* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Exercise physiology wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
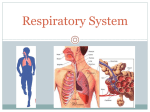
DNA AND CELLS Characteristics: quality of an organism DNA: material in life forms that transfers genetic characteristics Inherited: characteristics from parents Likeness: similarity Organism: individual living system Traits: distinguishing characteristic Cells: the basic unit of life Multicellular: composed of many cells Unicellular: composed of one cell Permeable: able to pass through Tissue: similar cells with a particular function Nucleus: the control center of a cell; where DNA is stored Mitochondria: the “power-house” of the cell; gives the cell energy Cell Wall: found only in plant cells; protects the cell Direct evidence: evidence you find yourself Indirect evidence: evidence that you do not collect yourself, but rely on evidence collected by others -Inherited traits are physical traits that we get from our parents’ DNA (hereditary) -learned traits are things that we have learned from others or from our environment -Only plant cells have cell walls to help the plant grow tall, strong, and rigid. -Cells are the basic unit of life -Multiple cells make up tissues; many tissues make up organs MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Fitness: state of being healthy bones: forms the substance of a skeleton, support the body cartilage: flexible connective tissue cardiac muscle: type of muscle in the heart contract: to draw together involuntary: muscle controlled without thinking about it (pumping heart) ligaments: tissues that connect bones, hold organs in place muscles: tissues that cause motion in the body when contracted musculoskeletal: muscular and skeletal systems skeletal muscle: muscle connected at either end with a bone smooth muscle: found in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, hair follicles tendons: connects muscle to bone -The skeleton has 3 jobs: to support the body, to protect organs, and to help with movement -there are three types of muscle: skeletal muscle (voluntary muscles-have to think about moving them),smooth muscle (involuntary, in our organs), and cardiac muscle (involuntary muscle, found in our hearts) -muscles help with movement by pulling bones, never pushing bones NERVOUS SYSTEM Made up of two systems: o o Central nervous system-made of brain and brain stem; controls all actions of the body Peripheral nervous system- made up of nerves; delivers messages from central nervous system to rest of body Central Nervous system: o Cerebrum-largest part of the brain; controls senses, thoughts, imagination o Cerebellum- “little brain”; controls movement and muscle coordination o Medulla and brain stem: connected to spinal cord; controls heart beat, breathing, digestive system Peripheral nervous system: o Nerve cells are called neurons o Neurons are made up of: Cell body: core Dendrites: carry messages to cell body (“doorway”) Axons: carry messages away from cell body (“exit”) CIRCULATORY AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS Cardiovascular system: consists of heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, blood; carries nutrients, energy, oxygen to cells in body o Arteries: thick and muscular, carry blood AWAY from heart o Veins: thinner than arteries, carry blood TO the heart o Capillaries: tiniest, connect larger arteries and veins; only one-cell wide o Plasma: liquid part of blood, contains blood’s proteins, carries cells o platelets: smallest blood cells to help form clots if you have an injury o Heart: organ that circulates blood; made up of four chambers o Atriums: top chambers of heart; left and right; hold blood coming into the heart and force it in to ventricles o Ventricles: bottom chambers of heart; left and right; thick walls push together to pump blood out of heart and into body o Aorta: moves blood from heart to the body (but not the lungs) o Pulmonary artery: moves blood from our heart to our lungs Red blood cells: carry oxygen to the body White blood cells: fight infections and diseases; very few in our blood; only about 1% Aerobic exercise: exercise where the body requires oxygen Anaerobic exercise: exercise where body does not require oxygen for short bursts of activity (ex. Sprinting) Blood Flow in the Heart: o Blood flows into heart (from all over body) o Enters right atrium. o o o o o o Into right ventricle. Pumped to lungs. Blood gets oxygen from air sacs in lungs, gets rid of carbon dioxide, blood flows from lungs. Goes to left atrium of heart. Flows into left ventricle. Blood pumped out of body through aorta. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM air sac: air-filled spaces in the body alveoli: very small air sacs; where air breathed in goes bronchial tubes: two tubes at the end of the trachea, brings in air from trachea and helps clean lungs; one tube goes to right lung, one to left diaphragm: sheet-like muscle separating the chest from the abdominal cavity; creates suction to draw in air and expand lungs lungs: two respiratory organs nasal passages (nasal cavity): helps with inhaling and exhaling of air through the nose trachea: windpipe; passage from pharynx to lungs pharynx: throat; collects incoming air from the nose and passes air to the trachea How oxygen from the air travels to cells inside your body: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Air enters nasal passages as you breathe in. Air travels through throat to trachea. Trachea divides into two tubes, the bronchial tubes. Bronchial tubes lead to lungs. In lungs, bronchial tubes divide into small branches called bronchioles. Air sacs (alveoli) found at ends of tine branches. In air sacs, oxygen in air passes to blood inside capillaries. Blood carries oxygen to heart, which pumps blood with oxygen throughout body. Diaphragm (thick sheet of muscle located at bottom of chest cavity) moves down during inhaling. Moves up when a person exhales. EXHALING: - Waste product is carbon dioxide, which is made by cells when sugars are turned into energy to keep cells alive. - Too much carbon dioxide = poison. - Blood cells absorb oxygen from air in alveoli (air sacs) and give up carbon dioxide. - Exhaled air has less oxygen and more carbon dioxide. There is still some oxygen in exhaled air, which explains why CPR is possible to help someone else breathe. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Food goes into mouth and is broken down mechanically (chewing) and chemically (saliva). Food is swallowed and moves down esophagus to your stomach Food is broken down even more in the stomach by stomach acids Food mush moves to the small intestine where water and nutrients are absorbed Mush moves to the large intestine where is compacted The compacted mush is now ready to be eliminated as waste