8th Grade Science Essential Vocabulary
... The act of breathing; The physical and chemical process by which an organism supplies its cells and tissues with oxygen needed for metabolism and to produce ...
... The act of breathing; The physical and chemical process by which an organism supplies its cells and tissues with oxygen needed for metabolism and to produce ...
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
... 2. Differentiate into specialised cells when required There are two types of stem cells, embryonic and tissue or adult stem cells Embryonic stem cells The blastocyst consists of a ball of embryonic stem cells All of the genes in an embryonic stem cell have the potential to be switched on The cell is ...
... 2. Differentiate into specialised cells when required There are two types of stem cells, embryonic and tissue or adult stem cells Embryonic stem cells The blastocyst consists of a ball of embryonic stem cells All of the genes in an embryonic stem cell have the potential to be switched on The cell is ...
Respiration in Organisms
... 20. Do the plants also respire? Yes, plants also respire like other organisms. They also take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. In the plant cells also oxygen is used to breakdown glucose into carbon dioxide and water with the release of energy. 21. How does a cockroach breathe? A ...
... 20. Do the plants also respire? Yes, plants also respire like other organisms. They also take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. In the plant cells also oxygen is used to breakdown glucose into carbon dioxide and water with the release of energy. 21. How does a cockroach breathe? A ...
THE NEURAL TUBE AND ITS SUBDIVISIONS
... middorsal region in front of the primitive node. Its lateral edges soon elevate to form the neural folds • With further development, the neural folds continue to elevate, approach each other in the midline, and finally fuse, forming the neural tube • The notochord (a midline rod of cells) stimulates ...
... middorsal region in front of the primitive node. Its lateral edges soon elevate to form the neural folds • With further development, the neural folds continue to elevate, approach each other in the midline, and finally fuse, forming the neural tube • The notochord (a midline rod of cells) stimulates ...
“White” Fibrous Tissue
... Moving body parts, such as the muscles of arms, legs Moving substances throughout the body, such as the muscles that make up the blood vessels Muscle Tissue Types: Striated (Skeletal) Muscle Visceral (Smooth) Muscle Cardiac Muscle ...
... Moving body parts, such as the muscles of arms, legs Moving substances throughout the body, such as the muscles that make up the blood vessels Muscle Tissue Types: Striated (Skeletal) Muscle Visceral (Smooth) Muscle Cardiac Muscle ...
biology - OoCities
... The release of thyroxine increases the metabolic rate of the body and in turn releases more heat. For example, when the weather is hot, less thyroxine is released and less heat is produced. The hypothalamus also plays a role in transmitting nerve messages to muscles, blood capillaries and sweat gla ...
... The release of thyroxine increases the metabolic rate of the body and in turn releases more heat. For example, when the weather is hot, less thyroxine is released and less heat is produced. The hypothalamus also plays a role in transmitting nerve messages to muscles, blood capillaries and sweat gla ...
cell wall - SCHOOLinSITES
... • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membranebound organelles. Most eukaryotic cells are microscopic, but are about 10 times larger than bacterial cells. • All living things that are not bacteria or archaea are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are calle ...
... • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membranebound organelles. Most eukaryotic cells are microscopic, but are about 10 times larger than bacterial cells. • All living things that are not bacteria or archaea are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are calle ...
C. Organ Level
... Connective tissue in contrast to epithelium consists of a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix; binds and supports other tissues There are 6 major types of connective tissues that shown illustrated in Diagram 3 A. Loose connective tissue – the most common connective ...
... Connective tissue in contrast to epithelium consists of a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix; binds and supports other tissues There are 6 major types of connective tissues that shown illustrated in Diagram 3 A. Loose connective tissue – the most common connective ...
File
... Capillaries leak because there are small gaps between the cells in the walls. Plasma and White Blood Cells can therefore leak out from the blood. Red blood cells can’t leak out because they are too large and have a fixed biconcave shape (not able to squeeze through small spaces). So plasma and white ...
... Capillaries leak because there are small gaps between the cells in the walls. Plasma and White Blood Cells can therefore leak out from the blood. Red blood cells can’t leak out because they are too large and have a fixed biconcave shape (not able to squeeze through small spaces). So plasma and white ...
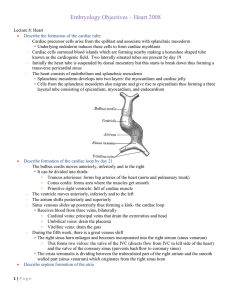
Embryology_Objectives heart 2008
... Initially the AV canal gives access only to the primitive left ventricle and is separated from bulbus cordis by bulbo ventricular flange which terminates midway The AV canal then enlarges to the right and blood passing through the AV orifice now has direct access to the left and right ventricles ...
... Initially the AV canal gives access only to the primitive left ventricle and is separated from bulbus cordis by bulbo ventricular flange which terminates midway The AV canal then enlarges to the right and blood passing through the AV orifice now has direct access to the left and right ventricles ...
body - SchoolNotes
... lymphocytes White blood cells of the immune system that recognize specific ...
... lymphocytes White blood cells of the immune system that recognize specific ...
Differential WBC count lab
... elements and a clear straw-colored portion called plasma. The formed element content of blood is around 47% in men and 42% in women. During this lab exercise, you will study the leukocytic portion of the formed elements in blood. This study will involve prepared blood slides. The formed elements of ...
... elements and a clear straw-colored portion called plasma. The formed element content of blood is around 47% in men and 42% in women. During this lab exercise, you will study the leukocytic portion of the formed elements in blood. This study will involve prepared blood slides. The formed elements of ...
3/3/2015 An Overview of Animal Diversity 1. General Features of Animals Chapter 32:
... Animal Reproduction & Development Most animals reproduce sexually with the diploid phase of the life cycle being dominant. Following fertilization, early animal development unfolds in the characteristic stages shown here. CLEAVAGE – rapid cell division without cell growth GASTRULATION – reorganizati ...
... Animal Reproduction & Development Most animals reproduce sexually with the diploid phase of the life cycle being dominant. Following fertilization, early animal development unfolds in the characteristic stages shown here. CLEAVAGE – rapid cell division without cell growth GASTRULATION – reorganizati ...
F212 2.6 Cell Division and Diversity
... Epithelial cells: Cells that constitute linings of surfaces and cavities Stem cell: Unspecialised cell able to express all of its genes and divide by mitosis The need for cell differentiation and specialisation Small organisms need a large surface area: volume ratio Obtain nutrients and gases th ...
... Epithelial cells: Cells that constitute linings of surfaces and cavities Stem cell: Unspecialised cell able to express all of its genes and divide by mitosis The need for cell differentiation and specialisation Small organisms need a large surface area: volume ratio Obtain nutrients and gases th ...
The Animal Kingdom and Sponges Laboratory
... By definition, most animals have a body composed of tissues. However, the sponges (Phylum Porifera) are an exception as they lack such tissues and are known as parazoans. Animals classified as eumetazoans develop from an embryo that develops through a process known as gastrulation. During gastrulati ...
... By definition, most animals have a body composed of tissues. However, the sponges (Phylum Porifera) are an exception as they lack such tissues and are known as parazoans. Animals classified as eumetazoans develop from an embryo that develops through a process known as gastrulation. During gastrulati ...
summary sheets - Kinross High School
... 23. Xylem vessels also transport minerals (such as nitrates and phosphates) dissolved in the water they carry. Xylem cells are surrounded by bands of lignin which strengthens the cell wall and allows it to withstand the pressure changes as water moves through the plant. 24. Sugar is transported up ...
... 23. Xylem vessels also transport minerals (such as nitrates and phosphates) dissolved in the water they carry. Xylem cells are surrounded by bands of lignin which strengthens the cell wall and allows it to withstand the pressure changes as water moves through the plant. 24. Sugar is transported up ...
chapter32
... 5. Most can respond adaptively to external stimuli and have well-developed sense organs and nervous system. They have muscular and nervous tissues. 6. Most reproduce sexually, with large non-motile eggs and small flagellated sperms. 7. The diploid zygote produced by fertilization divides by mitotic ...
... 5. Most can respond adaptively to external stimuli and have well-developed sense organs and nervous system. They have muscular and nervous tissues. 6. Most reproduce sexually, with large non-motile eggs and small flagellated sperms. 7. The diploid zygote produced by fertilization divides by mitotic ...
Phylum Cnidaria - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... • At one or both ends of the mouth is a ciliated groove called the siphonoglyph; generates a water current and brings food to the gastrovascular cavity ...
... • At one or both ends of the mouth is a ciliated groove called the siphonoglyph; generates a water current and brings food to the gastrovascular cavity ...
Animals Made of Stem Cells - New England Complex Systems Institute
... Somatic cells are created from stem cells by inducing near-permanent changes in gene expression. Formerly-random epigenetic mechanisms could have been adapted to make such changes in response to intense but transient chemical signals. In effect, this implies that Precambrian animals were built entir ...
... Somatic cells are created from stem cells by inducing near-permanent changes in gene expression. Formerly-random epigenetic mechanisms could have been adapted to make such changes in response to intense but transient chemical signals. In effect, this implies that Precambrian animals were built entir ...
Cells
... example, your heart is an organ. It is made mostly of cardiac muscle tissue. But your heart also has nerve tissue and tissues of the blood vessels that all work together to make your heart the powerful pump that it is. ...
... example, your heart is an organ. It is made mostly of cardiac muscle tissue. But your heart also has nerve tissue and tissues of the blood vessels that all work together to make your heart the powerful pump that it is. ...
Anatomy1 Review Questions
... 9.. The spleen is located in the right upper abdominopelvic quardrant. 10. Organ systems can be composed of cells or tissues, but not both. 11. The anatomical position is used as a standard reference point for directional terms regardless of the actual position of the body. 12. The thumb is lateral ...
... 9.. The spleen is located in the right upper abdominopelvic quardrant. 10. Organ systems can be composed of cells or tissues, but not both. 11. The anatomical position is used as a standard reference point for directional terms regardless of the actual position of the body. 12. The thumb is lateral ...
E1. - De Anza
... The lining of the small intestine, a digestive organ, is elaborated with fingerlike projections that expand the surface area for nutrient absorption (cross-section, SEM). ...
... The lining of the small intestine, a digestive organ, is elaborated with fingerlike projections that expand the surface area for nutrient absorption (cross-section, SEM). ...
Importance of Cell Division
... Genetically identical means that every cell that is produced has identical copies of a single, identical set of chromosomes. When cells in an organism undergo division, they all produce daughter cells, (two new cells), with exactly the same DNA. In asexual reproduction, the offspring simply goes thr ...
... Genetically identical means that every cell that is produced has identical copies of a single, identical set of chromosomes. When cells in an organism undergo division, they all produce daughter cells, (two new cells), with exactly the same DNA. In asexual reproduction, the offspring simply goes thr ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.