* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Structure and Function Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
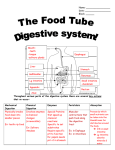
Animal Structure and Function Review 2011 AP Biology Ms. Tank Chapter 40 Vocab: Physiology Anatomy Epithelial tissue Endothermic Ectothermic Positive feedback Negative Feedback 1. What is the hierarchical organization of body plans? 2. What is the function of increased surface area in the small intestine and lungs? 3. Describe or draw cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, stratified squamous, and simple squamous epithelial cells. 4. Name the six major types of connective tissue in animals. 5. Describe the difference between ligaments and tendons 6. Name the three types of muscle tissue. 7. What are two adaptations to heat and cold? 8. Describe negative feedback and give an example. Also, explain how this is linked to homeostasis. 9. Describe countercurrent exchange in the dolphins fin or goose leg. 10. Describe the conditions that may have promoted the evolution of endotherms and ectotherms Chapter 41 Vocab: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Essential nutrients Gastrovascular cavity Alimentary canal Peristalsis 11. Explain the difference between malnourishment and undernourishment. 12. Describe each of the stages of food processing: ingestion, digestion, absorption and elimination 13. What is happening when your food goes “down the wrong tube”? 14. How do the following control movement of food through the digestive tract? Sphincters and peristalsis. 15. Describe where the following are made, where they are “dumped” into, and what their function is. a. Amylase b. HCL c. Pepsin d. Bile e. Buffer (into the small intestine) 16. The appendix is a vestigial structure. Explain what that means and what the function of it was in our ancestors. 17. What is the main function of each of the following a. Esophogus b. Stomach c. Small intestine d. Large intestine e. Oral cavity f. pancreas 18. Describe the structure of the small intestine 19. What is the reason for the four chambered stomach of the cow? Other organisms such as koala also rely on plant material for their diet. What structure allows for this? Chapter 42 Vocab: Systemic circuit Pulmonary circuit Bronchiole Alveoli 20. Trace the flow of blood through the body and the heart. 21. Know the structures of the heart (look at figure 42.7 in the text book) 22. What is the sound you hear when you hear a heart beat? 23. Describe blood pressure and what it means to take blood pressure (what are you measuring and how does a sphygmomanometer work) 24. Describe the walls of arteries capillaries and veins and why are they different. 25. Explain why the velocity of blood flow is lowest in the capillaries. 26. Explain why oxygen diffuses into the capillaries surrounding the alveoli 27. Explain the function of hemoglobin and how pH changes the affinity for oxygen. What term is used to describe this dissociation curve? 28. Describe the role of the diaphragm in breathing Chapter 43 Vocab: Innate immunity Acquired immunity Histamine Phagocytes Immunodeficiency Memory cells antigen 29. Describe what happens when you have an inflammatory response (such as when you get pricked by a needle) 30. Compare and contrast B and T cells. (include structure, function, where they mature, and what they give rise to). What is the difference between cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells. 31. Explain the treatment one would get if they were bit by a poisonous snake. 32. Explain why vaccinations work. What is floating around in your body that you didn’t have before? 33. Describe A, B and O blood type and their ability to donate and receive to each other. Chapter 44 Vocab: Osmolarity Osmosis Diffusion Filtrate 34. What type of challenges do salmon face when going from freshwater to salt water and how do they cope with it? What challenges do they face when going from saltwater to freshwater and how do they cope with it? 35. What are the three types of nitrogenous waste? Why have each of these evolved (explain using the environment in which each organism lives)? 36. Be able to label parts of the kidney and give the function of each structure. 37. Alcohol is an antidiuretic hormone inhibitor. Explain what this means. 38. What is the ultimate function of your kidneys? 39. What structure filters the blood and what is kept out of the filtrate? 40. Animals that reside in dry climates (desert) have really long loops of henle. Explain why this might be the case. Chapter 45 Vocab: Hormone Endocrine system Nervous system Thyroid gland Adrenal glands 40. Describe the 5 types of signaling in figure 45.2 in your text. 41. What are the four classes of hormones and which ones are water soluble? 42. Describe the difference in how water soluble and lipid soluble hormones signal target cells. 43. One hormone can have multiple effects in the body. Give an example of this (you may want to think about the fish) 44. What is the function of insulin and glucagon? What is it about insulin that links it to diabetes? 45. Why is the hypothalamus so important to the endocrine system? 46. What is the function of the pituitary gland? 47. Know the different types of hormones released from the pituitary and what they target. (look at figure 45.17 in the text). 48. What might be the effect of too little iodine? How does this affect your endocrine system? Chapter 46 Vocab: Sexual reproduction Asexual reproduction Spermatogenesis oogenesis cleavage organogenesis 49. Name some strategies for reproduction in other organisms (ex. Hermaphroditism, axsexual reproduction) 50. Where are gametes produced in human males and females? How are these similar? 51. Explain why the scrotum is able to adjust where the testis are located in response to temperature. 52. What is the reason for the build up of the endometrial lining in human females in response to an increase in estradiol? What happens if the egg is not fertilized? 53. What are the main sex hormones for males and females? 54. Explain how hormonal birth control works? 55. Why is maternal and fetal blood not mixed while in the uterus? Chapter 48 Vocab: Action potential Neurotransmitters 56. Be able to label the parts of the nerve cell 57. What is the function of the myelin sheath on the axon of nerve cells 58. Describe the structure of actin and myosin and how they work together for muscle contraction 59. Be able to describe the sequence of events for muscle contraction starting at the release of neurotransmitters being released to the muscle cell.