Connective Tissues
... Dense Connective Tissue: - consists mostly of collagen fibers Tendons- cords of dense connective tissue connecting muscle to bone Ligaments- connect bone to bone, can stretch a little ...
... Dense Connective Tissue: - consists mostly of collagen fibers Tendons- cords of dense connective tissue connecting muscle to bone Ligaments- connect bone to bone, can stretch a little ...
vet ch 1 and 2
... compose the central nervous system In addition, nerves extend from theses areas to other locations throughout the body ...
... compose the central nervous system In addition, nerves extend from theses areas to other locations throughout the body ...
Slide 1
... pleura Parietal pleura – outer layer Visceral pleura – directly on lung Pleural cavity – slit-like potential space filled with pleural fluid • Lungs can slide but separation from pleura is resisted (like film between 2 plates of glass) • Lungs cling to thoracic wall and are forced to expand and reco ...
... pleura Parietal pleura – outer layer Visceral pleura – directly on lung Pleural cavity – slit-like potential space filled with pleural fluid • Lungs can slide but separation from pleura is resisted (like film between 2 plates of glass) • Lungs cling to thoracic wall and are forced to expand and reco ...
Ethmoid Sinus
... indicate a typical ciliary beat frequency of 700 to 800 times a minute, with mucociliary transport occurring at a rate of 1cm/minute Goblet cells produce glycoproteins which are responsible for the viscosity and elasticity of mucus and respond to parasympathetic and sympathetic neural inputs. Betwee ...
... indicate a typical ciliary beat frequency of 700 to 800 times a minute, with mucociliary transport occurring at a rate of 1cm/minute Goblet cells produce glycoproteins which are responsible for the viscosity and elasticity of mucus and respond to parasympathetic and sympathetic neural inputs. Betwee ...
Anatomy and physiology of the nose and paranasal sinuses
... indicate a typical ciliary beat frequency of 700 to 800 times a minute, with mucociliary transport occurring at a rate of 1cm/minute Goblet cells produce glycoproteins which are responsible for the viscosity and elasticity of mucus and respond to parasympathetic and sympathetic neural inputs. Betwee ...
... indicate a typical ciliary beat frequency of 700 to 800 times a minute, with mucociliary transport occurring at a rate of 1cm/minute Goblet cells produce glycoproteins which are responsible for the viscosity and elasticity of mucus and respond to parasympathetic and sympathetic neural inputs. Betwee ...
METABOLISM
... the muscle cannot be held in a state of contraction for long. Energy for contraction comes from the ATP in the cells. When large amounts of energy are required, for example for a quick sprint, the glycogen stored in the muscle is converted into lactic acid, releasing energy. Only one quarter of the ...
... the muscle cannot be held in a state of contraction for long. Energy for contraction comes from the ATP in the cells. When large amounts of energy are required, for example for a quick sprint, the glycogen stored in the muscle is converted into lactic acid, releasing energy. Only one quarter of the ...
CONNECTIVE TISSUE I
... dense irregular CT in the periosteum on top of the bone. SLIDE 24 – AORTA (H&E STAIN), SLIDE 25 – AORTA (VVG STAIN FOR ELASTIN), ELASTIC FIBERS. It is often difficult to see some fibers without a special stain. In slide 24 you can make out elastic fibers arranged into wavy elastic laminae. Take your ...
... dense irregular CT in the periosteum on top of the bone. SLIDE 24 – AORTA (H&E STAIN), SLIDE 25 – AORTA (VVG STAIN FOR ELASTIN), ELASTIC FIBERS. It is often difficult to see some fibers without a special stain. In slide 24 you can make out elastic fibers arranged into wavy elastic laminae. Take your ...
Lecture #14 Date - Mrs. Tyler's Advanced Placement Biology
... (cuticle)~ molting, jointed appendages; open circulatory system (hemolymph); extensive cephalization ...
... (cuticle)~ molting, jointed appendages; open circulatory system (hemolymph); extensive cephalization ...
Face Formation - Open Source Medicine
... Pharyngeal Apparatus (1st observed in week 4) –ventral side (initially) o Major contributor to head & neck development, especially the area around the pharynx; most congenital abnormalities in head & neck region as a result of mistakes in transformation of apparatus to adult derivatives o Pharyngeal ...
... Pharyngeal Apparatus (1st observed in week 4) –ventral side (initially) o Major contributor to head & neck development, especially the area around the pharynx; most congenital abnormalities in head & neck region as a result of mistakes in transformation of apparatus to adult derivatives o Pharyngeal ...
Chapter 4
... blood---otherwise, your cells would have more than enough glucose right after a meal and starve in between meals and overnight. When you have an oversupply of glucose, the pancreas secretes insulin which stimulates the liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen. It also stimulates fat cells ...
... blood---otherwise, your cells would have more than enough glucose right after a meal and starve in between meals and overnight. When you have an oversupply of glucose, the pancreas secretes insulin which stimulates the liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen. It also stimulates fat cells ...
Head and Neck ppt - student.ahc.umn.edu
... includes head and face and tissues responsible for teeth development differentiation of nervous tissue from ectoderm differentiation of neural crest cells (ectoderm) differentiation of mesoderm ...
... includes head and face and tissues responsible for teeth development differentiation of nervous tissue from ectoderm differentiation of neural crest cells (ectoderm) differentiation of mesoderm ...
7 Head & Neck - University of Minnesota
... includes head and face and tissues responsible for teeth development differentiation of nervous tissue from ectoderm differentiation of neural crest cells (ectoderm) differentiation of mesoderm ...
... includes head and face and tissues responsible for teeth development differentiation of nervous tissue from ectoderm differentiation of neural crest cells (ectoderm) differentiation of mesoderm ...
Maintaining a Dynamic Equilibrium The Need for Homeostasis
... Maintaining water balance is a major concern for all living things. Plants as well as animals ...
... Maintaining water balance is a major concern for all living things. Plants as well as animals ...
Survey of the phyla: Porifera through Annelida
... Wanders in sub dermal connective tissue (eyes, tongue, scrotum) Africa ...
... Wanders in sub dermal connective tissue (eyes, tongue, scrotum) Africa ...
TISSUES AND OTHER LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... Plasma is the extracellular fluid matrix in the ground substance. It contains a large number of proteins such as Fibrinogen, Albumin, and Globulin to be transported to various parts of the animal body for various purposes. 5.3.3 Muscle tissue This is composed of long excitable cells containing paral ...
... Plasma is the extracellular fluid matrix in the ground substance. It contains a large number of proteins such as Fibrinogen, Albumin, and Globulin to be transported to various parts of the animal body for various purposes. 5.3.3 Muscle tissue This is composed of long excitable cells containing paral ...
The Metazoa
... ectoderm. This means that animals could efficiently deliver oxygen throughout their bodies without compromising the effectiveness of their outer skins (ectoderm) or size. This also meant that animals could evolve exoskeletons. ...
... ectoderm. This means that animals could efficiently deliver oxygen throughout their bodies without compromising the effectiveness of their outer skins (ectoderm) or size. This also meant that animals could evolve exoskeletons. ...
Three Domains Now Three Domains and 6 Kingdoms
... Sponges also have collared cells, but these form a larger, integrated structure supported by rigid spicules or organic tissue. The differentiation of cells required the evolution of Hox Genes (genes that dictate differing functions of cells) ...
... Sponges also have collared cells, but these form a larger, integrated structure supported by rigid spicules or organic tissue. The differentiation of cells required the evolution of Hox Genes (genes that dictate differing functions of cells) ...
Animal Structure and Function Review
... 1. What is the hierarchical organization of body plans? 2. What is the function of increased surface area in the small intestine and lungs? 3. Describe or draw cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, stratified squamous, and simple squamous epithelial cells. 4. Name the six ma ...
... 1. What is the hierarchical organization of body plans? 2. What is the function of increased surface area in the small intestine and lungs? 3. Describe or draw cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, stratified squamous, and simple squamous epithelial cells. 4. Name the six ma ...
BIOL 2401 Unit and Final Exam Study Guides
... 1. The cytoplasm of the skeletal muscle cell is called ... 2. The cell membrane of the skeletal muscle cell is called… 3. What are the four properties of the muscle? 4. Explain the diverse functions of the muscle tissue. 5. A skeletal muscle cell can also be called… 6. A group of muscle cells i ...
... 1. The cytoplasm of the skeletal muscle cell is called ... 2. The cell membrane of the skeletal muscle cell is called… 3. What are the four properties of the muscle? 4. Explain the diverse functions of the muscle tissue. 5. A skeletal muscle cell can also be called… 6. A group of muscle cells i ...
Document
... includes head and face and tissues responsible for teeth development differentiation of nervous tissue from ectoderm differentiation of neural crest cells (ectoderm) differentiation of mesoderm ...
... includes head and face and tissues responsible for teeth development differentiation of nervous tissue from ectoderm differentiation of neural crest cells (ectoderm) differentiation of mesoderm ...
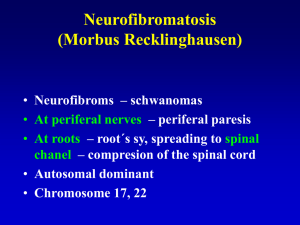
Vrodené a perinatálne získané ochorenia mozgu
... and granular cells • Gen ATM also risk of cancer ...
... and granular cells • Gen ATM also risk of cancer ...
Notes on Unit 4 – Nature`s Principles
... Most of the life processes of these cells are carried out either in the cytoplasm or in folds of the cell membrane, because they are lacking organelles. They are usually single-celled, however, can form biofilms, thin layers of millions of cells of different species that help each other with vario ...
... Most of the life processes of these cells are carried out either in the cytoplasm or in folds of the cell membrane, because they are lacking organelles. They are usually single-celled, however, can form biofilms, thin layers of millions of cells of different species that help each other with vario ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.