* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download note_ch13e_Ts
Survey
Document related concepts
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
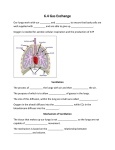
Class: Name: ( ) Date: 13 Gas exchange in humans 13.1 What does the human breathing system consist of? (Book 2, p.126) The human breathing system is specially developed for gas exchange. It consists of the respiratory tract and structures that help in breathing: rib cage (made up of ribs, sternum and vertebral column), external and internal intercostal muscles, and diaphragm. A B J K L C M D E N F G O H I P The human breathing system 44 Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Class: Name: ( Structure (1) A Nasal ) Date: Description Lined with a mucus-secreting cells b ciliated epithelial cells c blood capillaries d olfactory cells (嗅覺細胞) Guarded by hairs Makes up the rib cage to protect the lungs and the heart cavity (鼻腔) B Nostril (鼻孔) C (2) D Intercostal muscle (肋間肌) Controls the movement of the rib cage (3) Does not have any cartilage Lined with mucus-secreting cells and E Rib Bronchiole (肋骨) (小支氣管) ciliated epithelial cells F Inner pleural membrane (內胸膜) In contact with the lung G Outer pleural membrane (外胸膜) In contact with the internal intercostal muscles (4) Acts as a lubricant to help the lungs move easily inside the thoracic cavity during breathing Forms the respiratory surface (呼吸表面) where gas exchange takes place Where the respiratory tract and the alimentary canal meet Covers the entrance of the larynx to prevent choking (窒息) Made of cartilage to prevent it from collapsing Contains the vocal cords to produce sounds Supported by C-shaped cartilage (氣管) Lined with mucus-secreting cells and ciliated epithelial cells (支氣管) Supported by circular rings of cartilage Lined with mucus-secreting cells and H Pleural fluid (胸膜液) I (5) J Pharynx (咽) K (6) Epiglottis (會厭) L (7) Larynx (喉) M N (8) (9) Alveolus Trachea Bronchus (肺泡) ciliated epithelial cells O Lung (肺) P (10) Diaphragm (橫膈膜) Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Made up of alveoli, bronchioles and a large network of blood capillaries Separates the thoracic cavity from the abdomen 45 Class: Name: ( ) Date: Rib cage Transverse section through the trachea The structure of a lung Air flow along the respiratory tract: nostrils nasal cavity pharynx larynx (1) (4) 46 trachea air (2) sacs bronchi (3) (in lungs) (5) bronchioles alveoli (in lungs) (in lungs) Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Class: Name: ( ) Date: Go To … Practical 13.1 Examination of the mammalian breathing system (Student’s Book 2 p.127; Activity Book 2 p.87) Practical 13.2 Examination of the pig lung (Student’s Book 2 p.129; Activity Book 2 p.89) Filtering, moistening and warming of the incoming air (Book 2, p.130) Air contains dust particles, which would block the air passage, and (1) bacteria that may cause infection. The incoming air is filtered by the (2) (3) cilia hairs in the nostrils, and mucus and in the nasal cavity, trachea and bronchi. It is moistened by the (4) mucus and warmed by the (5) blood capillaries in the respiratory tract. Consequently, the air reaching the lungs is clean, moist and warm. Dust particles are removed from the respiratory tract Go To … Quick check (Student’s Book 2 p.130) Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 47 Class: Name: ( ) Date: 13.2 How does gas exchange take place in the alveoli? (Book 2, p.131) direction of blood flow blood capillary from pulmonary artery red blood cell alveolus O2 CO2 film of moisture blood capillary to pulmonary vein Gas exchange between an alveolus and a blood capillary The transport of oxygen from the atmosphere into the blood: 1 Oxygen is inhaled into the alveoli of the lungs. 2 Oxygen then (1) 3 Oxygen concentration is (2) dissolves in the film of moisture lining the alveoli. higher in the alveoli than in the blood capillaries. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the (3) blood capillaries . The transport of carbon dioxide from the blood into the atmosphere: 1 Carbon dioxide concentration is (4) higher in the blood capillaries than in the alveoli. Carbon dioxide then diffuses across the capillary walls and the alveolar epithelium into the (5) 2 alveoli . Carbon dioxide is exhaled out of the lungs. Note: Not all of the oxygen in the alveoli diffuses into the blood capillaries. 48 Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Class: Name: ( ) Date: The adaptations of the alveoli (Book 2, p.132) 1 The surface area of the alveoli is (1) large . There are about 700 millions of alveoli in the lungs, giving a total surface area of over 70 m2. 2 The alveoli are richly supplied with (2) and the blood capillaries is also (3) blood small . The distance between the alveoli . Therefore, a (4) steep concentration gradient is maintained to allow rapid diffusion of gases. alveolus network of blood capillaries Lung model 3 The layer of (5) epithelium of the alveoli is very thin. It is only one-cell thick. 4 The inner surface of the alveoli is kept (6) moist . This allows the gases to dissolve in the moisture before diffusing across the alveoli membranes. Go To … Practical 13.3 Examination of the mammalian air sacs (Student’s Book 2 p.132; Activity Book 2 p.91) Transport of respiratory gases (Book 2, p.133) 1 Transport of oxygen (Book 2, p.133) Red blood cells in the blood are specially adapted for carrying oxygen. Their (7) biconcave (雙凹) whole shape provides a large surface area for oxygen to diffuse in and out more efficiently. Their (8) disc shape shortens the distance so that oxygen reaches the inside of the red blood cells and combines with haemoglobin section (血紅蛋白) more quickly. The (9) haemoglobin molecules in the cytoplasm of the red blood cells are oxygen carriers. 98% of oxygen transported in blood is carried by haemoglobin. Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Red blood cell 49 Class: a Name: ( ) Date: In the alveoli (Book 2, p.133) In the alveoli, the oxygen concentration is (1) high due to breathing in fresh air. Oxygen dissolves and diffuses into red blood cells and combines with haemoglobin to form (2) oxyhaemoglobin (氧合血紅蛋白), which is then carried in the blood to the body cells. in alveoli (high oxygen concentration) haemoglobin + oxygen b oxyhaemoglobin In the body cells (Book 2, p.133) In the body cells, the oxygen concentration is (3) oxyhaemoglobin breaks down into (4) low owing to respiration. The haemoglobin and (5) oxygen . The oxygen then diffuses into the body cells. in body cells (low oxygen concentration) oxyhaemoglobin haemoglobin + oxygen How oxygen is transported in the blood 50 Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Class: Name: ( 2 Transport of carbon dioxide (Book 2, p.135) a In the body cells (Book 2, p.135) ) Date: Carbon dioxide produced in respiration by body cells reacts with water inside red blood cells to form (1) hydrogencarbonate cells and are carried in the (2) ions plasma . These ions diffuse out of the red blood to the alveoli. in body cells (high CO2 concentration) H+ + HCO3 CO2 + H2O b In the alveoli (Book 2, p.135) When blood reaches the alveoli, the hydrogencarbonate ions break down to (3) dioxide and (4) water carbon again. Carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli and is exhaled. in alveoli (low CO2 concentration) H+ + HCO3 CO2 + H2O How carbon dioxide is transported in the blood Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 51 Class: Name: ( ) Date: Go To … Practical 13.4 Study of the effects of oxygen and carbon dioxide on citrated chicken blood (Student’s Book 2 p.136; Activity Book 2 p.92) Section concept diagram (Student’s Book 2 p.137) Quick check (Student’s Book 2 p.137) 13.3 How does breathing take place? (Book 2, p.138) (1) Ventilation (換氣) is the movement of air over the respiratory surface to facilitate gas exchange across the surface. It is brought about by the breathing action in humans, which includes (2) inhalation (吸氣) and (3) exhalation (呼氣). Breathing is brought about by the movements of the ribs and the diaphragm. Their movements can be shown by the (4) (5) bell-jar rib-cage model and the model respectively. 1 Inhalation (Book 2, p.138) air 5 1a 1b 3a 3b 1a External intercostal muscles (6) contract 1b Ribs move upwards and (7) 2a Diaphragm muscles contract. 2b Diaphragm (8) 3a Volume of the thoracic cavity (9) 3b Pressure of the thoracic cavity (10) 4a Lungs expand. 4b Air pressure in the lungs is (11) outwards flattens . . . increases . 4a 4b 2a decreases lower than the atmospheric pressure. 2b 5 Air rushes into the lungs. The movements of the ribs and the diaphragm during inhalation 52 Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 . Class: Name: ( ) Date: 2 Exhalation (Book 2, p.138) air 5 1a 1b 1a External intercostal muscles (1) relax . 1b Ribs move downwards and (2) inwards 2a Diaphragm muscles relax. 2b Diaphragm returns to (3) 3a Volume of the thoracic cavity returns to original . 3a dome shape. 3b 4a volume. 4b 2a 2b 3b Pressure of the thoracic cavity (4) 4a Lungs contract. 4b Air pressure in the lungs is (5) increases . higher than the atmospheric pressure. 5 Air is forced out of the lungs. The movements of the ribs and the diaphragm during exhalation Exhalation is also contributed by the (6) recoiling (反彈) of the elastic lung tissue. Differences in composition between inhaled and exhaled air (Book 2, p.140) (7) Exhaled air can be collected by using the following set-up: exhaled air blow slowly into gas jar rubber tubing water water trough Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 53 Class: Name: ( Exhaled air contains (1) less ) Date: oxygen because some oxygen in the inhaled air has dissolved and has diffused from the alveoli into the blood. In contrast, (2) more carbon dioxide is present in exhaled air than in inhaled air, as carbon dioxide produced in respiration has diffused from the blood into the alveoli. Exhaled air is saturated with (3) water and warmer. Inhaled air (%) Exhaled air (%) 21 16 0.03 4 78 78 Variable Saturated 1 1 Oxygen Carbon dioxide Nitrogen Water vapour vapour Other gases Go To … Practical 13.5 Investigation of the differences in composition between inhaled and exhaled air (Student’s Book 2 p.140; Activity Book 2 p.94) Section concept diagram (Student’s Book 2 p.142) Quick check (Student’s Book 2 p.142) E 13.4 What is the relation of exercise to energy requirement, rates of respiration and ventilation? (Book 2, p.143) The (4) rate of breathing (呼吸率) is the number of breaths per minute. It measures how fast we breathe. The (5) depth of breathing (呼吸深度) is the volume of air breathed in after an exhalation. It can be measured by a data logger, a spirometer (肺量計) and a breath volume kit. Breath volume kit 54 Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Class: Name: Exercise (1) ( increases ) Date: both the rate and the depth of breathing. Exercise ↓ Energy requirement of muscle cells increases ↓ Rate of respiration in muscle cells increases ↓ Rate of ventilation increases (to supply more oxygen to and remove carbon dioxide from muscle cells) ↓ Both rate of breathing and depth of breathing increase Graphs showing the rate and depth of breathing (a) at rest and (b) during exercise Since an extra amount of oxygen is required to oxidize the (2) lactic acid produced during anaerobic respiration of muscles, it takes some time for the rate and the depth of breathing to return to normal after exercise. Go To … Practical 13.6 Study of the effect of exercise on breathing using a breath volume kit (Student’s Book 2 p.143; Activity Book 2 p.97) Practical 13.7 Study of the effect of exercise on breathing using a data logger (Student’s Book 2 p.144; Activity Book 2 p.99) Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 55 Class: Name: ( ) Date: 13.5 What are the health hazards caused by smoking? (Book 2, p.146) (1) Tars (焦油) cause extra mucus secretion in the respiratory tract and prevent the cilia from removing dust particles in the respiratory tract. The smoke irritates (刺激) the (2) bronchi and causes them to contract. This makes breathing more difficult and reduces the amounts of gases for exchange. (3) Nicotine (尼古丁) in cigarette is an addictive drug which increases the heart rate and the blood pressure. Smoking increases the natural (4) abortion rate (流產率) in pregnant women. The physical and mental development of babies born to women who smoke during pregnancy is affected. Smoking may lead to many diseases, e.g. lung cancer, (5) emphysema (肺氣腫) and coronary heart disease (冠心病). Go To … STS connection 13.1 Relationship between smoking and the incidence of emphysema and lung cancer (Student’s Book 2 p.146; Activity Book 2 p.102) Review (Student’s Book 2 p.147) Summary concept diagram (Student’s Book 2 p.148) 56 Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 Class: Name: ( ) Date: Practice question The diagram below shows an alveolus and its associated blood capillary of a heavy smoker. X a According to the diagram, state two adaptations of the alveoli for gas exchange. (2 marks) Alveoli have a large surface area to volume ratio. / The thin epithelium provides a short distance for rapid diffusion of gases. / Blood capillaries are in close contact with the alveoli. (1m x 2) b Name the gas that moves from the alveolar air to the blood. Explain how this happens. (4 marks) Oxygen (1m).The oxygen concentration is higher in the alveoli than in the blood capillaries (1m). Oxygen then dissolves in the film of moisture lining the alveolis (1m) and diffuses from the alveoli into the blood capillaries (1m). c Substance X deposited on the inner surface of the alveolus comes from cigarette smoke. What is substance X? (1 mark) Tar (1m). d According to the diagram, explain how gas exchange is affected by substance X. (2 marks) Substance X deposits on the inner surface of the alveolus reduces the surface area for gas exchange (1m) and makes the diffusion of gases more difficult (1m). Total: 9 marks - END - Certificate Biology - New Mastering Basic Concepts Oxford University Press 2005 57