* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOL 105 S 2014 QZM2 QA 140207.1
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
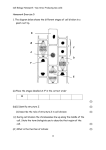
Biology 105 – Human Biology QZM 2 Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL General Anatomy & Physiology MATCH the Indicated Regions with their respective Anatomical Term. See Column V for Choices. Page 1 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: QZM 2 Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL MATCH the CONSTITUENTS and FUNCTIONS with their appropriate Anatomical System QUESTIONS SELECT CONSTITUENTS ANSWERS GENERAL FUNCTIONS CODE 20. Consciousness, thought, electrochemical signaling and homeostasis 21. External defense, thermal homeostasis 22. External ventilation 23. Maceration, salivation, digestion, defecation 24. Oxygen, carbon-dioxide and nutrient transport 25. Voluntary Movement, Motility, Mobility 26. A. B. C. D. E. A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD SYSTEM Cardiovascular Digestive Endocrine Integumentary Lymphatic / Immune Muscular Nervous Reproductive Respiratory Skeletal Urinary Choose the CORRECT order (1-5) of decreasing complexity/organization. (1) tissues, (2) organ systems, (3) cells, (4) organs, (5) organism (1) cells, (2) organ systems, (3) tissues, (4) organs, (5) organism (1) tissues, (2) organs, (3) organ systems, (4) cells, (5) organism (1) cells, (2) tissues, (3) organs, (4) organ systems, (5) organism (1) organism, (2) organ systems, (3) organs, (4) tissues, (5) cells Page 2 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: QZM 2 Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL Life of Cells A. B. C. D. E. 27. The size of a metabolizing cell is limited by its extracellular matrix. function. nuclear size. surface area-to-volume ratio. genome size. 28. The stage in a cell's life cycle in which the chromosomes are at opposite poles of the cell and the cellular cleavage is nearly complete is called A. prophase. B. interphase. C. metaphase. D. telophase. E. anaphase. 29. A. B. C. D. E. During the process of mitosis, chromatids separate during prophase. metaphase. interphase. telophase. anaphase. Reproductive System 30. The female structure that corresponds to the male penis is the A) vagina. B) clitoris. C) vestibule. D) labia minora. E) labia majora. 31. The reproductive system A) produces and transports gametes. B) stores and nourishes gametes. C) produces FSH and LH. D) A and B only E) all of the above Page 3 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology QZM 2 Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL 32. The urinary system is exclusive to the A) gonads. B) ducts that receive and transport the gametes. C) accessory glands and organs that secrete fluids. D) external genitalia. E) female urethra. 33. ________ are formed at the end of meiosis. A) Spermatogonia B) Primary spermatocytes C) Spermatids D) Secondary spermatocytes E) Spermatozoa 34. Sperm cells are stored primarily in the A) seminiferous tubules. B) straight tubules. C) lobules. D) interstitial areas. E) epididymis. 35. The anatomical order order in which sperm pass through these structures from the testes to the penis is A) 1, 3, 4, 2. B) 4, 3, 1, 2. C) 4, 1, 2, 3. D) 4, 1, 3, 2. E) 1, 4, 3, 2. 36. The cell commonly called the egg, or ovum, is more correctly called the A) oocyte. B) oogonia. C) primary oocyte. D) secondary oocyte. E) zygote. 37. The process of oogenesis produces ________ viable ovum/ova. A) one B) two C) three D) four E) eight Page 4 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology QZM 2 Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL 38. Fertilization normally occurs in the A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fertilization of the ovum usually occurs A) within one hour of ovulation. B) as much as three to four days following ovulation. C) in the ovary. D) in the upper 1/3 of the uterine tube. E) in the uterus. 41. The period of gestation when the rudiments of all major organ systems appear is the ________ trimester(s). A) first B) second C) third D) first and second E) second and third Page 5 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology QZM 2 Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL 42. The division of the zygote into two blastomeres is referred to as A) cleavage. B) implantation. C) placentation. D) embryogenesis. E) fertilization. Answer: A 43. The extraembryonic membrane that forms a fluid-filled sac is the A) yolk sac. B) amnion. C) allantois. D) chorion. E) decidua. Genetics 44. The transmission of genetic information from generation to generation is termed A) inheritance. B) polygenics. C) capacitation. D) development. E) embryology. 45. Paired chromosomes are called A) homologous chromosomes. B) heterozygous chromosomes. C) homozygous chromosomes. D) autosomal chromosomes. E) alleles. 46. The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are called A) homologous chromosomes. B) homozygous chromosomes. C) heterozygous chromosomes. D) autosomal chromosomes. E) alleles. Page 6 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology QZM 2 Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL 47. If an individual carries a pair of alleles that are the same, he or she is ________ for the trait. A) homologous B) homozygous C) heterozygous D) autosomal E) polygenic 48. If an individual carries two different alleles for the same trait, he or she is ________ for the trait. A) homologous B) homozygous C) heterozygous D) autosomal E) polygenic 49. If the parents are AA and aa, the offspring are expected to be A) sterile. B) Aa. C) AA. D) aa. 50. In simple inheritance, A) phenotypic characteristics are determined by a single pair of alleles. B) phenotypic characteristics are determined by multiple alleles. C) phenotypic characteristics are determined by the action of a single gene. D) phenotypic characteristics are controlled by regulator genes on a chromosome other than the one that has the structural genes. E) phenotypic characteristics are determined by the genes on the Y chromosome. Page 7 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology QZM 2 Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL THIS PAGE PURPOSELY LEFT BLANK Page 8 of 9 478160075 Biology 105 – Human Biology Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: QZM 2 Instructor: Spring 2014 55244 and 61816 4 Units UVC1 St. Helena F 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LEC F 1:00 PM - 3:50 PM LAB M 9:00 AM - 11:50 AM LAB RIDDELL CHOICES CODE A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE ABCD ABCE ABDE I Cardiovascular Connective Digestive Embryonic Endocrine Epithelial Excretory Ingestion Integuementary Joints Limbic Lymphatic / Immune Meninigeal Muscular Nervous Neuromuscular Reproductive Respiratory Skeletal Urinary II Atoms Organ Organelle System Tissue III Anterior Bi-lateral Frontal Inferior Lateral Oblique Posterior Sagittal Superior Transverse IV Adipose Blood Cardiac Cartilage Connective Epithelial Erythrocyte Muscle Nervous Ovary Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Teste V Acromial Antebrachial Antecubital Axillary Brachial Buccal Calcaneal Carpal Cephalic Cranial Crural Dorsal Facial Femoral Frontal Gluteal Inguinal Lumbar Manual Mental Oculus Olecranal Oris Page 9 of 9 V continued Patellar Pedal Phalanges Popliteal Sacral Scapular Sternal Sural Tarsal Thoracic Umbilicus 478160075