Morphometric evaluation of dural venous sinuses: anatomical study
... Introduction: Knowledge of the normal anatomical variations of venous sinuses is important for clinicians and radiologist for investigations and diagnosing various pathologies of dural venous sinuses like thrombosis, embolism and fistula etc. The detailed morphometric study of dural venous sinuses i ...
... Introduction: Knowledge of the normal anatomical variations of venous sinuses is important for clinicians and radiologist for investigations and diagnosing various pathologies of dural venous sinuses like thrombosis, embolism and fistula etc. The detailed morphometric study of dural venous sinuses i ...
Radiological anatomy of the liver
... people with a rather steep visceral surface only the inferior border itself can be tangential to beam and will not often present true outline against intraperitoneal fat. The inferior border of the left lobe is rarely visible on plain ...
... people with a rather steep visceral surface only the inferior border itself can be tangential to beam and will not often present true outline against intraperitoneal fat. The inferior border of the left lobe is rarely visible on plain ...
using a lighted scope on a thin t
... An indirect inguinal hernia leaves the abdominal cavity lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels and enters the inguinal canal through the deep inguinal ring. Commonly, these hernias traverse the entire inguinal canal, leave the canal through the superficial inguinal ring, and enter the scrotum. T ...
... An indirect inguinal hernia leaves the abdominal cavity lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels and enters the inguinal canal through the deep inguinal ring. Commonly, these hernias traverse the entire inguinal canal, leave the canal through the superficial inguinal ring, and enter the scrotum. T ...
Module 2
... Topographic anatomy is an approach to anatomical study based on regions, parts, or divisions of the body (e.g., the foot or the inguinal region), emphasizing the relationships of various systemic structures (e.g., muscles, nerves, and arteries) within that area; distinguished from systemic anatomy. ...
... Topographic anatomy is an approach to anatomical study based on regions, parts, or divisions of the body (e.g., the foot or the inguinal region), emphasizing the relationships of various systemic structures (e.g., muscles, nerves, and arteries) within that area; distinguished from systemic anatomy. ...
Splanchlology
... undergone a peculiar modification, the cells having become cornified and elongated into dense, imbricated, brush-like processes. They contain also a number of elastic fibers, which render them firmer and more elastic than the papillae of mucous membrane generally. The larger and longer papillae of ...
... undergone a peculiar modification, the cells having become cornified and elongated into dense, imbricated, brush-like processes. They contain also a number of elastic fibers, which render them firmer and more elastic than the papillae of mucous membrane generally. The larger and longer papillae of ...
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
... Many people choose to have an operation as soon as polyps are found, rather than wait until there are large polyps. As more polyps will continue to develop after others have been removed, it becomes too difficult to remove all the polyps. Most people with FAP eventually opt to have surgery to remove ...
... Many people choose to have an operation as soon as polyps are found, rather than wait until there are large polyps. As more polyps will continue to develop after others have been removed, it becomes too difficult to remove all the polyps. Most people with FAP eventually opt to have surgery to remove ...
Localisation of hypogastric nerves and pelvic plexus in relation to
... a plane of loose areolar tissue. The parietal fascia contains several layers and encloses the hypogastric nerves. There is often a further loose areolar plane posterior to the hypogastric nerves and anterior to a further leaf of the parietal fascia. The pelvic splanchnic nerves are not shown in this ...
... a plane of loose areolar tissue. The parietal fascia contains several layers and encloses the hypogastric nerves. There is often a further loose areolar plane posterior to the hypogastric nerves and anterior to a further leaf of the parietal fascia. The pelvic splanchnic nerves are not shown in this ...
Workshop 12
... Relevance of the topic: for the diagnosis of diseases of the abdominal cavity you have to know their projection on the anterior abdominal wall; and to select the location, method and direction of incision during surgery on abdominal organs you have to know the features of topographic anatomical stru ...
... Relevance of the topic: for the diagnosis of diseases of the abdominal cavity you have to know their projection on the anterior abdominal wall; and to select the location, method and direction of incision during surgery on abdominal organs you have to know the features of topographic anatomical stru ...
Acland`s DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 6
... the left atrium by way of the four pulmonary veins, two from the right lung, two from the left. The left atrium, like the right one, has a blind pouch, the left auricle or atrial appendage, which projects upwards and forwards. In diastole, the blood that's in the left atrium passes forwards into the ...
... the left atrium by way of the four pulmonary veins, two from the right lung, two from the left. The left atrium, like the right one, has a blind pouch, the left auricle or atrial appendage, which projects upwards and forwards. In diastole, the blood that's in the left atrium passes forwards into the ...
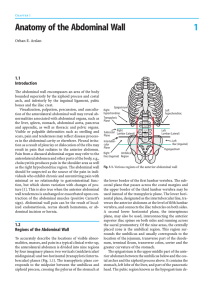
1 Anatomy of the Abdominal Wall
... A simplified division of the anterolateral abdomen uses two imaginary planes that run through the umbilicus, one passing horizontally and the other vertically. The four quadrants separated by these planes divide the anterior abdomen into the right and left upper and lower quadrants. In summary, the ...
... A simplified division of the anterolateral abdomen uses two imaginary planes that run through the umbilicus, one passing horizontally and the other vertically. The four quadrants separated by these planes divide the anterior abdomen into the right and left upper and lower quadrants. In summary, the ...
Urogynecology Definitions
... Painful urination, often burning-like pressure which is most pronounced toward the end of the stream. Enterocele: Displacement of the small intestine into the upper part of the vagina Fecal incontinence: Accidental loss of stool. Frequency: The need to urinate more often than normal (more than every ...
... Painful urination, often burning-like pressure which is most pronounced toward the end of the stream. Enterocele: Displacement of the small intestine into the upper part of the vagina Fecal incontinence: Accidental loss of stool. Frequency: The need to urinate more often than normal (more than every ...
I. Review of literature related to peritoneal catheter care
... renal disease who were not able to carry out the continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis treatment themselves were given assistance by district nurses. During the study period questionnaires were sent to both the district and the hospital nurses and the study period was 58 months of continuous amb ...
... renal disease who were not able to carry out the continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis treatment themselves were given assistance by district nurses. During the study period questionnaires were sent to both the district and the hospital nurses and the study period was 58 months of continuous amb ...
The Relationships between Asterion, the Transverse
... * Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand ** Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand Background: Anatomical localization of the venous sinuses in the posterior cranial fossa is impor ...
... * Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand ** Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand Background: Anatomical localization of the venous sinuses in the posterior cranial fossa is impor ...
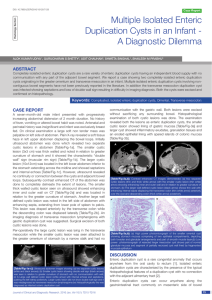
Multiple Isolated Enteric Duplication Cysts in an Infant
... Multiple enteric duplication cysts have been reported previously in the literature with oesophageal duplication cyst associated with small bowel duplication being the most common combination. Other varieties of multiple enteric duplication cysts generally involve contiguous segments of bowel loops s ...
... Multiple enteric duplication cysts have been reported previously in the literature with oesophageal duplication cyst associated with small bowel duplication being the most common combination. Other varieties of multiple enteric duplication cysts generally involve contiguous segments of bowel loops s ...
CH18 Gasto Uro emergency
... – Progressive, develops over months/years – Eventually dialysis or transplant is required. ...
... – Progressive, develops over months/years – Eventually dialysis or transplant is required. ...
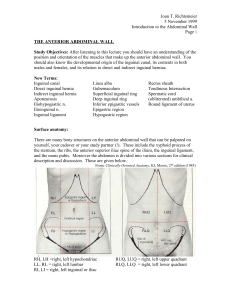
Introduction to the Abdomen
... Joan T. Richtsmeier 5 November 1999 Introduction to the Abdominal Wall Page 8 closure of the anterior abdominal wall after the umbilical cord is ligated at birth. Hernias may also occur through defects in the linea alba. The inguinal region is the most common site of hernias and hernias in this are ...
... Joan T. Richtsmeier 5 November 1999 Introduction to the Abdominal Wall Page 8 closure of the anterior abdominal wall after the umbilical cord is ligated at birth. Hernias may also occur through defects in the linea alba. The inguinal region is the most common site of hernias and hernias in this are ...
The inguinal canal
... An indirect inguinal hernia arises lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels, the protrusion following the path of the spermatic cord or round ligament through the deep inguinal ring into the inguinal canal. With an indirect inguinal hernia bowel can easily pass down the inguinal ...
... An indirect inguinal hernia arises lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels, the protrusion following the path of the spermatic cord or round ligament through the deep inguinal ring into the inguinal canal. With an indirect inguinal hernia bowel can easily pass down the inguinal ...
Abnormal Stools and Bowel function
... first part of the small intestine. Blood will look like tar after it has been exposed to the body's digestive juices as it passes through the intestines. Certain medications that contain Iron or Bismuth may also produce black stools. This type of stool requires investigation and should be reported t ...
... first part of the small intestine. Blood will look like tar after it has been exposed to the body's digestive juices as it passes through the intestines. Certain medications that contain Iron or Bismuth may also produce black stools. This type of stool requires investigation and should be reported t ...
The inguinal canal :
... In new born the deep inguinal ring is almost directly posterior to the superficial inguinal ring (opposite to each other in children) Its margins are called crura (medial and lateral crus) give attachment to the external spermatic fascia ...
... In new born the deep inguinal ring is almost directly posterior to the superficial inguinal ring (opposite to each other in children) Its margins are called crura (medial and lateral crus) give attachment to the external spermatic fascia ...
Anatomical variants of the emissary veins
... Additionally, aplasia of the sigmoid sinus and development of the PSS were revealed on the contralateral side (Fig. 2). The leading emissary veins are elaborate on the supra, middle, and inferior thirds of the sigmoid sinus. Thus the triplets of these venous pathways are the lower or posterior condy ...
... Additionally, aplasia of the sigmoid sinus and development of the PSS were revealed on the contralateral side (Fig. 2). The leading emissary veins are elaborate on the supra, middle, and inferior thirds of the sigmoid sinus. Thus the triplets of these venous pathways are the lower or posterior condy ...
The deep inguinal ring
... •Polar inversion, in which the testis and epididymis are completely inverted •Imperfect descent (cryptorchidism): Incomplete descent, in which the testis, although traveling down its normal path, fails to reach the floor of the scrotum. It may be found within the abdomen, within the inguinal canal, ...
... •Polar inversion, in which the testis and epididymis are completely inverted •Imperfect descent (cryptorchidism): Incomplete descent, in which the testis, although traveling down its normal path, fails to reach the floor of the scrotum. It may be found within the abdomen, within the inguinal canal, ...
(PID) Pelvic inflammatory disease - A
... Veres needle withdrawn and operating laparoscope inserted (accomodates Kleppinger or scissors) Trocars inserted (sleeve may or may not be used) Ports established to accommodate camera in one (umbilical incision) and other instruments needed in the other (May reattach silastic tubing to one of the tr ...
... Veres needle withdrawn and operating laparoscope inserted (accomodates Kleppinger or scissors) Trocars inserted (sleeve may or may not be used) Ports established to accommodate camera in one (umbilical incision) and other instruments needed in the other (May reattach silastic tubing to one of the tr ...
Anatomy of the nerves and ganglia of the aortic plexus in males
... made through the linea alba and the anterior wall of the peritoneal sac, exposing the peritoneal cavity. A horizontal incision at the level of the umbilicus was made from the right to the left midaxillary line to divide the anterior body wall into four segments. An oblique incision along the root of ...
... made through the linea alba and the anterior wall of the peritoneal sac, exposing the peritoneal cavity. A horizontal incision at the level of the umbilicus was made from the right to the left midaxillary line to divide the anterior body wall into four segments. An oblique incision along the root of ...
topography of the anterior lateral wallof the abdomen
... 6. The operation which completely removes the cause of the disease (pathological area) is 1) The radical 2) The palliative 3) The simultaneous 4) The urgent 7. The operation which is aimed at either making the condition of the patient better or to eliminate any life-threatening symptoms is 1) The ra ...
... 6. The operation which completely removes the cause of the disease (pathological area) is 1) The radical 2) The palliative 3) The simultaneous 4) The urgent 7. The operation which is aimed at either making the condition of the patient better or to eliminate any life-threatening symptoms is 1) The ra ...
Ozone Enema Protocol
... Homozone followed by the juice of 1/2 lemon. This aids in evacuating the bowel in the morning. Do not take any anti-oxidants for at least 12 hours before your ozone enema. These include such neutriceuticals such as Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Bioflavinoids, Selenium, Ginko Biloba, Alpha Lipioc Acid, SOD, ...
... Homozone followed by the juice of 1/2 lemon. This aids in evacuating the bowel in the morning. Do not take any anti-oxidants for at least 12 hours before your ozone enema. These include such neutriceuticals such as Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Bioflavinoids, Selenium, Ginko Biloba, Alpha Lipioc Acid, SOD, ...
Mesentery

The mesentery is a fold of membranous tissue that arises from the posterior wall of the peritoneal cavity and attaches to the intestinal tract. Within it are the arteries and veins that supply the intestine. The term can be used narrowly to denote just the material that supplies the jejunum and ileum of the small intestine, or broadly to include the right, left and transverse mesocolon, mesoappendix, mesosigmoid and mesorectum.The human mesentery, also called the mesenteric organ, mainly comprises the small intestinal mesentery, the right, left and transverse mesocolon, mesosigmoid and mesorectum. Conventional teaching has described the mesocolon as a fragmented structure; the small intestinal mesentery, transverse and sigmoid mesocolon all terminate at their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. Recent advances in gastrointestinal anatomy have demonstrated that the mesenteric organ is actually a single, continuous structure that reaches from the duodenojejunal flexure to the level of the distal mesorectum. This simpler concept has been shown to have significant implications.