* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy1 Review Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
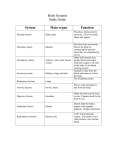
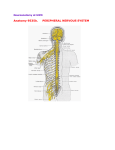
Anatomy1 Review Questions (part II) Mo Elkerdany, DDS, PhD True-False questions: Mark “A” for true statements and “B” for false statements. 1. Gross anatomy is the study of body structures visible to the eye. 2. Embryology is the study of the changes in embryos and fetuses from conception to birth. 3. Developmental anatomy is the study of the changes in an individual from birth through old age. 4. Serous membranes secrete a watery lubricating fluid. 5. Visceral pericardium covers the surface of the heart, while parietal pericardium lines the walls of the heart. 6. Serous membranes are very thin, double- layered structures. 7. Serous membranes are divided into parietal and visceral membranes with a potential space between the two. 8. The reproductive system works independently of all other systems. 9.. The spleen is located in the right upper abdominopelvic quardrant. 10. Organ systems can be composed of cells or tissues, but not both. 11. The anatomical position is used as a standard reference point for directional terms regardless of the actual position of the body. 12. The thumb is lateral to the body. 13. A parasagittal plane is any sagittal plane except the median. 14. The parietal pleura would represent a serous membrane covering the lungs. 15. The dorsal cavity contains the pleural and pericardial cavities. Page 2 16. A vertical section through the body, dividing it into left and right, is called sagittal. 17. Macrophages are present in loose connective tissue, and they develop form white blood cells called neutrophils. MATCHING QUESTION: 18. Plays a role in the synthesis of steroidbased hormones and proteins. 19. The actual site of protein synthesis. A. RIBOSOMES 20. Hollow cytoskeletal elements that act as organizers for the cytoskeleton. B. MICROTUBULES C. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM 21. Dense spherical bodies in the nucleus that are the synthesis site for ribosomal RNA. 22. Houses DNA and RNA. D. NUCLEOLI E. NUCLEUS 23. Are remarkably dynamic organelles, constantly growing out from the centromere, disassembling, and then reassembling. 24. Are small, dark-staining granules composed of proteins and a variety of RNA. 25. It is an extensive system of interconnected tubes and parallel membranes enclosing fluid-filled cavities, or cisternae. 26. Some of these organelles float freely in the cytoplasm, while others are attached to membranes. 27. It dictates the kinds and the amounts of proteins to be synthesized at any one time in response to signals acting on the cell. True-False questions: Mark “A” for true statements, and “B” for false statements. 28. The maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) exists the skull through foramen ovale. Page 3 29. Cranial nerves III, IV, and VI are motor nerves to the muscles of the eyeball, and they exit the skull through the optic foramen of the sphenoid bone. 30. Monosynaptic reflex employs two neurons and one synapse. 31. The clavicle develops by endochondral ossification. 32. Simple squamous epithelium is best suited for exchange of substances and is found in capillaries and lung alveoli 33. Muscles of mastication are supplied by the mandibular nerve. 34. There are approximately 600 striated muscles in the human body. 35. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves in the human body. 36. Connective tissues are both protective and glandular. 37. Urine passes from the distal tubules of the nephrons into the collecting ducts, each of which receives urine from several nephrons and runs straight through the cortex into the deep medulla. 38. The urethra is a thin-walled tube that drains urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. 39. During “reabsorption”, most of the nutrients, water, and essential ions are reclaimed from the filtrate, and returned to the blood from the proximal convoluted tubules. 40. Parietal cells of the gastric mucosa, produce the stomach’s hydrochloric acid (HCl), while the chief cells secrete pepsinogen. 41. The pharynx connects the nasal cavity and the oral cavity to the larynx and esophagus. 42. The stomach lies in the left hyochondriac, epigastric, and umbilical regions of the abdomen. 43. Most of the blood in the systemic circulation is found in arteries. 44. The renal vein carries filtered blood from the kidney, and opens into the inferior vena cava. 45. What is the origin, insertion, and action of A. Extrinsic muscles of the tongue B. Muscles of the neck C. Muscles of mastication 46. What is the action and motor nerve supply of extrinsic muscles of the eye? Which cranial nerves are sensory to the eye? 47. How the human joints are classified? Give examples for each. 48. How “Synovial Joints” are classified? Give examples for each. 49. Describe the anatomy of the “Nephron”. State the function of each part. Describe the blood supply and the pathway of blood of the kidney.