Organ
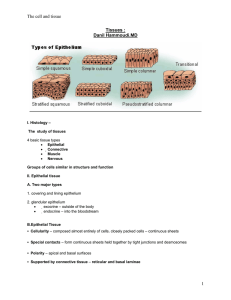
... Cells group together to form tissues and tissues group together to form organs. We will learn about tissue groups in plants and animals and the cells of which they are made. The four (4) major groups of tissues in animals are: 1. Nervous Tissue 2. Epithelial Tissue 3. Connective Tissue 4. Muscular T ...
... Cells group together to form tissues and tissues group together to form organs. We will learn about tissue groups in plants and animals and the cells of which they are made. The four (4) major groups of tissues in animals are: 1. Nervous Tissue 2. Epithelial Tissue 3. Connective Tissue 4. Muscular T ...
The general features of respiratory system
... The general features of respiratory system Structural and functional classifications of respiratory system The general structure, function and role of each organ making up the respiratory system ...
... The general features of respiratory system Structural and functional classifications of respiratory system The general structure, function and role of each organ making up the respiratory system ...
OBJ 4 5 6 7
... layer of cells lining the inner surface of the gastrula endoderm ectoderm mesoderm ...
... layer of cells lining the inner surface of the gastrula endoderm ectoderm mesoderm ...
BIOL212ch32APR2012
... • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes • Their cells lack cell walls • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have a common structure, function, ...
... • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes • Their cells lack cell walls • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have a common structure, function, ...
human body systems informational textbook
... are open, blood flows to the heart. When they are closed, blood flows away from the heart. Arteries and capillaries do not have valves. Blood moves in the right direction through the arteries and capillaries by the pumping of the heart. The picture on the right shows some of the body’s larger blood ...
... are open, blood flows to the heart. When they are closed, blood flows away from the heart. Arteries and capillaries do not have valves. Blood moves in the right direction through the arteries and capillaries by the pumping of the heart. The picture on the right shows some of the body’s larger blood ...
connective tissue
... connective, muscle, and nervous. A. Epithelial tissue lines the body’s surface, openings, and tubes in the body, such as blood vessels. Epithelial tissues are groups of cells arranged together in sheets. ...
... connective, muscle, and nervous. A. Epithelial tissue lines the body’s surface, openings, and tubes in the body, such as blood vessels. Epithelial tissues are groups of cells arranged together in sheets. ...
Solutions for all Natural Sciences Grade 9 Learner`s Book
... organised according to topics and each topic is structured in the same way: Topic opener page: The topic starts with a full-colour photograph of something that is related to the content of the topic. ‘What you will learn about in this topic’ lists the content to be covered in the topic. There is als ...
... organised according to topics and each topic is structured in the same way: Topic opener page: The topic starts with a full-colour photograph of something that is related to the content of the topic. ‘What you will learn about in this topic’ lists the content to be covered in the topic. There is als ...
Tissues - Sinoe Medical Association
... o Simple columnar epithelium is made up of a single layer of cells that are longer than they are wide. o The nucleus is also closer to the base of the cell. o The small intestine is a tubular organ lined with this type of tissue. o Unicellular glands called goblet cells are scattered throughout the ...
... o Simple columnar epithelium is made up of a single layer of cells that are longer than they are wide. o The nucleus is also closer to the base of the cell. o The small intestine is a tubular organ lined with this type of tissue. o Unicellular glands called goblet cells are scattered throughout the ...
Chapter 2: Basic Biological Principles Lesson 2.2: Structural and
... The answer to these questions is clear once you know how a cell functions. To carry out life processes, a cell must be able to quickly pass substances into and out of the cell. For example, it must be able to pass nutrients and oxygen into the cell and waste products out of the cell. Anything that e ...
... The answer to these questions is clear once you know how a cell functions. To carry out life processes, a cell must be able to quickly pass substances into and out of the cell. For example, it must be able to pass nutrients and oxygen into the cell and waste products out of the cell. Anything that e ...
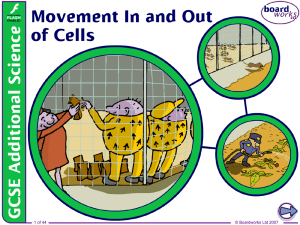
2. Movement In and Out of Cells
... the air. This is called diffusion. Where is the smell strongest? The smell is strongest at the sock. The smell becomes weaker further away from the sock. 4 of 44 ...
... the air. This is called diffusion. Where is the smell strongest? The smell is strongest at the sock. The smell becomes weaker further away from the sock. 4 of 44 ...
01st lecture
... • All proteins have a fixed sequence of amino acids. This must be exactly (re)produced in the biosynthesis. • The sequence is stored in the DNA encoded (genetic code, 64 different base triplets). This information is transcripted to mRNA in the nucleus. • The mRNA moves out of nucleus an the assembly ...
... • All proteins have a fixed sequence of amino acids. This must be exactly (re)produced in the biosynthesis. • The sequence is stored in the DNA encoded (genetic code, 64 different base triplets). This information is transcripted to mRNA in the nucleus. • The mRNA moves out of nucleus an the assembly ...
Chapter 10
... The oldest proglottids at the end of a tapeworm are filled with eggs, and are said to be adult. female. pregnant. mature. gravid. ...
... The oldest proglottids at the end of a tapeworm are filled with eggs, and are said to be adult. female. pregnant. mature. gravid. ...
answerstoevenquestions
... occludentes with each other, but they have only a limited ability to form caveolae, relying instead mostly on receptor-mediated transport to transfer material between the capillary lumen and the neural tissue of the central nervous system. Therefore, most macromolecules injected into the capillary l ...
... occludentes with each other, but they have only a limited ability to form caveolae, relying instead mostly on receptor-mediated transport to transfer material between the capillary lumen and the neural tissue of the central nervous system. Therefore, most macromolecules injected into the capillary l ...
32animalevolution
... need to meet the environment equally well from all sides. – Animals that move actively are bilateral, such that the head end is usually first to encounter food, danger, and other stimuli. ...
... need to meet the environment equally well from all sides. – Animals that move actively are bilateral, such that the head end is usually first to encounter food, danger, and other stimuli. ...
The main passageway that leads to the lungs from the throat is the
... 4. The oxygen-carrying molecule in blood is ________________________________. 5. The main job of the respiratory system is to get _______________________ into the body and _______________________________ out of the body. 6. The walls of the trachea are made up of rings of __________________________ ...
... 4. The oxygen-carrying molecule in blood is ________________________________. 5. The main job of the respiratory system is to get _______________________ into the body and _______________________________ out of the body. 6. The walls of the trachea are made up of rings of __________________________ ...
contd.
... • Carnivores typically have short digestive tubes that produce enzymes to break down meat. Animals don’t produce enzymes that can break down the tough cellulose in plant tissue. • Some herbivores, such as cattle, have a four-part stomach, each with a special function. The largest stomach part is a p ...
... • Carnivores typically have short digestive tubes that produce enzymes to break down meat. Animals don’t produce enzymes that can break down the tough cellulose in plant tissue. • Some herbivores, such as cattle, have a four-part stomach, each with a special function. The largest stomach part is a p ...
ap-lab-ex-6 - Anatomy and Physiology
... type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliary action. Location: Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the ...
... type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliary action. Location: Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the ...
Chapter 1: The Human Body
... Sagittal any plane parallel to the midsagittal or median plane vertically dividing the body into unequal left and right portions Transverse plane dividing the body into superior and inferior portions Viscera the organs of a cavity ...
... Sagittal any plane parallel to the midsagittal or median plane vertically dividing the body into unequal left and right portions Transverse plane dividing the body into superior and inferior portions Viscera the organs of a cavity ...
Digestive Systems: The Anatomy of Representative Vertebrates
... cells in the cavity lining, and further digestion occurs inside the food vacuoles in these cells. This is intracellular digestion. Food absorbed by the cells lining the gastrovascular cavity supplies all cells of the body. When animals increase in size and complexity, diffusion from the digestive ca ...
... cells in the cavity lining, and further digestion occurs inside the food vacuoles in these cells. This is intracellular digestion. Food absorbed by the cells lining the gastrovascular cavity supplies all cells of the body. When animals increase in size and complexity, diffusion from the digestive ca ...
C H A P T E R
... appear a few days later. The limb buds have a core of lateral plate mesoderm (which forms bones, tendons, cartilage, and connective tissue) covered by a layer of ectoderm. Early in week 5, the upper limb forms a paddle-shaped hand plate. A foot plate forms in the lower limb bud in the sixth week. Di ...
... appear a few days later. The limb buds have a core of lateral plate mesoderm (which forms bones, tendons, cartilage, and connective tissue) covered by a layer of ectoderm. Early in week 5, the upper limb forms a paddle-shaped hand plate. A foot plate forms in the lower limb bud in the sixth week. Di ...
Red Blood Cells
... and acts as a solvent to dissolve materials such as waste products, salts, glucose, food molecules, vitamins, hormones and proteins that are carried by the blood to all parts of the body. What is Plasma Continue ...
... and acts as a solvent to dissolve materials such as waste products, salts, glucose, food molecules, vitamins, hormones and proteins that are carried by the blood to all parts of the body. What is Plasma Continue ...
phylum-cnidaria
... • carnivorous • radial symmetry • have stinging cells called cnidocytes which contain nematocysts • nematocysts are poison filled harpoons used for catching prey ...
... • carnivorous • radial symmetry • have stinging cells called cnidocytes which contain nematocysts • nematocysts are poison filled harpoons used for catching prey ...
Integumentary System PowerPoint
... Important for calcium metabolism- calcium is not absorbed in the digestive tract without vitamin D ...
... Important for calcium metabolism- calcium is not absorbed in the digestive tract without vitamin D ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.