Connective tissue - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Found at apical region of most epithelial tissues types Some proteins in plasma membrane of adjacent cells are fused Prevent certain molecules from passing between cells of epithelial tissue ...
... Found at apical region of most epithelial tissues types Some proteins in plasma membrane of adjacent cells are fused Prevent certain molecules from passing between cells of epithelial tissue ...
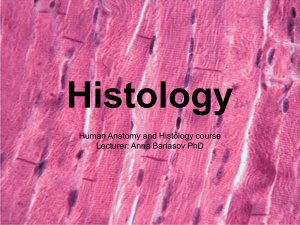
Human Anatomy and Histology course Lecturer: Anna Barlasov PhD
... Location: Ducts of adult sweat glands and esophageal glands and part of male urethra. Function: Protection and limited secretion and absorption. ...
... Location: Ducts of adult sweat glands and esophageal glands and part of male urethra. Function: Protection and limited secretion and absorption. ...
Module 2 - Stony Brook University School of Medicine
... 10. floor of anterior cranial fossa 11. superior orbital fissure 12. sagittal suture ...
... 10. floor of anterior cranial fossa 11. superior orbital fissure 12. sagittal suture ...
Document
... the internal environment and correct any changes – Receptors - provide information about stimuli – Control center - tells what a particular value should be (includes a set point) – Effectors - elicit responses that change conditions in the internal environment ...
... the internal environment and correct any changes – Receptors - provide information about stimuli – Control center - tells what a particular value should be (includes a set point) – Effectors - elicit responses that change conditions in the internal environment ...
HS I Endocrine System Worksheet 1 Choose the best answer to
... Choose the best answer to complete each statement. 1. A _______ (globulin, gland) is any organ that produces a secretion. 2. Endocrine glands are organized groups of tissues which use materials from the blood or lymph to make new compounds called _________ (hormones, hordeolums) 3. Endocrine gl ...
... Choose the best answer to complete each statement. 1. A _______ (globulin, gland) is any organ that produces a secretion. 2. Endocrine glands are organized groups of tissues which use materials from the blood or lymph to make new compounds called _________ (hormones, hordeolums) 3. Endocrine gl ...
AHS I
... Choose the best answer to complete each statement. 1. A _______ (globulin, gland) is any organ that produces a secretion. 2. Endocrine glands are organized groups of tissues which use materials from the blood or lymph to make new compounds called _________ (hormones, hordeolums) 3. Endocrine glands ...
... Choose the best answer to complete each statement. 1. A _______ (globulin, gland) is any organ that produces a secretion. 2. Endocrine glands are organized groups of tissues which use materials from the blood or lymph to make new compounds called _________ (hormones, hordeolums) 3. Endocrine glands ...
Document
... Appendix: Embryonic development of cranial sensory and motor cell columns in the Brainstem ...
... Appendix: Embryonic development of cranial sensory and motor cell columns in the Brainstem ...
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 15: Animal Function Question No. 1 of
... Gastrulation is an invagination of cells during the blastula phase of development to form a digestive cavity, called archenteron, and two separate germ layers, called an ectoderm (internal endoderm). Often, a mesoderm develops between them. There is only one opening to the digestive cavity, which is ...
... Gastrulation is an invagination of cells during the blastula phase of development to form a digestive cavity, called archenteron, and two separate germ layers, called an ectoderm (internal endoderm). Often, a mesoderm develops between them. There is only one opening to the digestive cavity, which is ...
Chapter 1
... Superior: Needs to be in reference to another part. What does it mean? Inferior: Opposite of superior, what does it mean? Anterior: Means the same as ventral in humans. Where does it refer to? Posterior Means the same as dorsal in humans. What is it referring to? Medial means towards the ___________ ...
... Superior: Needs to be in reference to another part. What does it mean? Inferior: Opposite of superior, what does it mean? Anterior: Means the same as ventral in humans. Where does it refer to? Posterior Means the same as dorsal in humans. What is it referring to? Medial means towards the ___________ ...
Unit 1 - unilus website
... E.coli Bacterial Cells (All diagrams above Adopted from Biology, 2009) ...
... E.coli Bacterial Cells (All diagrams above Adopted from Biology, 2009) ...
Unit 1 - unilus website
... E.coli Bacterial Cells (All diagrams above Adopted from Biology, 2009) ...
... E.coli Bacterial Cells (All diagrams above Adopted from Biology, 2009) ...
p2 - Y13HSC
... Nervous tissue is the main component of nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, nerves. The nervous tissue regulates and controls the body function. Nervous tissue has two types, one is neurones and the second is neuroglia. Nervous tissues that stem throughout the body are all made up of sp ...
... Nervous tissue is the main component of nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, nerves. The nervous tissue regulates and controls the body function. Nervous tissue has two types, one is neurones and the second is neuroglia. Nervous tissues that stem throughout the body are all made up of sp ...
Document
... First blood cells develop with the earliest blood vessels Mesenchyme cells cluster into blood islands Late in the second month Liver and spleen take over blood formation ...
... First blood cells develop with the earliest blood vessels Mesenchyme cells cluster into blood islands Late in the second month Liver and spleen take over blood formation ...
Collins CSEC® Biology Workbook answers A1
... soil erosion and a build-up of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The balance of nature is being disrupted by organisms being removed from ecosystems or added into ecosystems where they are not naturally found. Ecosystems are being destroyed for activities such as mining and construction, which resul ...
... soil erosion and a build-up of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The balance of nature is being disrupted by organisms being removed from ecosystems or added into ecosystems where they are not naturally found. Ecosystems are being destroyed for activities such as mining and construction, which resul ...
Word - New Haven Science
... 4. Some elements, such as iron (“Fe”) and aluminum (“Al”), are classified as metals because they have similar properties. Individual metallic elements have distinct characteristic properties (for example, sodium (“Na”) is a light, soft metal that is nonmagnetic, while iron is a magnetic metal that i ...
... 4. Some elements, such as iron (“Fe”) and aluminum (“Al”), are classified as metals because they have similar properties. Individual metallic elements have distinct characteristic properties (for example, sodium (“Na”) is a light, soft metal that is nonmagnetic, while iron is a magnetic metal that i ...
Bryozoa & Echinodermata
... • usually external fertilization (eggs and sperm are shed into the water where fertilization occurs) • indirect development with the presence of a free-swimming, bilateral larval stage (some have direct development) ...
... • usually external fertilization (eggs and sperm are shed into the water where fertilization occurs) • indirect development with the presence of a free-swimming, bilateral larval stage (some have direct development) ...
BIOL 105 S 2014 QZM2 QA 140207.1
... C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fertilization of the ovum usuall ...
... C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fertilization of the ovum usuall ...
The Special Senses
... absorbs light and prevents its scattering • Neural layer, which contains: – Photoreceptors that transduce light energy – Bipolar cells and ganglion cells – Amacrine and horizontal cells ...
... absorbs light and prevents its scattering • Neural layer, which contains: – Photoreceptors that transduce light energy – Bipolar cells and ganglion cells – Amacrine and horizontal cells ...
iv splanchnology
... histamine, prostaglandins, vasopressin and collagenase. Granular cells become loose and follicular cells weak. Just before ovulation blood cease in the area and it changes in colour. First meiotic division is finalised and the oocytes enters the oviducts. If not fertilised within 24 h it degenerates ...
... histamine, prostaglandins, vasopressin and collagenase. Granular cells become loose and follicular cells weak. Just before ovulation blood cease in the area and it changes in colour. First meiotic division is finalised and the oocytes enters the oviducts. If not fertilised within 24 h it degenerates ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.