Respiratory System Chapter 15
... Tertiary bronchi then continue to branch into smaller & smaller bronchi & then into very narrow bronchioles This branching patterns creates the “bronchial tree” ...
... Tertiary bronchi then continue to branch into smaller & smaller bronchi & then into very narrow bronchioles This branching patterns creates the “bronchial tree” ...
1 Chapter 140: Cochlear Anatomy and Central Auditory Pathways
... microvilli, and are sealed by tight junctions (see Fig. 140-10). A trilaminar basement membrane lies between the two cell layers. The cells facing perilymph have a squamous shape and are loosely joined together. Reissner's membrane appears to be freely permeable to water, but it restricts paracellul ...
... microvilli, and are sealed by tight junctions (see Fig. 140-10). A trilaminar basement membrane lies between the two cell layers. The cells facing perilymph have a squamous shape and are loosely joined together. Reissner's membrane appears to be freely permeable to water, but it restricts paracellul ...
PTA 198 Anatomy and Physiology
... 7. Be able to identify/locate the endocrine glands on charts and models, also explain/describe hormones produced by each gland, the effect of these hormones, their target tissue and disorders associated with increased or decreased production.. a. Hypothalamus: neurosecretory cells, infundibulum Horm ...
... 7. Be able to identify/locate the endocrine glands on charts and models, also explain/describe hormones produced by each gland, the effect of these hormones, their target tissue and disorders associated with increased or decreased production.. a. Hypothalamus: neurosecretory cells, infundibulum Horm ...
Chapter 25
... v. Saliva is 99.5% water and 0.5% solutes; notable solutes include: a. bacteriolytic lysozyme b. salivary amylase which initiates starch digestion c. lingual lipase (secreted by lingual glands on the tongue) which initiates triglyceride digestion vi. Chemical stimulation (by food molecules) of recep ...
... v. Saliva is 99.5% water and 0.5% solutes; notable solutes include: a. bacteriolytic lysozyme b. salivary amylase which initiates starch digestion c. lingual lipase (secreted by lingual glands on the tongue) which initiates triglyceride digestion vi. Chemical stimulation (by food molecules) of recep ...
Unit 18.1: Sponges, Cnidarians, Flatworms, and
... length. As their name suggests, they have a round body. This is because they have a pseudocoelom. This is one way they differ from flatworms. Another way is their complete digestive system. It allows them to take in food, digest food, and eliminate wastes all at the same time. Roundworms have a toug ...
... length. As their name suggests, they have a round body. This is because they have a pseudocoelom. This is one way they differ from flatworms. Another way is their complete digestive system. It allows them to take in food, digest food, and eliminate wastes all at the same time. Roundworms have a toug ...
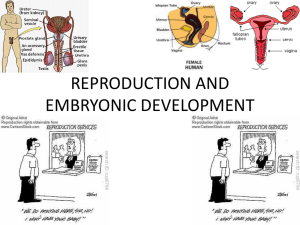
unit 12- reproductive system
... The uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes or oviducts) measure about five inches in length. At one end, there is an expanded infundibulum or the funnel-shaped, open, distal end of the uterine tube near the ovaries. The infundibulum contains the fimbriae or finger-like projections at the end of the infundib ...
... The uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes or oviducts) measure about five inches in length. At one end, there is an expanded infundibulum or the funnel-shaped, open, distal end of the uterine tube near the ovaries. The infundibulum contains the fimbriae or finger-like projections at the end of the infundib ...
practice exam
... Aorta attached to right ventricle and pulmonary trunk attaches to left; both continue doing what they do normally Problem: Blood gets from right ventricle to aorta to circulation into right atrium (HAS NO OXYGEN); blood from left ventricle to pulmonary trunk into LUNGS (HAS OXYGEN ALREADY) Problem f ...
... Aorta attached to right ventricle and pulmonary trunk attaches to left; both continue doing what they do normally Problem: Blood gets from right ventricle to aorta to circulation into right atrium (HAS NO OXYGEN); blood from left ventricle to pulmonary trunk into LUNGS (HAS OXYGEN ALREADY) Problem f ...
I. Blood and Blood Cells
... • Red blood cells are biconcave in shape. • The shape of red blood cells allow them to have an increased surface area for the transport of gases. • Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrying protein in red blood cells. • Each red blood cell is about one-third hemoglobin by volume. ...
... • Red blood cells are biconcave in shape. • The shape of red blood cells allow them to have an increased surface area for the transport of gases. • Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrying protein in red blood cells. • Each red blood cell is about one-third hemoglobin by volume. ...
Think of it as a fluid- filled sac floating in a fluid
... o Stereocilia and kinocilia are embedded in otolithic membrane…a gelatinous mat that sits on top of the macula). o The membrane is weighted down by the otoliths. These are crystals embedded in superficial surface of the membrane. The weight makes the membrane move more due to inertia. SEMICURCULAR C ...
... o Stereocilia and kinocilia are embedded in otolithic membrane…a gelatinous mat that sits on top of the macula). o The membrane is weighted down by the otoliths. These are crystals embedded in superficial surface of the membrane. The weight makes the membrane move more due to inertia. SEMICURCULAR C ...
Structure and Function of Animals syllabus
... cell membrane potential in that area manages to reach as high as –5 0 mV (from the resting potential of – 7 0 mV), the voltage-gated sodium channels in that region of the membrane open up. The voltage at which the voltage-gated channels open is called the threshold potential, so the threshold potent ...
... cell membrane potential in that area manages to reach as high as –5 0 mV (from the resting potential of – 7 0 mV), the voltage-gated sodium channels in that region of the membrane open up. The voltage at which the voltage-gated channels open is called the threshold potential, so the threshold potent ...
ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer
... membrane…a gelatinous mat that sits on top of the macula). o The membrane is weighted down by the otoliths. These are crystals embedded in superficial surface of the membrane. The weight makes the membrane move more due to inertia. SEMICURCULAR CANALS These are three partial circles within the bony ...
... membrane…a gelatinous mat that sits on top of the macula). o The membrane is weighted down by the otoliths. These are crystals embedded in superficial surface of the membrane. The weight makes the membrane move more due to inertia. SEMICURCULAR CANALS These are three partial circles within the bony ...
Leaving Cert Biology Notes - Learning Outcomes 2014
... Define as All cells derived by division of other living cells Unit of heredity made up of genes, non-coding (junk) DNA and proteins. (1n): number of chromosomes in a cell with 1 set of chromosomes (2n): number of chromosomes in a cell with 2 sets of chromosomes Define as: division of cell to form tw ...
... Define as All cells derived by division of other living cells Unit of heredity made up of genes, non-coding (junk) DNA and proteins. (1n): number of chromosomes in a cell with 1 set of chromosomes (2n): number of chromosomes in a cell with 2 sets of chromosomes Define as: division of cell to form tw ...
Unit 2 - Cells and Systems Learning Pack (Science In Action 8
... materials that organisms need to grow, develop, and reproduce. All of the processes that occur inside the organism to sustain its life are called the organism’s metabolism. Responding To The Environment A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. The organism’s reaction to this sti ...
... materials that organisms need to grow, develop, and reproduce. All of the processes that occur inside the organism to sustain its life are called the organism’s metabolism. Responding To The Environment A stimulus is anything that causes a response in an organism. The organism’s reaction to this sti ...
Moore_Timothy_LIfe Science Semester 1 Assessment
... (10 pts) 31. The concentration of sugar is higher inside a cell than outside the cell. The concentration of water inside the cell is lower than it is outside. Sugar cannot pass through the cell membrane. Over time, what will happen to the concentrations of water and sugar? What is the name of this p ...
... (10 pts) 31. The concentration of sugar is higher inside a cell than outside the cell. The concentration of water inside the cell is lower than it is outside. Sugar cannot pass through the cell membrane. Over time, what will happen to the concentrations of water and sugar? What is the name of this p ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... 1. I can label the anatomy of a cnidarian. 2. I can describe the life cycle of a cnidarian. 3. I can differentiate between the different classes of ...
... 1. I can label the anatomy of a cnidarian. 2. I can describe the life cycle of a cnidarian. 3. I can differentiate between the different classes of ...
AS 12-13 Cards 1-137_Layout 1
... conchae. The medial wall or nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, the vomer bone, and the septal cartilage. The rest of the framework of the nose consists of several plates of cartilage, specifically, the lateral nasal cartilage and the greater and lesser alar cartil ...
... conchae. The medial wall or nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, the vomer bone, and the septal cartilage. The rest of the framework of the nose consists of several plates of cartilage, specifically, the lateral nasal cartilage and the greater and lesser alar cartil ...
Ch01 Anatomy basics
... views to study body parts frontal (coronal) cut divides front and back sagittal cut divides right and left transverse cut divides upper and lower Cross section Longitudinal ...
... views to study body parts frontal (coronal) cut divides front and back sagittal cut divides right and left transverse cut divides upper and lower Cross section Longitudinal ...
Cells, diffusion and osmosis - Pearson-Global
... of the cell gradually died, so that it ended up as a hollow tube with a wall containing lignin as well as cellulose. xylem vessel ...
... of the cell gradually died, so that it ended up as a hollow tube with a wall containing lignin as well as cellulose. xylem vessel ...
عرض تقديمي في PowerPoint
... condenses to a small size, and its final remnant is absorbed or extruded from the cell. At the same time, the endoplasmic reticulum is also reabsorbed Reticulocytes pass from bone marrow into blood capillaries by diapedesis In the blood stream the remaining basophilic material will disappear in 1- ...
... condenses to a small size, and its final remnant is absorbed or extruded from the cell. At the same time, the endoplasmic reticulum is also reabsorbed Reticulocytes pass from bone marrow into blood capillaries by diapedesis In the blood stream the remaining basophilic material will disappear in 1- ...
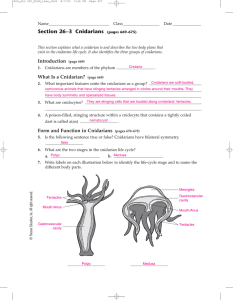
Section 26–3 Cnidarians
... carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around their mouths. They have body symmetry and specialized tissues. ...
... carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around their mouths. They have body symmetry and specialized tissues. ...
Section 26–3 Cnidarians - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around their mouths. They have body symmetry and specialized tissues. ...
... carnivorous animals that have stinging tentacles arranged in circles around their mouths. They have body symmetry and specialized tissues. ...
STB 112 Theory - Unesco
... The body is covered by epidermis and its ciliated. They lock of mouth, pharynx and intestines. There is no skeleton, no respiratory system. Gaseous exchange is through the epidermis. Excretory system is made of large flame cells. Nervous system is highly organized and forms a tiny ‘brain’ and the he ...
... The body is covered by epidermis and its ciliated. They lock of mouth, pharynx and intestines. There is no skeleton, no respiratory system. Gaseous exchange is through the epidermis. Excretory system is made of large flame cells. Nervous system is highly organized and forms a tiny ‘brain’ and the he ...
Boundless Study Slides
... • bilaminar Formed of, or having, two laminae, or thin plates. • chorion The protective and nutritive membrane that attaches higher vertebrate fetuses to the uterus. • embryonic disk The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the embryonic disk (or disc), composed of a layer of prismatic cells, t ...
... • bilaminar Formed of, or having, two laminae, or thin plates. • chorion The protective and nutritive membrane that attaches higher vertebrate fetuses to the uterus. • embryonic disk The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the embryonic disk (or disc), composed of a layer of prismatic cells, t ...
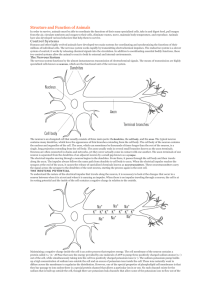
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.