Emergency Medical Training Services
... 3. Forms continuous sheets that contain no blood vessels. 4. May be classified according to shape. a. Squamos (flat and scalelike). b. Cuboidal (cube-shaped). c. Columnar (more tall than wide). 5. May also be classified according to arrangement. a. Simple (single layer of same-shaped cells). b. Stra ...
... 3. Forms continuous sheets that contain no blood vessels. 4. May be classified according to shape. a. Squamos (flat and scalelike). b. Cuboidal (cube-shaped). c. Columnar (more tall than wide). 5. May also be classified according to arrangement. a. Simple (single layer of same-shaped cells). b. Stra ...
Chapter 16: Cells - The Units of Life
... run the ovens and other equipment, power the lights, and heat the building. The bakery’s products require ingredients such as dough, sugar, and fillings, that must be stored, assembled, and baked. The bakery’s products are packaged and shipped to different locations. A manager is in charge of the en ...
... run the ovens and other equipment, power the lights, and heat the building. The bakery’s products require ingredients such as dough, sugar, and fillings, that must be stored, assembled, and baked. The bakery’s products are packaged and shipped to different locations. A manager is in charge of the en ...
Lecture 1
... Fusiform, about 4cm long Whitish mucosal columnar epithelial lining differentiates it from the more reddish lining of the esophagus Numerous papillae which pass the collecting duct from a thick bed of glands. Papillae can be moistened for parasitic lesions Relations: ventrally with the left lobe of ...
... Fusiform, about 4cm long Whitish mucosal columnar epithelial lining differentiates it from the more reddish lining of the esophagus Numerous papillae which pass the collecting duct from a thick bed of glands. Papillae can be moistened for parasitic lesions Relations: ventrally with the left lobe of ...
The 6 Stages of Nutrition
... science we call nutrition. Nutrition is the physiological process of building strong, healthy cells from the nutrients we obtain from the foods we eat. In other words, diet is what we eat, but nutrition is what our cells actually receive. Nutrition is an ongoing process of feeding, renewing and prot ...
... science we call nutrition. Nutrition is the physiological process of building strong, healthy cells from the nutrients we obtain from the foods we eat. In other words, diet is what we eat, but nutrition is what our cells actually receive. Nutrition is an ongoing process of feeding, renewing and prot ...
Orbital Lymphoma - University of Louisville Ophthalmology
... DFE: OD WNL, OS: 2-3+ disc edema, choroidal folds present ...
... DFE: OD WNL, OS: 2-3+ disc edema, choroidal folds present ...
The Integumentary System
... and skin, prevents hair from becoming brittle, and slows water loss from the skin Sebum is bactericidal and reduces the number of bacteria residing on the surface of the skin The glands are regulated by hormones and while relatively inactive in childhood become activated in both sexes during ...
... and skin, prevents hair from becoming brittle, and slows water loss from the skin Sebum is bactericidal and reduces the number of bacteria residing on the surface of the skin The glands are regulated by hormones and while relatively inactive in childhood become activated in both sexes during ...
Cell Review
... across but not larger molecules. This kind of membrane is called a semi-permeable membrane. Take a look at side A of diagram 3.6. It shows a container divided into two parts by an artificial semi-permeable membrane. Water is poured into one part while a solution containing salt is poured into the ot ...
... across but not larger molecules. This kind of membrane is called a semi-permeable membrane. Take a look at side A of diagram 3.6. It shows a container divided into two parts by an artificial semi-permeable membrane. Water is poured into one part while a solution containing salt is poured into the ot ...
Anatomy and development of the atrial septum.
... 2. Limbus fossa ovalis: It is a sickle shaped fold that surrounds the upper, anterior and posterior margins of the fossa ovalis. It represents lower free margins of the septum secundum. 3. Foramina venarium minimarium: Venae cordis minimi open through these ...
... 2. Limbus fossa ovalis: It is a sickle shaped fold that surrounds the upper, anterior and posterior margins of the fossa ovalis. It represents lower free margins of the septum secundum. 3. Foramina venarium minimarium: Venae cordis minimi open through these ...
Skeletal System
... and skin, prevents hair from becoming brittle, and slows water loss from the skin Sebum is bactericidal and reduces the number of bacteria residing on the surface of the skin The glands are regulated by hormones and while relatively inactive in childhood become activated in both sexes during ...
... and skin, prevents hair from becoming brittle, and slows water loss from the skin Sebum is bactericidal and reduces the number of bacteria residing on the surface of the skin The glands are regulated by hormones and while relatively inactive in childhood become activated in both sexes during ...
Document
... The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body where it is exchanged at the alveoli with carbon dioxide The blood transports oxygen to the cells where it is used in cellular respiration and picks up carbon dioxide, the waste product of the cells, and transports it back to the alveoli. ...
... The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body where it is exchanged at the alveoli with carbon dioxide The blood transports oxygen to the cells where it is used in cellular respiration and picks up carbon dioxide, the waste product of the cells, and transports it back to the alveoli. ...
05 Introduction to Splanchnology. General anatomy of the dig
... Position: extends from the lower border of cricoid cartilage to the level of sternal angle (between T4-T5 vertebrae) where it divides into right and left principal bronchi Structure features Consists of about 16-20 Cshaped incomplete tracheal cartilages for patency connected by smooth muscle and c ...
... Position: extends from the lower border of cricoid cartilage to the level of sternal angle (between T4-T5 vertebrae) where it divides into right and left principal bronchi Structure features Consists of about 16-20 Cshaped incomplete tracheal cartilages for patency connected by smooth muscle and c ...
Cloning and Stem Cells
... cells, which normally produce insulin needed to maintain low blood sugar levels. It may be possible to direct stem cells in culture to turn into insulinproducing cells, which may then be transplanted into diabetic patients. Embryonic stem cells, as well as adult stem cells from various tissues inclu ...
... cells, which normally produce insulin needed to maintain low blood sugar levels. It may be possible to direct stem cells in culture to turn into insulinproducing cells, which may then be transplanted into diabetic patients. Embryonic stem cells, as well as adult stem cells from various tissues inclu ...
Chapter 21- Respiratory
... the lungs at the hilus (medial depression). Once in the lungs the primary bronchi divide into secondary bronchi (lobar bronchi), three on the right and two of the left. The secondary bronchi divide into the tertiary bronchi (segmented bronchi) which continue to divide into more numerous but narrower ...
... the lungs at the hilus (medial depression). Once in the lungs the primary bronchi divide into secondary bronchi (lobar bronchi), three on the right and two of the left. The secondary bronchi divide into the tertiary bronchi (segmented bronchi) which continue to divide into more numerous but narrower ...
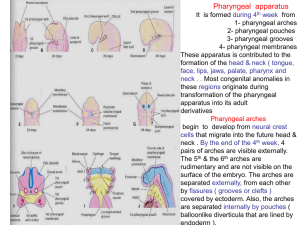
03-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... is covered externally by ectoderm & internally by endoderm. The original mesenchyme is derived from mesoderm in the third week. During the 4th week most of the mesenchyme is derived from neural crest cells which are the major source of the arches connective tissue ( bone, cartilage and ligaments) . ...
... is covered externally by ectoderm & internally by endoderm. The original mesenchyme is derived from mesoderm in the third week. During the 4th week most of the mesenchyme is derived from neural crest cells which are the major source of the arches connective tissue ( bone, cartilage and ligaments) . ...
Intro Notes (new)
... -_______________- ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them. ! - ___________ Digestion- breakdown of ingested foods. ! - _______________ - all the chemical reactions that occur in the body ! - ______________- removal of wastes from the body ! - ______________- cellular and orga ...
... -_______________- ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them. ! - ___________ Digestion- breakdown of ingested foods. ! - _______________ - all the chemical reactions that occur in the body ! - ______________- removal of wastes from the body ! - ______________- cellular and orga ...
Phylum Platyhelminthes
... • A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. • The digestive cavity is the only body cavity in a flatworm. ...
... • A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity that is lined with tissue derived from mesoderm. • The digestive cavity is the only body cavity in a flatworm. ...
Question paper - Unit B731/02 - Modules B1, B2, B3 - Higher
... Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the boxes above. Please write clearly and in capital letters. Use black ink. HB pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Answer all the questions. Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your ...
... Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the boxes above. Please write clearly and in capital letters. Use black ink. HB pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Answer all the questions. Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your ...
A is for Acoelomates:
... The members of the lophophorates have a food gathering structure called a lophophore. The lophophore is a circular or horseshoe-shaped organ developed from the body wall. It has tentacles covered with cilia that develop from the coelom. These tentacles surround the mouth. The cilia create currents o ...
... The members of the lophophorates have a food gathering structure called a lophophore. The lophophore is a circular or horseshoe-shaped organ developed from the body wall. It has tentacles covered with cilia that develop from the coelom. These tentacles surround the mouth. The cilia create currents o ...
Neural Anatomy and Images
... tc: optic tectum td: trochlear decussation tg: trigeminal ganglion tgt: tegmentum tptc: tract of the posterior tubercular commissure tvc: tegmental ventral commissure vg: vagal nerve vt: ventral thalamus (aka. pre-thalamus) ...
... tc: optic tectum td: trochlear decussation tg: trigeminal ganglion tgt: tegmentum tptc: tract of the posterior tubercular commissure tvc: tegmental ventral commissure vg: vagal nerve vt: ventral thalamus (aka. pre-thalamus) ...
Slide 1
... pleura Parietal pleura – outer layer Visceral pleura – directly on lung Pleural cavity – slit-like potential space filled with pleural fluid Lungs can slide but separation from pleura is resisted (like film between 2 plates of glass) Lungs cling to thoracic wall and are forced to expand and reco ...
... pleura Parietal pleura – outer layer Visceral pleura – directly on lung Pleural cavity – slit-like potential space filled with pleural fluid Lungs can slide but separation from pleura is resisted (like film between 2 plates of glass) Lungs cling to thoracic wall and are forced to expand and reco ...
The Respiratory System
... pleura Parietal pleura – outer layer Visceral pleura – directly on lung Pleural cavity – slit-like potential space filled with pleural fluid Lungs can slide but separation from pleura is resisted (like film between 2 plates of glass) Lungs cling to thoracic wall and are forced to expand and reco ...
... pleura Parietal pleura – outer layer Visceral pleura – directly on lung Pleural cavity – slit-like potential space filled with pleural fluid Lungs can slide but separation from pleura is resisted (like film between 2 plates of glass) Lungs cling to thoracic wall and are forced to expand and reco ...
Terminology
... An alveolus is a lung air sac where gas exchange with the blood occurs. Amitosis Amitosis is the anatomical term given to cell reproduction by direct division. The nucleus becomes constricted in the middle, forming an hour-glass shape and then divides into two. This is followed by a division of the ...
... An alveolus is a lung air sac where gas exchange with the blood occurs. Amitosis Amitosis is the anatomical term given to cell reproduction by direct division. The nucleus becomes constricted in the middle, forming an hour-glass shape and then divides into two. This is followed by a division of the ...
Sample Chapter - Viva Online Learning
... Although cells differ in their shape and size, but their basic structure is same. A cell can be divided into the following three parts. ...
... Although cells differ in their shape and size, but their basic structure is same. A cell can be divided into the following three parts. ...
Tissues - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Tissues are communities of cells working together to perform a function for the organism. Remember at all times that we are still talking about CELLS! Even though commonly we think of organs as heart, lungs, kidney etc. that other tissues are also called organs such as muscles, bones etc. ...
... Tissues are communities of cells working together to perform a function for the organism. Remember at all times that we are still talking about CELLS! Even though commonly we think of organs as heart, lungs, kidney etc. that other tissues are also called organs such as muscles, bones etc. ...
(from mesoderm) (a)
... • Tissues are collections of specialized cells isolated from other tissues by membranous layers • During development, three germ layers give rise to the tissues and organs of the animal embryo ...
... • Tissues are collections of specialized cells isolated from other tissues by membranous layers • During development, three germ layers give rise to the tissues and organs of the animal embryo ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.