osmosis + Diffusion - 30 • Explain Diffusion with an example Cells Osmosis + Diffusion - 30 • The movement of particles or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration • Ex. Hairspray particles spreading through a room • Ex. Food dye diffusing through water Cells Osmosis + Diffusion - 40 • Explain the word equilibrium and how it applies to osmosis and diffusion • Draw an image that displays or shows an equilibrium condition Cells Osmosis + Diffusion - 40 • Equilibrium is a state of balance • It is when molecules are evenly spaced or distributed throughout a space Cells Osmosis + Diffusion -50 Which side has a HIGHER CONCENTRATION of Water? Which direction will the water particles move if the dotted line down the center represents a membrane permeable to water? Cells Osmosis + Diffusion - 50 • The right side has a higher water concentration • Water would move from right to left…. The water level on the right would go down to balance the solution on the other side Respiratory System- 10 • What is the main point of the respiratory system? • What important function does it serve? Respiratory System- 10 • We have a respiratory system to breath • We require OXYGEN to feed our cells… we also need to get rid of Carbon Dioxide Gas • The respiratory system is designed to exchange these gases in our lungs Respiratory System - 20 • Does your respiratory system have any methods to protect itself from unwanted dust particles from being taken in to your lungs? Respiratory System- 20 - Nose Hair (Cilia) - Cilia lining your trachea - Mucous lining your nasal cavity, throat, and windpipe Respiratory System- 30 • What is the scientific name for the windpipe of the respiratory system? • How is this tube structurally different than the food tube? Respiratory System- 30 Trachea is strong and made up of cartilage This is so that the change in air pressure when we breathe doesn’t cause the tube to collapse TRACHEA Respiratory System- 40 • Explain the following picture… What is happening here and what are these structures called? Respiratory System- 40 • ALVEOLI (microscopic air sacs in the lungs) • They are covered with tiny capillaries (blood vessels) and this is where gas exchange happens • Oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and CO2 diffuses back into the alveoli and is exhaled Respiratory System- 50 • There is an analogy that the Respiratory System can be compared to an tree flipped upside down Explain the analogy. What would the tree trunk, the largest branches, the smaller branches, and the twigs with leaves would represent within the respiratory system…. Respiratory System- 50 Trunk ---- Trachea (Windpipe) 2 Largest Branches ----Right and Left Bronchus Smaller Branches ----Bronchioles Twigs (Leaves) ----Alveoli (air sacs) Digestive System-10 • What types of Digestion happen in the mouth • Explain two different types of digestion and give an example of how this works… Digestive System-10 • Mechanical Digestion (Physical Breakdown) --- teeth physically breaking food into smaller pieces • Chemical Breakdown (Chemical Reactions) --- Saliva contains Enzymes which begin digesting food Digestive System- 20 • Identify the parts of the digestive system based on the diagram Digestive System- 20 • Esophagus • Stomach • Small Intestine Digestive System - 30 Other than stomach acid… how does the stomach contribute to digestion? Digestive System- 30 • Acid + Enzymes (chemical helpers) create Gastric Juice • Stomach muscles fold, unfold, “churn” and rotate food around Digestive System- 40 • Explain what peristalsis is and how it contributes to digestion or the digestive process Digestive System- 40 • Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when food is swallowed. Digestive System- 50 • Small Intestine vs. Large Intestine. • What are the major differences? Which comes first in the digest tract? What are the differences in function? What are the structural differences? Digestive System- 50 Small Intestine: Very thin… extremely long (3 times the height of your body) This is where nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream Large Intestine: Three times as thick as the small intestine. Much shorter. This is where liquids and water are reabsorbed Circulatory System - 10 • How many chambers are in the heart and what are they all called? Circulatory System - 10 4 Chambers in the Heart Circulatory System - 20 How many valves are in the heart? What is the purpose of valves? Circulatory System - 20 4 Valves • Valves prevent blood from flowing backwards or in the wrong direction. They act as one way only “trapdoors” Circulatory System - 30 What direction does blood travel when it is in Veins? What direction does blood travel when it is in Arteries? Circulatory System - 30 Veins carry blood back TOWARDS the heart Arteries carry blood AWAY from the heart Circulatory System - 40 • What are the 4 Components of Blood and what does each component do? Circulatory System - 40 Component of Blood Function Percentage Red Blood Cells Carry oxygen and nutrients through bloodstream Attack germs and fight disease Liquid portion of blood Clot blood and heal wounds or damaged vessels 44% White Blood Cells Plasma Platelets 0.5% 55% 0.5% Circulatory System - 50 • Explain the difference between “Red Blood” and “Blue Blood” • Where would you find Red Blood and where would you find Blue Blood both in the heart and in the vessels. • Are there any exceptions? Circulatory System - 50 Red Blood – Oxygenated Blue Blood – Deoxygenated Red Blood – LEFT SIDE of HEART Blue Blood – RIGHT SIDE of HEART Blue (Veins… most of time) Red (Arteries… most of time) * Exception * Pulmonary Artery and Vein Grab Bag - 10 • What are the 6 Essential Nutrients that all food can break down into • These 6 things are the simple and smallest molecular nutrients Grab Bag – 10 Protein Fats Carbohydrates Vitamins Minerals Water Grab Bag - 20 What is the name of the LARGEST and STRONGEST Artery in the Body? Where can it be found? Grab Bag – 20 Aorta The aorta takes blood from the Left Ventricle, directs it out of the heart… and toward all cells of the body Grab Bag - 30 • When Blood is returning from the cells of the body it comes back through a network of veins. • These veins grow larger and larger toward the heart. What are the names of the largest veins that attach to the right atrium of the heart Grab Bag – 30 •Superior Vena Cava •Inferior Vena Cava Grab Bag - 40 Label Number 3. 4. 5. 10. Grab Bag – 40 • 3. Arm • 4. Course Focusing Lens • 5. Fine Focusing Lens • 10. Stage Grab Bag - 50 • Explain how body systems are interconnected or interdependent (how do they rely on each other)? Grab Bag – 50 Blood Connects Digestive, Respiratory, Circulatory • Blood absorbs Nutrients in Digestive System • *Blood picks up oxygen and drops of carbon dioxide in Respiratory system • *Blood circulates body in Circulatory system Heart and Lungs Depend on each other • Heart pumps blood to lungs to be reoxygenated • Systems need one another!