* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Workshop 12
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
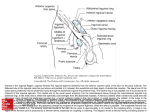
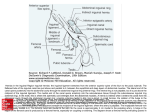
Workshop 12 Topic. Surgical anatomy of the anterior lateral abdominal wall. Anatomical and physiological justification of the accesses to the abdominal cavity. Surgical treatment of umbilical hernias and hernias of linea alba. Topographical anatomy of the inguinal region. Surgical anatomy of inguinal canal and its content. Surgical anatomy and surgical treatment of inguinal hernias. Relevance of the topic: for the diagnosis of diseases of the abdominal cavity you have to know their projection on the anterior abdominal wall; and to select the location, method and direction of incision during surgery on abdominal organs you have to know the features of topographic anatomical structure of different parts of the anterior lateral abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias are one of the most common surgical diseases. For the successful treatment it is necessary to know the mechanism of this disease, anatomical and physiological features of inguinal region, to be able to choose the method of plastics of hernia gates, taking into account topographical and anatomical relationships of the nerves and vessels that are located there. Purpose of the lesson: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Learn the projection of the abdomen on anterior lateral abdominal wall. Master the technique of laparotomy and give anatomical and physiological justification of median, paramedian, trans- and pararectal, oblique, transverse and combined incisions. Learn the principles of the surgeries and methods of plastics of hernia gates with umbilical hernias and hernias of linea alba. Examine the causes of oblique and direct inguinal hernias. Learn how to perform plastics of anterior and posterior walls of inguinal canal. Master the technique of surgery on strangulated inguinal hernias. Control questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Boundaries of the abdomen. Division into regions. Projections of organs of the abdominal cavity on the anterior lateral abdominal wall. Topographical anatomy of the unpaired regions of anterior lateral abdominal wall. Structure of the vagina of m. rectus abdominis and linea alba on different levels towards the navel. Structural features of the navel. Topographical anatomy of the paired regions of anterior lateral abdominal wall. Anatomical and physiological justification of median, paramedian, trans- and pararectal, oblique, transverse and combined incisions. Laparatomy. Performance technique. Principles of the surgeries and methods of plastics of hernia gates with umbilical hernias and hernias of linea alba. Topographical anatomy of inguinal region. Surgical anatomy of the inguinal canal in normal conditions and with inguinal hernias. Inguinal gap and pathogenesis of direct inguinal hernias. The content of the inguinal canal. The process of testicular descent and pathogenesis of the congenital oblique inguinal hernias. Abdominal hernias. Classification. Elements of hernia. Surgical anatomy of the oblique inguinal hernia. Surgical anatomy of the direct inguinal hernia. The main stages of hernial dissection and methods of plastics of hernial gates with oblique and direct inguinal hernias. Disadvantages and complications of hernial dissection. Features of surgical treatment of strangulated hernias. Practical skills: 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. Show on the body: regions of the anterior lateral abdominal wall muscles of the anterior lateral abdominal wall vessels and nerves of the anterior lateral abdominal wall holes and walls of canalis inguinalis linea arcuata et linea semilunata vagina of the m. rectus abdominis and her content Make and justify median, paramedian, trans- and pararectal, transverse and oblique incisions. Make plastics of hernial gates with umbilical hernias (Meyo, Sapejko, Lexer) and hernias of linea alba (Sapejko, Napalkov). Show on the body: a. epigastrica superficialis a. circumflexa humeri superficialis aa. pudendae externae a. epigastrica inferior inguinal canal, its holes, walls and content inguinal gap Perform methods of plastics of the anterior wall of inguinal canal: by Girard by Spasokukotskiy with the seam of Kimbarovskiy by Martinov Perform methods of strengthening of the posterior wall of inguinal canal: by Bassini by Kukudzhanov by Postempskiy Demonstrate basic stages of surgery with strangulated inguinal hernia. Computer questions for the practical training №12 Surgical anatomy of the anterior lateral abdominal wall. Anatomical and physiological justification of the accesses to the abdominal cavity. Surgical treatment of umbilical hernias and hernias of linea alba. Topographical anatomy of the inguinal region. Surgical anatomy of inguinal canal and its content. Surgical anatomy and surgical treatment of inguinal hernias. 1. Name the boundaries of inguinal segment 2. Name the arteries that are located in inguinal area 3. Identify sources of innervation of the front-lateral abdominal wal 4. What are the organs that are projected in the right inguinal area 5. Identify formations that are projected in the left inguinal area 6. Identify bodies that are projected in the hypochondriaca sinistra region 7. What organs are projected in the regio epigastrica 8. What organs are located in the regio hypochondriaca sinistra 9. What organs are projected in region hypochondriaca dexter 10. What is projected in regio umbilicalis 11. What is projected in regio abdominalis lateralis sinistra 12. What is projected in regio pubica 13. Why do patients with pneumonia feel pain in the abdominal wall 14. Identify the weak places of anterior abdominal wall to the average line 15. Identify the weak places of anterior abdominal wall in lateral part 16. What anatomical formations are located between inner oblique and transverse abdominal muscles 17. How is the front wall of vagina of the direct abdominal muscle formed above the navel 18. How is the front wall of the vagina of direct abdominal muscle formed below the navel 19. How is the posterior wall of the vagina of direct abdominal muscle formed below the navel 20. What layers does the navel consist of 21. What approaches to embryo to the umbilical ring on top 22. What approaches to embryo to the umbilical ring below 23. What vessels go in the vagina of direct abdominal muscle 24. Identify the basic types of vertical laparotomic invasions 25. What is the gateway for umbilical hernia 26. Does the incision of the m. rectus in the transverse direction threaten the funcion 27. Does the incision of the m. rectus in the paramedian direction threaten the funcion 28. Does the incision of the m. rectus in the pararectal direction threaten the funcion 29. Is the function of m. rectus abdominis disturbed when nn. intercostales in the spinal region are cut 30. Name the authors who made the main methods of operations if inguinal hernias 31. Name the authors who made the main methods of surgery in abdomen hernias of white line 32. What incision is performed at the treatment of umbilical hernia by the method of Sapezhko 33. How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Lexer 34. How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Sapezhko 35. How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Meyo 36. How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Meyo 37. What are the boundaries of the inguinal area 38. Name arteries that are situated in the inguinal area 39. Name organs that are projected in the right inguinal area 40. Name organs that are projected in the left inguinal area 41. Anterior wall of the inguinal canal in normal 42. Superior wall of the inguinal canal 43. Inferior wall of the inguinal canal 44. Posterior wall of the inguinal canal 45. What strengthened the back wall of inguinal canal 46. Superficial inguinal ring is limited laterally and from below by 47. Superficial inguinal ring is limited laterally and from the top by 48. Superficial inguinal ring is limited medially and from the top by 49. Superficial inguinal ring is limited from below and from behind by 50. What strengthened the medial area of posterior wall of the inguinal canal 51. What forms of the inguinal gap do you know 52. What determines the shape of the inguinal gap 53. Name the medial border of the inguinal gap 54. Name the superior border of the inguinal gap 55. Name the inferior border of the inguinal gap 56. Name weak places of the anterior abdominal wall of the lateral abdominal region 57. What anatomic formations are located if the tissue between m. obliquus internus and m. transversus abdominis 58. Name the elements of the spermatic cord 59. What nerve accompanies spermatic cord and lies in front and above of it 60. What nerve accompanies spermatic cord and lies below and behind it 61. What artery approaches to the spermatic cord from the behind 62. What are the topographical features of a. epigastrica inferior 63. What makes the gates of the oblique inguinal hernia 64. What makes the gates of the direct inguinal hernia 65. What makes the hernial bag in the congenital hernia 66. In what direction is hernial ring dissected in the oblique inguinal hernia 67. In what direction is hernial ring dissected in the direct inguinal hernia 68. What hole does the direct inguinal hernia go through 69. What is the relation of hernia bag to the spermatic cord in the oblique congenital inguinal hernia 70. What is the relation of hernia bag to the spermatic cord in the direct inguinal hernia 71. In oblique inguinal hernia a. epigastrica inferior is located 72. In direct inguinal hernia a. epigastrica inferior is located 73. What wall of the inguinal canal is weakened in the oblique inguinal hernia 74. What layers cover the hernial bag in the oblique inguinal hernia 75. What layers cover the hernial bag in the direct inguinal hernia 76. Specify methods of herniotomy that strengthen the anterior wall of the inguinal canal 77. Specify methods of herniotomy that strengthen the posterior wall of the inguinal canal 78. What structure is fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Girard 79. What structure is fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Martinov 80. How is duplicate by the method of Martinov made 81. What tissues are fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Bassini 82. What tissues are fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Postempskiy 83. How if duplicate by the method of Postemskiy made 84. Name the authors of the main methods of surgeries in inguinal hernias ? Name the boundaries of inguinal segment: + the line that connects both the front upper illiac spina, lateral edge straight muscle of the abdomen, inguinal ligament -the line that connects both the front upper illiac spina, white line of the abdomen, inguinal ligament -arcus costalis and processus xiphoideus, crista illiaca, Lig. inguinalis -linea bicostarum, lateral edge of straight muscle of the abdomen, inguinal ligament ? Name the arteries that are located in inguinal area: +a. epigastrica superficialis, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis, aa. pudendae externae, a. epigastrica inferior -a. epigastrica superficialis, a. epigastrica superior, a. epigastrica inferior, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis, aa. pudendae externae -a. epigastrica superficialis, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis et profunda, aa. pudendae externae -a. epigastrica superior et inferior, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis et profunda, aa. pudendae externae ? Identify sources of innervation of the front-lateral abdominal wall: + lower 6 intercostal nerves, n. ilioinguinalis, n. iliohypogastricus - intercostal nerves, n. ilioinguinalis, n. iliohypogastricus, n. genitofemoralis - intercostal nerves, n. ilioinguinalis, n. iliohypogastricum, n. genitofemoralis, n. obturatorius -lower 6 intercostal nerves, n. ilioinguinalis, n. iliohypogastricus, r. genitalis n. genitofemoralis ? What are the organs that are projected in the right inguinal area: + cecum, Appendix vermicularis,ureter - cecum, Appendix vermicularis,ureter , rectum - cecum, Appendix vermicularis, urinary bladder - intestine sygmoideus, cecum, Appendix vermicularis ? Identify formations that are projected in the left inguinal area: + sigmoid colon, ureter - sigmoid colon, rectum, ureter - cecum, sigmoid colon, ureter - cecum, sigmoid colon, ureter, rectum ? Identify bodies that are projected in the hypochondriaca sinistra region: + liver (right lobe), flexura coli dextra, gall blader, the upper end of the right kidney, right adrenal gland - liver, pars superior duodeni, gall blader, flexura coli dextra, the upper end of the right kidney and right adrenal gland - liver, gall blader, pilloric part of the stomach, pars superior duodenum, right kidney and right adrenal gland - liver, gall blader, pars superior and pars descendens duodenum, right kidney i right adrenal gland ? What organs are projected in the regio epigastrica? + liver, stomach, pars superior duodenum, flexura duodenojejunalis, pancreas, aorta, celiac plexus - liver (left part and some right) stomach (body part and pilloric part), pars superior duodenum, pancreas, gates kidney, aorta, celiac plexus - liver, stomach, colon transversum, pars superior duodenum, pancreas, aorta, celiac plexus - liver, stomach, pancreas, gall blader, pars superior duodenum, aorta, celiac plexus ? What organs are located in the regio hypochondriaca sinistra? + stomach, spleen, tail of pancreas, flexura coli sinistra, left kidney, adrenal gland - stomach, spleen, tail of pancreas, left kidney, flexura duodenojejunalis - stomach (cardia, the bottom part of the body), spleen, tail of pancreas, gland, aorta, inferior vena cava, left kidney ,adrenal gland - stomach, spleen, the left liver fraction, tail of pancreas, flexura coli sinistra, left kidney ,adrenal gland ? What organs are projected in region hypochondriaca dexter? + colon ascendens, ileum, right kidney, right ureter -colon ascendens, pars descendens duodenum, ileum, right kidney, right ureter -colon ascendens, right kidney, right adrenal gland, ileum, right ureter -colon ascendens, right kidney, jejunum, right ureter, pancreas ? What is projected in regio umbilicalis? + curvatura ventriculi major, colon transversum, duodenal , kidney gate, thin intestine, aorta, v. cava inferior -gaster (part of the body, pilloric part and large curvature) duodenal, intestines, gates kidney, aorta, v. cava inferior - gaster, colon transversum, duodenal, gates kidneypancreas, thin intestine, aorta, v. cava inferior - gaster duodenal, pancreas, kidney gate ,loop intestines, aorta, v. cava inferior ? What is projected in regio abdominalis lateralis sinistra? + colon descendens, loop jejunum, left ureter, the left kidney, -colon descendens, loop jejunum, left ureter, the left kidney, pancreas tail -colon descendens, loop jejunum, left kidney, the left adrenal gland, left ureter, flexura duodenojejunalis -colon descendens, loop jejunum, left kidney , left ureter, aorta ? What is projected in regio pubica? + loop of thin intestine, urinary bladder, part syhmopodibnoyi intestine, uterus, ureters - loop of thin intestine, urinary bladder, syhmopodibna colon, uterus, rectum - loop of thin intestine, urinary bladder (filled), sygmoideus intestine, caecum, uterus, ureters - urinary bladder (filled), sygmoideus intestine, colon descendens, rectum, uterus, ureters ? Why do patients with pneumonia feel pain in the abdominal wall ? + nn. intercostales innerv pleura and stomach muscles -nn. intercostales and n. phrenicus innerv pleura and stomach muscles -nn. intercostale innerv muscles of the abdomen, and n. phrenicus pleura -nn. intercostales innerv abdominal muscles and pleura , and n. phrenicus peritoneum ? Identify the weak places of anterior abdominal wall to the average line: + umbilical ring, white line of the abdomen - umbilical ring, white line of the abdomen, the spyheliyeva line -inguinal channel ,umbilical ring, white line of the abdomen - umbilical ring, rhombus Lesgafta-Hrynfelta, whute line of the abdomen ? Identify the weak places of anterior abdominal wall in lateral part: + Spigheli line, inguinal channel - canalis obturatorius, inguinal channel -Pititi trigonum, inguinal channel - inguinal channel, rhombus lumbalis ? What anatomical formations are located between inner oblique and transverse abdominal muscles? + nn. intercostales, n. subcostalis, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinalis, aa. intercostales posterior, a. lumbales, r. ascendens a. circumflexa ilium profunda -nn. intercostales, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinalis, aa. intercostales anteriores et posteriores, aa. lumbalis -nn. intercostales, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinales, aa. intercostales posteriores, a. epigastrica superior -nn. intercostales, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinalis, aa. intercostales posteriores, aa. lumbales, a. epigastrica inferior ? How is the front wall of vagina of the direct abdominal muscle formed above the navel? + aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle of the abdomen, superficial aponeurosis of the internal oblique sheet of muscle belly - aponeurosis external oblique muscle of abdomen - aponeurosis external oblique muscle of the abdomen, superficial and deep aponeurosis of the internal leaves of oblique abdomen muscle -by all three aponeurosis of abdomen muscle ? How is the front wall of the vagina of direct abdominal muscle formed below the navel? + all three aponeurosis of abdomen muscle - aponeurosis external oblique muscle of abdomen - aponeurosis external oblique muscle of the abdomen, superficial and deep aponeurosis of the internal leaves of oblique abdomen muscle aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle of the abdomen, superficial aponeurosis of the internal oblique sheet of muscle belly - ? How is the posterior wall of the vagina of direct abdominal muscle formed below the navel? + fascia transversa -by all three aponeurosis of abdomen muscle -aponeurosis transverse muscle of the abdomen and the deep sheet of aponeurosis of the internal oblique muscle - aponeurosis transverse muscle of abdomen ? What layers does the navel consist of? + skin, scar tissue, tire umbilical cord, transverse fascia, peritoneum - skin, subcutaneous tissue, transverse fascia, peritoneum - skin, subcutaneous tissue, superficial fascia, transverse fascia, peritoneum - skin, transverse fascia, three aponeurosis of abdomen muscle, peritoneum ? What approaches to embryo to the umbilical ring on top? + umbilical vein - umbilical arteries -urachus -Arantsiyev duct ? What approaches to embryo to the umbilical ring below? + umbilical arteries, urachus -Arantsiyev ducts -lig. teres hepatis - umbilical vein ? What vessels go in the vagina of direct abdominal muscle? + a. et v. epigastrica superior, a. et v. epigastrica inferior, aa. intercostales -a. et v. epigastrica superior, a. et v. epigastrica inferior -a. et v. epigastrica superior, a. et v. epigastrica inferior, a. et v. epigastrica superficialis -a. thoracia interna, a. et v. intercostales ? Identify the basic types of vertical laparotomic invasions: + median, paramedial, transrectal, perarectal - median, paramedial, transrectal, perarectal, Fedorov cut - median, paramedial, transrectal, perarectal, Mc Berneya-Volkovych D`yakonova cut - median, paramedial, transrectal, perarectal, Kocher cut ? What is the gateway for umbilical hernia? + anulus umbilicalis -white line of the abdomen -fossa inguinalis lateralis -fossa inguinalis medialis ? Does the incision of the m. rectus in the transverse direction threaten the funcion? + No -Yes ? Does the incision of the m. rectus in the paramedian direction threaten the funcion? + No -Yes ? Does the incision of the m. rectus in the pararectal direction threaten the funcion? + Yes -No ? Is the function of m. rectus abdominis disturbed when nn. intercostales in the spinal region are cut? + No -Yes ? Name the authors who made the main methods of operations if inguinal hernias: + Lexer, Meyo, Sapezhko -Girard, Spasokukotskiy, Lexer -Lexer, Bassini, Sapezhko -Girard, Postemskiy, Meyo ? Name the authors who made the main methods of surgery in abdomen hernias of white line: + Sapezhko, Napalkov -Lexer, Meyo -Spasokukotskiy, Sapezhko -Lexer, Napalkov, Sapezhko ? What incision is performed at the treatment of umbilical hernia by the method of Sapezhko? + longitudinal, avoiding the navel from left -double cross bordering hernia protrusion -horyzontal cut around hernial protrusion - longitudinal, avoiding navel case ? How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Lexer? + by imposing kisette seam around the umbilical ring overlay node and seam front wall direct abdomen muscle -seam right edge of the aponeurosis to the back wall of vagina left-direct abdomen muscle and left aponeurosis flap to the front wall of vagina direct muscle -hernia gates are crossing, seam the lower edge of the aponeurosis by L-shaped sutures to the posterior surface of the upper flap and the free upper edge flap seam by nodal seams to the front surface of the lower flap -vertical cut from left and right the front wall direct muscle, by nodal internal seams stitched edges aponeurosis, and then, external\ ? How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Sapezhko? +hernia gate expand vertical lines cut of white line, sew edge white line to the back wall vagina direct muscle and the other end sew to white line to the front wall vagina direct muscle from opposite side - by imposing kisette seam around the umbilical ring overlay node and seam front wall direct abdomen muscle -vertical cut from left and right the front wall direct muscle, by nodal internal seams stitched edges aponeurosis, and then, external -hernia gates are crossing, seam the lower edge of the aponeurosis by L-shaped sutures to the posterior surface of the upper flap and the free upper edge flap seam by nodal seams to the front surface of the lower flap ? How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Meyo? + hernia gates are crossing, seam the lower edge of the aponeurosis by L-shaped sutures to the posterior surface of the upper flap and the free upper edge flap seam by nodal seams to the front surface of the lower flap -vertical cut from left and right the front wall direct muscle, by nodal internal seams stitched edges aponeurosis, and then, external - hernia gate expand vertical lines cut of white line, sew edge white line to the back wall vagina direct muscle and the other end sew to white line to the front wall vagina direct muscle from opposite side - by imposing kisette seam around the umbilical ring overlay node and seam front wall direct abdomen muscle ? How is the plastics of hernial gates performed by the method of Meyo? + hernia gate cut up and down the white line, sew edge of white line to the back wall vagina of direct muscle and the other end to white line to the front wall muscle vagina direct opposite side -hernial gate are cut by cross incision, the lower edge of the aponeurosis L-shaped seams stitch to the rear surface of the upper flap and the free upper edge flap also unambiguously fixed to the front surface of the lower valve -vertically cut from left and right the front vaginal wall of direct muscles, nodal internal seams stitched edges aponeurosis, and then, external -by imposition of kisette seam around the hernial gates and overlay 2 - 3 key seams on front vaginal wall of direct muscles ? What are the boundaries of the inguinal area: +line that connects crista iliaca anterior superior dextra et sinistra, lateral edge of m. rectus abdominis, inguinal ligament -line that connects crista iliaca anterior superior dextra et sinistra, linea alba, inguinal ligament -arcus costalis and processus xiphoideus, cristae iliacae, inguinal ligaments -linea bicostarum, margo lateralis m. rectus abdominis, inguinal ligament ? Name arteries that are situated in the inguinal area: +a. epigastrica superficialis, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis, aa. pudendae externae, a. epigastrica inferior -a. epigastrica superficialis, a. epigastrica superior, a. epigastrica inferior, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis, aa. pudendae externae -a. epigastrica superficialis, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis et profunda, aa. pudendae externae -a. epigastrica superior et inferior, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis et profunda, aa. pudendae externae ? Name organs that are projected in the right inguinal area: +cecum, appendix, ureter -cecum, appendix, ureter, rectum -cecum, appendix, bladder -colon sigmoideum, cecum, appendix ? Name organs that are projected in the left inguinal area: +colon sigmoideum, ureter -colon sigmoideum, rectum, ureter -colon sigmoideum, cecum, ureter -colon sigmoideum, cecum, ureter, rectum ? Anterior wall of the inguinal canal in normal: +aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus, fibers of m. obliquus abdominis internus -m. obliqus abdominis externus -m. obliquus abdominis externus et internus -aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus ? Superior wall of the inguinal canal: +margo inferior m. obliquus abdominis internus, margo inferior m. transversus abdominis -aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus -aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus, margo inferior m. obliquus abdominis internus et m. transversus abdominis -lig. inguinale ? Inferior wall of the inguinal canal: +lig. inguinale -lig. pectineale -margo inferior m. obliquus abdominis internus -lig. inguinale, lig. lacunare ? Posterior wall of the inguinal canal: +fascia transverse, aponeurotic fibers of m. obliquus internus abdominis et m. transversus abdominis -aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus -fascia transversa -Hesselbach ligament, Henle ligament ? What strengthened the back wall of inguinal canal? +Hesselbach ligament, Henle ligament -Cooper ligament -ligamentum lacunare -Henle ligament ? Superficial inguinal ring is limited laterally and from below by: +crus laterale -crus mediale -lig. reflexum -fibrae intercruralis ? Superficial inguinal ring is limited laterally and from the top by? +fibrae intercruralis -crus laterale -crus mediale -falx inguinalis ? Superficial inguinal ring is limited medially and from the top by? +crus mediale -crus mediale, fibrae intercruralis -lig. reflexum -falx inguinalis ? Superficial inguinal ring is limited from below and from behind by? +lig. reflexum -crus mediale -lig. pectineale -lig. lacunare ? What strengthened the medial area of posterior wall of the inguinal canal? +falx inguinalis -lig. interfoveolare -lig. lacunare -lig. pectineale ? What forms of the inguinal gap do you know? +slit-like, oval, triangular -slit-like -oval -triangular ? What determines the shape of the inguinal gap? +standing height of the internal oblique muscle of the abdomen, the standing high of transverse muscle of the abdomen, narrow inferior part of m. rectus abdominis -standing height of the internal oblique muscle of the abdomen, the standing high of transverse muscle of the abdomen -narrow inferior part of m. rectus abdominis -place of divergence of the fibers of aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus ? Name the medial border of the inguinal gap: +margo lateralis vaginae m. rectus abdominis -intrafossal ligament -inguinal ligament -margo inferior m. obliquus abdominis internus ? Name the superior border of the inguinal gap: +margo inferior m. obliquus abdominis internus, margo inferior m. transversus abdominis -falx inguinalis -intrafossal ligament -inguinal ligament ? Name the inferior border of the inguinal gap: +inguinal ligament -ligamentum lacunare -Cooper ligament -falx inguinalis ? Name weak places of the anterior abdominal wall of the lateral abdominal region: +linea semilunaris, inguinal canal -canalis obturatorius, canalis inguinalis -lumbar triangle, canalis inguinalis -canalis inguinalis, rhombus lumbalis ? What anatomic formations are located if the tissue between m. obliquus internus and m. transversus abdominis? +nn. intercostales, n. subcostalis, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinalis, aa. intercostales posterior, a. lumbales, r. ascendens a. circumflexa ilium profunda -nn. intercostales, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinalis, aa. intercostales anteriores et posteriores, aa. lumbalis -nn. intercostales, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinales, aa. intercostales posteriores, a. epigastrica superior -nn. intercostales, n. iliohypogastricus, n. ilioinguinalis, aa. intercostales posteriores, aa. lumbales, a. epigastrica inferior ? Name the elements of the spermatic cord: +a. testicularis, plexus testicualris, plexus pampiniformis, ductus deferens, a. ductus deferentis, plexus deferentioalis, processus vaginalis peritonaei -a. testicularis, plexus pampiniformis, ductus deferens, a.ductus deferentis, processus vaginalis peritonaei -a. testicularis, v. testicularis, ductus deferens, a. cremasterica, processus vaginalis peritonaei -a. testicularis, plexus testicularis, plexus pampiniformis, ductus deferens, a. ductus deferentis, plexus deferentialis, processus vaginalis peritonaei, a. cremasterica, n. ilioinguinalis, r. genitalis n. genitofemoralis ? What nerve accompanies spermatic cord and lies in front and above of it? +n. ilioinguinalis -n. iliohypogastricus -r. genitalis n. genitofemoralis -r. femoralis n. genitofemoralis ? What nerve accompanies spermatic cord and lies below and behind it? +r. genitalis n. genitofemoralis -n. ilioinguinalis -n. iliohypogastricus -r. femoralis n. genitofemoralis ? What artery approaches to the spermatic cord from the behind? +a. cremasterica -a. testicularis -a. ductus deferens -a. epigastrica inferior ? What are the topographical features of a. epigastrica inferior: +departs from a. iliaca externa, goes it the preperitoneal tissue behind the inguinal ligament, crosses the external edge of m. rectus abdominis and goes into the vagina of m. rectus abdominis, makes an anastomosis with a. epigastrica superior -departs from a. iliaca interna, goes it the preperitoneal tissue behind the inguinal ligament, crosses the external edge of m. rectus abdominis, makes an anastomosis with a. epigastrica superior -departs from a. iliaca communis, goes it the preperitoneal, makes plica umbilicalis lateralis, goes into the vagina of m. rectus abdominis, locates between the anterior wall of vagina and muscle -departs from a. iliaca externa, makes plica umbilicalis medialis, goes in parallel to external edge of m. rectus abdominis, makes anastomosis with a. epigastrica superior ? What makes the gates of the oblique inguinal hernia? +fossa inguinalis lateralis -fossa inguinalis medialis -fossa femoralis -anulus umbilicalis ? What makes the gates of the direct inguinal hernia? +fossa inguinalis medialis -fossa inguinalis lateralis -fossa supravesicalis -fossa femoralis ? What makes the hernial bag in the congenital hernia? +processus vaginalis peritonei -fascia spermatica interna -fascia spermatica externa -fascia cremasterica ? In what direction is hernial ring dissected in the oblique inguinal hernia? +upwards and laterally -upwards and medially -downwards and medially -downwards and laterally ? In what direction is hernial ring dissected in the direct inguinal hernia? +upwards and medially -upwards and lateralli -downwards and medially -downwards and laterally ? What hole does the direct inguinal hernia go through? +annulus inguinalis superficialis -anulus inguinalis profundus -fossa inguinalis lateralis -fossa inguinalis medialis ? What is the relation of hernia bag to the spermatic cord in the oblique congenital inguinal hernia? +located inside of fascia spermatica interna, surrounded by elements of spermatic cord -located behind fascia spermatica interna -located medially to spermatic cord -located laterally to spermatic cord ? What is the relation of hernia bag to the spermatic cord in the direct inguinal hernia: +located behind fascia spermatica interna, medially to spermatic cord -located inside of fascia spermatica interna -located laterally to spermatic cord -located below and behind the spermatic cord ? In oblique inguinal hernia a. epigastrica inferior is located: +medially to the hernial bag -laterally to the hernial bag -behind the hernial bag -abobe the hernial bag ? In direct inguinal hernia a. epigastrica inferior is located: +laterally to the hernial bag -medially to hernial bag -behind the hernial bag -above the hernial bag ? What wall of the inguinal canal is weakened in the oblique inguinal hernia? +anterior and posterior -anterior -posterior -inferior ? What layers cover the hernial bag in the oblique inguinal hernia? +skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis, fascia cremasterica, m. cremaster, fascia spermatica interna, preperitoneal tissue -skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis, fascia transversa, preperitoneal tissue -skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis -skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis, fascia transversa,, fascia spermatica interna ? What layers cover the hernial bag in the direct inguinal hernia? +skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis, fascia transversa, preperitoneal tissue -skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis -skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis, fascia cremasterica, m. cremaster, fascia spermatica interna, preperitoneal tissue -skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia superficialis, fascia transversa, fascia spermatica interna ? Specify methods of herniotomy that strengthen the anterior wall of the inguinal canal: +Girard, Spasokukotskiy, Martinov -Girard, Martinov, Bassini -Girard, Bassini, Postempskiy -Girard, Kimbarovskiy, Martinov ? Specify methods of herniotomy that strengthen the posterior wall of the inguinal canal: +Bassini, Postempskiy -Bassini, Postempskiy, Kukudzhanov -Bassini, Kimbarovskiy, Postempskiy -Bassini, Kukudzhanov, Postempskiy, Kimbarovskiy ? What structure is fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Girard? +inferior edges of m. obliquus internus and m. transversus abdominis; second layer of seams stitches the superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus -inferior edges of m. obliquus internus and m. transversus abdominis -aponeurosis m. obliquus externus abdominis, m. obliquus internus and m. transversus abdominis -m. obliquus internus abdominis, m. transversus abdominis, fascia transversa ? What structure is fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Martinov? +aponeurosis m. obliquus abdominis externus, m. obliquus abdominis internus, m. transversus abdominis -inferior edges of m. obliquus abdominis internus and m. transversus; second layer of seams stitches the superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus -inferior edges of m. obliquus internus and m. m transversus abdominis -m. obliquus abdominis internus, m. transversus abdominis, fascia transversa ? How is duplicate by the method of Martinov made? +superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is stitched to the inguinal ligament; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the external leaf -superior leaf of aponeurosis with m. obliquus internus and m. transversus are stitched to the inguinal ligament; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the external leaf -aponeurosis m. obliquus externus, m. obliquus internus, m. transversus and the edge of m. rectus abdominis are stitched to the inguinal ligament; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus adbominis externus is fixed to the superior leaf -inferior edge of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is stitched to the inguinal ligament; supreior edge of aponeurosis m. obliquus adbominis externus is fixed to the inferior ? What tissues are fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Bassini? +m. obliquus internus, m. transversus, fascia transversa, edge of m. rectus abdominis -superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus -aponeurosis m. obliquus externus, m. obliquus internus, m. transversus -m. obliquus internus, m. transversus, fascia transversa ? What tissues are fixed to the inguinal ligament by the method of Postempskiy? +superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus, m. obliquus internus, m. transversus and fascia transversa and the edge of m. rectus abdominis -aponeurosis m. obliquus externus, , m. obliquus internus, m. transversus -m. obliquus internus, m. transversus and fascia transversa -superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus ? How if duplicate by the method of Postemskiy made? +the edge of m. recrus abdominis is stitched to the inguinal ligament and periosteum of the pubic bone; superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus with its muscles and fascia transversa are fixed to the inguinal ligament; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the superior leaf under the spermatic cord -superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the inguinal ligament; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the superior leaf -superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus with its muscles is fixed to the inguinal ligament; ; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the superior leaf -inferior edge of m. obliquus internus and m. transversus with fascia transversa are fixed to the inguinal ligament; second layer of seams stitch the superior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus to the inguinal ligament; inferior leaf of aponeurosis m. obliquus externus is fixed to the superior leaf ? Name the authors of the main methods of surgeries in inguinal hernias: +Girard, Spasokukotskiy, Martinov, Bassini, Postempskiy, Kukudzhanov -Girard, Spasokukotskiy, Sapezhko, Martinov, Bassini, Postempskiy -Girard, Spasokukotskiy, Meyo, Bassini, Martinov, Kimbarovskiy -Girard, Spasokukotskiy, Martinov, Bassini, Мeyo