* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiration in Organisms
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Exercise physiology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
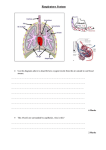
Respiration in Organisms 1. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race? When the athlete runs fast, rate of respiration increases in his body so there is more demand for oxygen in his muscles. So, he breathes faster and deeper so that his blood can carry more oxygen to the muscles. 2. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration- In both types of respiration glucose is broken down to release energy in the cells. Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respirationS.No Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration 1. Glucose is broken down with the use of Glucose is broken down without the use of oxygen. oxygen. 2. Complete breakdown of glucose with the Incomplete breakdown of glucose takes release of CO2, H2O and energy takes place to give CO2, alcohol and energy. place. 3. It takes place in Human beings and Plants. It takes place in Yeast and Human muscle cells during heavy exercise. 3. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air? When we inhale a lot of dust laden air, the dust gets into the nasal cavity and irritates the lining of the cavity. As a result we sneeze so that the dust particles get expelled from the nasal cavity and a dust free, clean air enters our body. 4. Tick the correct answer: a. In cockroaches, air enters the body throughi. Lungs ii. Gills iii. Spiracles iv. Skin b. During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation ofi. Carbon dioxide ii. Lactic acid iii. Alcohol iv. Water c. Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest isi. 9–12 ii. 15–18 iii. 21–24 iv. 30–33 d. During exhalation, the ribsi. Move outwards ii. Move downwards iii. Move upwards iv. Do not move at all 5. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II: Column I Column II a. Yeast i. Earthworm b. Diaphragm ii. Gills c. Skin iii. Alcohol d. Leaves iv. Chest cavity e. Fish v. Stomata f. Frog vi. Lungs and skin vii. Tracheae 6. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false: i. During heavy exercise the breathing rate of a person slows down. ii. Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. False False iii. Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs. iv. The fishes have lungs for respiration. v. The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation. True False True 10. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them becausea. At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air. b. The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground. c. The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground. d. The pressure of air is higher than that on the ground. 11. What is a Cell? A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of living organisms. Our body is made up of thousands of such cells, which perform different functions. Human Cheek Cells 12. What functions do cells perform? Cell of an organism perform different functions such as nutrition, transportation, excretion and reproduction. 13. Why do living organisms respire? Cells of living organisms perform different functions. To perform these functions they need energy. So, all living organisms respire to get energy from the food. 14. What is Cellular Respiration? The process of breakdown of food in the cells with the release of energy is called cellular respiration. 15. Where does Cellular Respiration take place? Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all living organisms. 16. Define the followinga. Inhalation- The taking in of air rich in oxygen into the body is called inhalation. b. Exhalation- The release of air rich in carbon dioxide from the body is called exhalation. c. Breathing Rate- The number of times a person breathes in a minute is termed as the breathing rate. d. Breath- One inhalation followed by one exhalation is called a breath. 16. Distinguish between Respiration and Breathing. S.No Respiration Breathing 1. Breakdown of glucose takes place inside Only inhalation and exhalation of air takes the cells. place. There is no breakdown of glucose. 2. Energy is released in the cells Energy is not released. 3. It takes place inside the cells (Intracellular) It takes place outside the cells. (Extracellular) 17. Why do we get muscular cramps after heavy exercise? During heavy exercise such as fast running, cycling or walking for many hours the demand for energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to the muscles for respiration is limited. So, anaerobic respiration takes place in the muscle cells to fulfill the demand of energy. The partial breakdown of glucose produces lactic acid. The accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps. 18. Name the organs found in our respiratory system. The organs in our respiratory system are- Nose with two nostrils, wind pipe and lungs. 19. Write the respiratory organs of the following animalsa. Human beingsPair of lungs b. CockroachTrachea c. Earth wormMoist Skin d. FrogsLungs and Moist Skin e. FishGills 20. Do the plants also respire? Yes, plants also respire like other organisms. They also take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. In the plant cells also oxygen is used to breakdown glucose into carbon dioxide and water with the release of energy. 21. How does a cockroach breathe? A cockroach has small openings on the sides of its body. These openings are called spiracles. Cockroaches have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles. Tracheae Tracheal System of Cockroach 22. How do an Earthworm and a fish breathe? Earthworm breathes through moist skin in which the exchange of gases takes place by diffusion. Fish use gills for exchange of gases. Fishes take in water that passes through the gills. The blood flowing in the gills releases carbon dioxide into the water and takes dissolved oxygen from water. The water carrying carbon dioxide passes out of the body of the fish. Gill Water taken in through the mouth _____________________________________________________________________________ K. P. Singh, Biology Department, Delhi Public School, Mathura Refinery Nagar, Mathura