* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The sensory organs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
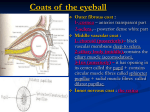
The sensory organs Chapter one The visual organ consists of eyeball and accessory organs of eye. Section one the Eyeball 一、The structure of eyeball The eyeball comprises the wall of the eyeball and the contents enclosed by it. (一) The Wall of Eyeball It consists of three tunics(layers), from outside inwards, which are the fibrous tunic,the vascular tunic and retina. 1 The fibrous tunic(outer supporting layer) consists of the sclera behind and the cornea in front. 1) The sclera a. features: posterior five-sixths of the outer layer . strong , white and opaque b. scleral venous sinus (Schlemm’ canal) 2) The cornea a. features: anterior one-sixth of the outer layer. transparent and non-vascular, but rich nerve terminals 2. The vascular tunic consists of the iris, the ciliary body and the choroid 1) The iris a. location and shape b. pupil c. sphincter and dilator pupillae d. iridocorneal angle e. colour : brown , dark , blue .depends upon the number and placement of pigment cells (melanocytes) 2) The ciliary body a. location and shape b. ciliary ring and ciliary processes c. ciliary muscle d. ciliary zonule(suspensory ligament) e. function: produce aqueous humor 3) The choroid a. location and shape : posterior two thirds of choroid b. features : numerous blood vessels and pigment cells 3. The inner tunic (the retina) 1) Division: the optic part, ciliary part and iridial part 2)Construction: two layers →outer pigmented layer and inner neuroretina(photoreceptors: rod and cone cells) 3) Optic disc (blind spot) 4) Macula lutea : fovea centralis→vision is sharpest (二) The contents of the eyeball include the aqueous humor, the vitreous body and the lens .With the cornea altogether to form the refractive media. l. The chambers of the eye : between the cornea and the lens; and divided into the anterior and the posterior chambers by the iris .It is filled with aqueous humor. 2. The aqueous humor : produced by the capillaries of the ciliary processes. It is colourless, transparent and watery fluid. 3. The lens 1) Location : lies between the iris and the vitreous body. 2) Features: nerves transparent and elastic, biconvex body lacking vessels and 3)Structures: outer cortex and inner nucleus 4. The vitreous body colourless, transparent and jelly-like substance . It fills the space between the lens and the retina (the vitreous chamber) Section two the accessory organs of eye The accessory organs of the eye includes the eyelid, the conjunctiva, the lacrimal apparatus, the extraocular muscles and the fasciae. 一、 The eyelids (or palpebrae) include the upper and lower eyelids 1 Structures:Palpebral fissure, lacrimal papilla and punctum 2 Layers: skin, subcutaneous areolar tissue, orbicularis oculi, tarsus, and conjunctiva. 二、The conjunctiva Division: bulbar conjunctiva , palpebral conjunctiva and conjunctival fornix 三、The Lacrimal Apparatus consists of the lacrimal gland and tbe lacrimal passages 1 The lacrimal gland : lies in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit 2 The lacrimal passages 1) The lacrimal punctum 2) The lacrimal ductule (canaliculus) 3) The lacrimal sac 4) The nasolacrimal duct 四、The extraocular muscles 1 The four rectus muscles the medial and lateral rectuses, the superior and posterior rectuses 2 The two oblique muscles the superior obliquus (superior oblique m. ) and the inferior obliguus (inferior oblique m. ) 3 The levator palpebrae superioris 五、The connective tissue in the Orbit 1 The adipose body of orbit 2 The sheath of eyeball(the capsule of Tenon) 3 The episcleral space Section three The blood vessels of eye 一、The arteries of eye supplied by the ophthalmic artery 1 The central artery of retina: superior and inferior nasal retinal arteries, superior and inferior temporal retinal arteries 2 The short posterior ciliary arteries: supply the choroid coat and ciliary process 3 The long posterior ciliary arteries: supply the iris 二、The veins of eye 1 The ophthalmic veins :the superior and the inferior ophthalmic v. 2 The central vein of retina Chapter two the vestibulocochlear organ The vestibulocochlear organ is divided into three parts: the external, middle and internal ears. Section one the external ear The external ear consists of the auricle, external acoustic meatus and tympanic membrane. l The auricle 2 The external acoustic meatus extends from the externa1 acoustic pore to the tympanic membrane 1) Two parts: lateral part : the cartilaginous part ( one-third ) medial part : the bony part (two-thirds ) 2) Direction: passes medially, its lateral part runs forwards and upwards, and then backwards and the medial part runs forwards and downwards 3 The tympanic membrane oval in form, thin and semi-transparent 1) Two parts: tense part (lower three fourths of tympanic membrane) and flaccid part(upper one fourth ) 2) The umbo 3) Cone of light: lie anteroinferior to the tense part of umbo Section two the middle ear Tbe middle ear lies between the external and inner ears, and includes three parts: the tympanic cavity, the auditory tube and the mastoid cells. 1 The tympanic cavity l) The walls of the tympanic cavity →six walls: a. The tegmental wall (superior wall) b. The jugular wall (inferior wall) c. The carotid wall (anterior wall) d. The mastoid wall (posterior wall) e. The membranous wall (lateral wall) f. The labyrinthine wall (medial wall) 2) The auditory ossicles three ossicles: the malleus, incus and stapes The muscles of the tympanic cavity :the tensor tympani and the stapedius 2 The auditory tube (Eustachian tube) the channel through which the tympanic cavity communicates with the nasopharynx. 3 The mastoid cells spaces in the mastoid procese of the temporal bone Section three the internal ear The internal (inner) ear lies in the petrous part of the temporal bone and consists of two parts: the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. 一、 The bony labyrinth three parts :the cochlea ,the vestibule and the semicircular canals 1 The cochlea: looks like the shell of a snail and composed of the bony canal 2 The vestibule: the central part of the bony labyrinth. On its lateral wall, there are two openings: the fenestra vestibuli and the fenestra cochleae . On the posterior wall of the vestibule there are the five openings of the semicircular canals. On its anterior wall a large opening communicates with the scala vestibuli. 3 The semicircular canals three in number, anterior (superior), posterior and lateral semicircular canal 二、 The membranous labyrinth from before backwards, includes: the cochlear duct, the utricle and saccule, and the membranous semicircular ducts. 1 The cochlear duct a. section of the cochlea: shows three channels the scala tympani, scala vestibuli and the cochlear duct b. the cochlear duct(transverse section) three walls : superior wall→the vestibular membrane lateral wall→the thickend endosteum inferior wall→ the basilar membrane(spiral membrane) and the outer part of the lamina of modiolus The spiral organ on the basilar membrane 2 The utricle and saccule The maculae are the organs of static balance 3 The semicircular ducts The ampullary crests are the organs of kinetic balance. 三、The conduction of sound 四、 The internal acoustic meatus The Peritoneum 一、Introduction The Peritoneum is serous membrane in the body which covers on the inner surfaces of the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and the outer surfaces of the vicera of the abdominal and pelvic cavities. 1 Division of the peritoneum : the parietal peritoneum and visceral peritoneum 2 The peritoneal cavity 3 The difference between the abdominal cavity and the peritoneal cavity 4 function: absorptive capacity , secretion, supportion and phagocytosis. 二、 The Relationship between viscera and peritoneum 1 The intraperitoneal viscera : completely surrounded by peritoneum 2 The interperitoneal viscera : not completely wrapped 3 The retroperitoneal viscera : covered by peritoneum only on their anterior surface. Such as: the kidneys, ureters, suprarenal glands, pancreas, the middle and inferior parts of rectum, etal. 三、Structures formed by the peritoneum 1 The omentum a. the lesser omentum : include the hepatogastric ligament and hepatoduodenal ligament . Hepatoduodenal ligament enclose the proper hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein and common bile duct. b. the greater omentum : made up of four layers . begin from the the stomach and commencement of the duodenum and end the transverse colon . c. the omental bursa and omental(epiploic) foramen(Winslow’ foramen) 2. The mesenteries and mesocolons such as the mesentery (of the small intestine), mesoappendix , transverse mesocolon and sigmoid mesocolon 3. The ligaments 4. The peritoneal folds , recesses and pouches a. the rectovesical pouch in the male b. the rectouterine pouch (of Douglas) and vesicouterine pouch 5. Subdivision of peritoneal cavity The endocrine system 一、Introduction 1 The composition of the endocrine system :the endocrine tissues and organs. 2 The endocrine tissues : The islets of Langerhans of pancreas, the ovarian follicles and corpora lutea of the ovary and the interstitial tissue of the testes 3 The endocrine organs : the hypophysis (pituitary), thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal (suprarenal) glands, the thymus and pineal body 4 The endocrine glands: no ducts . secrete hormones . 5 Function of the endocrine system : metabolism, development and growth , reproduction, et al. 二、The endocrine organs 1. The hypophysis(pituitary gland) a. location: in the hypophysial fossa of the body of sphenoid bone b. division: adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis c. function 2. The thyroid gland a. location: in the neck region with one lobe on either side of the larynx and trachea b. structures : lateral lobes and isthmus c. function: thyroxin 3. The parathyroid glands a. location: lie on the dorsal surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid b. function: parathyroidin 4. The suprarenal (or adrenal) glands a. location : on the medial part of the kidney behind the peritoneum b. construction: outer cortex and inner medulla c. functions: steroid hormone and epinephrine(adrenalin) ,norepinephrine 5. The pineal body a. location: protruding from the roof of the third ventricle of the diencephalon. b. function: secret melatonin 6. The thymus :located in the upper mediastinum posterior to the sternum 7. The pancreas a. location b. the endocrine part of the pancreas : Langerkans (islets of pencreas) c. function: produce insulin 8. The ovary: the ovarian follicle(the endocrine tissues): produce estrogen the corpus luteum :produce progesterone 9. The testis interstitial tissue : produce testosterone