Life Science
... Chapter 1 – Structure of Living Things •Lesson 1 – Cells •Lesson 2 – From Cells to Organisms •Lesson 3 – Diversity of Organisms ...
... Chapter 1 – Structure of Living Things •Lesson 1 – Cells •Lesson 2 – From Cells to Organisms •Lesson 3 – Diversity of Organisms ...
cnidarians ppnt 2011
... b. Dioecious- sperm & egg are produced in separate sexes. EX: jellyfish ...
... b. Dioecious- sperm & egg are produced in separate sexes. EX: jellyfish ...
Evolution of bilateral symmetry
... • All pseudocoelomates lack a defined circulatory system, but most have a oneway digestive tract (meaning mouth and anus now) • In all pseudocoelomates, the pseudocoel serves as a hydrostatic skeleton ...
... • All pseudocoelomates lack a defined circulatory system, but most have a oneway digestive tract (meaning mouth and anus now) • In all pseudocoelomates, the pseudocoel serves as a hydrostatic skeleton ...
Chapter 4: Tissue Level of Organization
... Tissues: collections of specialized cells and cell products that perform a limited number of functions. Histology: the study of tissues Interstitial Fluid: the fluid found between cells, within a tissue, or between tissues ...
... Tissues: collections of specialized cells and cell products that perform a limited number of functions. Histology: the study of tissues Interstitial Fluid: the fluid found between cells, within a tissue, or between tissues ...
Hematology PowerPoint
... squeeze through the intercellular spaces of capillary walls to fight infection in neighboring tissues. This process is called? ...
... squeeze through the intercellular spaces of capillary walls to fight infection in neighboring tissues. This process is called? ...
File
... Cardiovascular system: consists of heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, blood; carries nutrients, energy, oxygen to cells in body o Arteries: thick and muscular, carry blood AWAY from heart o Veins: thinner than arteries, carry blood TO the heart o Capillaries: tiniest, connect larger arteries and v ...
... Cardiovascular system: consists of heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, blood; carries nutrients, energy, oxygen to cells in body o Arteries: thick and muscular, carry blood AWAY from heart o Veins: thinner than arteries, carry blood TO the heart o Capillaries: tiniest, connect larger arteries and v ...
external/ internal intercostals and the diaghragm
... blood. Oxygen leaves the alveoli lung membrane diffuse into the capillary and attach to the hemoglobin as oxyhemoglobin. While carbon dioxide leaves the capillary and enters the alveoli. Interrnal Respiration Process: Oxygen leaves the arterial blood capillary and enters the body cell and the carbon ...
... blood. Oxygen leaves the alveoli lung membrane diffuse into the capillary and attach to the hemoglobin as oxyhemoglobin. While carbon dioxide leaves the capillary and enters the alveoli. Interrnal Respiration Process: Oxygen leaves the arterial blood capillary and enters the body cell and the carbon ...
human body - Westminster College
... tissues. Students know the sequential steps of digestion and the roles of teeth and the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and colon in the function of the digestive system. Students know the role of the kidney in removing cellular wastes from blood and converting it to uri ...
... tissues. Students know the sequential steps of digestion and the roles of teeth and the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and colon in the function of the digestive system. Students know the role of the kidney in removing cellular wastes from blood and converting it to uri ...
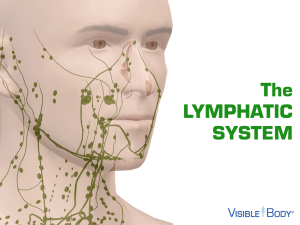
The LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
... which are located in the back of your throat, are commonly known as just “tonsils.” ...
... which are located in the back of your throat, are commonly known as just “tonsils.” ...
Fall Semester Review Pre-AP Science 7
... 40. Briefly describe the five functions of the skeletal system. a. Support and Shape b. Protects Organs c. Produces red and white blood cells d. Movement e. Stores minerals (calcium and phosphorus) 41. How is the structure of the rib bones related to their function? Bones are flat to provide protect ...
... 40. Briefly describe the five functions of the skeletal system. a. Support and Shape b. Protects Organs c. Produces red and white blood cells d. Movement e. Stores minerals (calcium and phosphorus) 41. How is the structure of the rib bones related to their function? Bones are flat to provide protect ...
review for the biology regents exam
... TISSUES – groups of cells that are specialized to do certain jobs (including muscle and nerve tissue) • Specialization or differentiation is the process that changes a stem cell into a specialized cell • Stem cells are cells that have not yet been specialized • Almost all cells have a complete set o ...
... TISSUES – groups of cells that are specialized to do certain jobs (including muscle and nerve tissue) • Specialization or differentiation is the process that changes a stem cell into a specialized cell • Stem cells are cells that have not yet been specialized • Almost all cells have a complete set o ...
Porifera and Cnidaria
... water into pores and out the opening on top of sponge- collects food Choanocytes in the interior layer draw water through the ostia that penetrate the body wall. The water leaves through the osculum. ...
... water into pores and out the opening on top of sponge- collects food Choanocytes in the interior layer draw water through the ostia that penetrate the body wall. The water leaves through the osculum. ...
Groups of Living Things Ppt
... mammary glands to produce milk for young, and have hair. ▪ Examples include ▪ Monotremes such as a platypus and echidna ▪ Marsupials such as kangaroos, koalas, and opossums. ▪ Placental such as humans, bears, and dogs. ▪ Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that lack a cell wall and chloroplasts. ...
... mammary glands to produce milk for young, and have hair. ▪ Examples include ▪ Monotremes such as a platypus and echidna ▪ Marsupials such as kangaroos, koalas, and opossums. ▪ Placental such as humans, bears, and dogs. ▪ Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that lack a cell wall and chloroplasts. ...
Animal_evolutionary_..
... These animals lack an enclosed body cavity; the only "body cavity" is the lumen of the digestive tube. The space between the gut and the body wall is filled with a more or less solid mass of mesodermal tissue. The major example of this is the phylum Platyhelminthes, the flatworms. Minor examples: Ph ...
... These animals lack an enclosed body cavity; the only "body cavity" is the lumen of the digestive tube. The space between the gut and the body wall is filled with a more or less solid mass of mesodermal tissue. The major example of this is the phylum Platyhelminthes, the flatworms. Minor examples: Ph ...
File
... 13. What structures are inside the small intestine that enables the small intestine to absorb nutrients? Villi 14. What happens in the large intestine? Water is absorbed and any undigested material is compacted into a solid waste so that it can be eliminated from the body. 15. What is the main purpo ...
... 13. What structures are inside the small intestine that enables the small intestine to absorb nutrients? Villi 14. What happens in the large intestine? Water is absorbed and any undigested material is compacted into a solid waste so that it can be eliminated from the body. 15. What is the main purpo ...
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia
... groups of coelomates achieve this adult anatomy in entirely different ways. Other ontogenetic features also suggest that although the protostomes and deuterostomes share a common ancestor, they are distinct and monophyletic unto themselves. Consider the following and discuss. 1. What phylum might yo ...
... groups of coelomates achieve this adult anatomy in entirely different ways. Other ontogenetic features also suggest that although the protostomes and deuterostomes share a common ancestor, they are distinct and monophyletic unto themselves. Consider the following and discuss. 1. What phylum might yo ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... of the blood vessels and leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues. These symptoms can be treated with antihistamines or antiprostaglandins. Increased blood flow delivers monocytes and neutrophils to a site of infection. As they arrive, these leukocytes roll along the inside walls of blood vessels u ...
... of the blood vessels and leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues. These symptoms can be treated with antihistamines or antiprostaglandins. Increased blood flow delivers monocytes and neutrophils to a site of infection. As they arrive, these leukocytes roll along the inside walls of blood vessels u ...
Nervous System: concussion: a temporary disturbance of the brain`s
... and carry impulses toward the cell body. axon: the one threadlike extension called an axon that carries impulses away from the cell body. An axon branches at its ends. cell body: the cell body consists of a nucleus – the control center of the cell – in a sack of fluid contained within an outer skin ...
... and carry impulses toward the cell body. axon: the one threadlike extension called an axon that carries impulses away from the cell body. An axon branches at its ends. cell body: the cell body consists of a nucleus – the control center of the cell – in a sack of fluid contained within an outer skin ...
EOC Review 2015 answer key A
... 11) List the 5 levels of organization in order. Cells – tissue – organs- organ system - organism 12) List and give an example of the four types of body tissues. Muscular: heart, skeletal muscles, smooth muscle lines digestive tract Epithelial: skin, lines organs Nervous: brain, spinal cord and perip ...
... 11) List the 5 levels of organization in order. Cells – tissue – organs- organ system - organism 12) List and give an example of the four types of body tissues. Muscular: heart, skeletal muscles, smooth muscle lines digestive tract Epithelial: skin, lines organs Nervous: brain, spinal cord and perip ...
Cells - P5 GE Science 2011
... Producing new cells • Our bodies increase in size as we grow. • This is due to an increase in the number of cells in the body. • Cells increase in number by dividing themselves. • The nucleus and cytoplasm of one cell divide to produce two cells. • The two new cells later divide into four cells. • ...
... Producing new cells • Our bodies increase in size as we grow. • This is due to an increase in the number of cells in the body. • Cells increase in number by dividing themselves. • The nucleus and cytoplasm of one cell divide to produce two cells. • The two new cells later divide into four cells. • ...
Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -proteins made by ribosomes are modified here proteins go from primary to secondary or tertiary levels -enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to protein ex: glucose attached to proteins they become part of external structure helps plants and fungi build cell walls and animal cells build prot ...
... -proteins made by ribosomes are modified here proteins go from primary to secondary or tertiary levels -enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to protein ex: glucose attached to proteins they become part of external structure helps plants and fungi build cell walls and animal cells build prot ...
1 Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -proteins made by ribosomes are modified here proteins go from primary to secondary or tertiary levels -enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to protein ex: glucose attached to proteins they become part of external structure helps plants and fungi build cell walls and animal cells build prot ...
... -proteins made by ribosomes are modified here proteins go from primary to secondary or tertiary levels -enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to protein ex: glucose attached to proteins they become part of external structure helps plants and fungi build cell walls and animal cells build prot ...
Connective Tissue - White Plains Public Schools
... If large amounts are present the tissue can appear yellow. Elastin tends to deplete as people age, resulting in wrinkled or stretched out skin. One might note the “pregnancy pouch” many women have many years after having a baby. In part, the leftover skin is a result of inadequate elastin, and also ...
... If large amounts are present the tissue can appear yellow. Elastin tends to deplete as people age, resulting in wrinkled or stretched out skin. One might note the “pregnancy pouch” many women have many years after having a baby. In part, the leftover skin is a result of inadequate elastin, and also ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.