* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
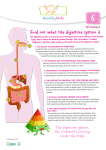
Name:____ANSWER KEY_____________Date:______________________Class:_______ Human Body Systems Unit Test: Study Guide 1. What is homeostasis? Maintaining a stable internal environment. 2. Which body system that sends messages back and forth between the brain and other parts of the body? AND What are the cells of this system called? The Nervous System; Nerve cells=neurons 3. Which organ system makes blood cells? Skeletal System 4. Which specific type of body tissue can contract or shorten? Muscle Tissue 5. What are THREE (3) functions of the skeletal system? Support the body Protect internal organs Produce blood cells (inside of bones, in marrow) 6. How do pairs of muscles work together? Describe. Muscles work in pairs-when one muscle contracts (or tightens) it pulls the bone in one direction, while the other muscle in the pair relaxes. To return the bone to its original position, the second bone contracts, pulling the bone in the opposite directions, and the first one relaxes. 7. How does the skin protect the body from disease? A barrier in the first line of defense that prevents pathogens from entering the body. Also, helps to eliminate wastes that the body is getting rid of and maintain homeostasis. 8. What is the strong connective tissue that holds joints together? ligaments 9. What are the THREE (3) types of muscle tissue? Smooth Cardiac Skeletal 10. Which types of muscle tissue(s) is striated? Cardiac and skeletal 11. What carries needed materials including gases and nutrients around the body? (2) Veins and arteries (blood vessels in the circulatory system) 12. What are THREE (3) functions of the digestive system? Break food down into usable forms Help remove waste products from your body Absorb nutrients from the food you eat 13. What structures are inside the small intestine that enables the small intestine to absorb nutrients? Villi 14. What happens in the large intestine? Water is absorbed and any undigested material is compacted into a solid waste so that it can be eliminated from the body. 15. What is the main purpose of the small intestine? To absorb nutrients from the food particles that have been broken down 16. What is peristalsis? Waves of muscle contractions that push food through the digestive tract 17. In what part of the respiratory system does gas exchange occur? Oxygen enters into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide exits the bloodstream by entering the alveoli, or tiny air sacs on the lungs 18. The respiratory system brings what substance to the body? Oxygen 19. What is the main function of the excretory system? To remove wastes from the body 20. What do kidneys do? (bean-shaped) filter ALL of the body’s blood and remove wastes 21. What is excretion? Getting rid of waste products –the main job of the excretory system 22. When fertilization occurs, what is formed? A zygote 23. Sperm are MADE in the:_testes______which are located in the __scrotum_______? 24. Which cell structure directs the cell’s activities and houses genetic information? The nucleus 25. What specific type of muscle is only found in the heart? Cardiac 26. How does skin help to regulate body temperature? Skin has sweat glands-allows you to sweat when your body is too hot; perspiration (or sweat) then evaporates, which cools your body off. 27. What are THREE (3) functions of the cardiovascular or circulatory system? Transport needed substances (oxygen & nutrients) to all of the cells in the body Transport wastes (such as carbon dioxide) away from the cells Transport cells, substances that fight disease, and messages throughout the body 28. What type of blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart? Arteries 29. What is the main purpose/function of white blood cells? To fight disease-they find and destroy pathogens 30. What is the process of the digestive system? Mouth-mechanical digestion occurs by chewing food and breaking food particles into smaller pieces; chemical digestion starts breaking down food even more because saliva contains digestive enzymes Peristalsis pushes food down the esophagus into the stomach In the stomach, chemical digestion occurs again, as stomach acids & enzymes break food down into a usable for. Mechanical digestion also occurs as the muscles of the stomach contract and churn food into chyme, a milkshake-like substance. Food is then stores here for several hours, until moving to the small intestine. In the small intestine, chemical digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed. Nutrients that the body will use enter into the bloodstream through the villi, in the walls of the small intestine. All water and wastes from any undigested food leaves the small intestine and goes into the large intestine. Here, water is absorbed and undigested materials are compacted into a solid, and is ready to be eliminated from the body. 31. Bile is produced in what organ? Liver 32. What does bile do?? Breaks down fat 33. In what organ is urine stored until the body is ready to release it? Bladder 34. What is the term to describe the chemical process in which oxygen and glucose react to release energy in body cells? Cellular Respiration 35. Why do we go through the process of cellular respiration?? To obtain energy for our cells-so that our cells can carry out all of the processes necessary to live; NOT to get oxygen-oxygen and glucose are REQUIRED “ingredients” that our body has to have in order for cellular respiration to occur (in order for our cells to actually obtain energy) 36. What is the name of the small flap of tissue that seals off the trachea during swallowing? Epiglottis 37. What are the bronchi? (& what do they look like?) Pair of tubes that branch off of the trachea and into the lungs; the tubes keep dividing into smaller and smaller tubes, and resembles the branches of a tree. 38. When the nervous system makes you feel hungry or thirsty, what body process is it “helping” out? Homeostasis 39. What is a change or signal in the environment that makes an organism react? Stimulus 40. What is the thick column of nervous tissue that links the brain to the nerves in the peripheral nervous system called? Spinal column or spinal cord 41. Pain is an important sensation. Why? Pain helps alert your body of danger; when you feel brain, your brain has already received the message and has made your body respond 42. It begins to rain. You close the window. What is your action called? Response 43. Fill in the flow chart: Cells are grouped together to form __tissues___ __organs______ ___organ systems____ __organisms_____. 44. What is the pigment melanin’s function in the skin? Gives the skin its color; helps to protect the skin from burning (sunburn) 45. What does immunity do for the body? Immunity is the body’s ability to recognize and destroy pathogens BEFORE they can cause disease 46. What type of cells are considered “diploid”? What does this mean? Somatic or body cells-“double” the # of chromosomes-46, or 23 pairs in EACH cell 47. What type of cells are considered “haploid”? What does this mean? Gametes or sex cells (eggs and sperm)-“half” the # chromosomes-23 in EACH cell 48. What are the THREE (3) types of blood vessels? Arteries-carry blood AWAY from the heart, to all of the cells in the body Veins-carry blood TOWARDS the heart, from all of the body cells Capillaries-connect artiers and veins (like a “train station”); allow the gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) to occur between veins and arteries 49. During respiration, what is breathed in and what is breathed out? Oxygen is breathed in and carbon dioxide is breathed out 50. In which blood vessels are gases exchanged between blood and body cells? Capillaries 51. A group of similar cells that perform a similar functions is known as what? Tissues 52. Paired up, which TWO (2) body systems fight viral infections like the flu? Immune & circulatory 53. Which is the most complex level of organization in the human body? Organ systems 54. Movement is possible by which TWO (2) body systems working together? Skeletal & muscular 55. Which organs produce eggs in the female reproduction system? Ovaries 56. What are phagocytes and how do they help the body fight disease? A particular type of white blood cell (involved in the inflammatory response); engulfs pathogens and destroys them by breaking them down 57. What are somatic cells? Body cells, all cells EXCEPT for gametes (sex cells) 58. What makes gametes and somatic cells different from each other? Gametes have half the # of chromosomes (23-haploid), while somatic cells (aka body cells) have 46 chromosomes (diploid). Somatic cells reproduce through mitosis, while gametes go through meiosis.