7 grade life science review packet
... 1. The cell theory states that all living things are made up of a. organisms b. cells c. tissues d. proteins 2. When cells similar in structure & function join together, they form a. tissues b. organs c. systems d. organisms 3. A sac in the cytoplasm of a cell that stores water, food, and other mate ...
... 1. The cell theory states that all living things are made up of a. organisms b. cells c. tissues d. proteins 2. When cells similar in structure & function join together, they form a. tissues b. organs c. systems d. organisms 3. A sac in the cytoplasm of a cell that stores water, food, and other mate ...
B8.3 Revision Notes
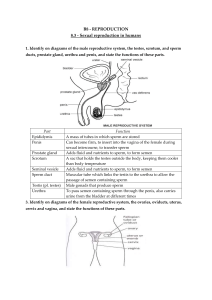
... Directs an ovum (egg) from the ovary into the oviduct Contains follicles in which ova (eggs) are produced Carries an ovum to the uterus, with propulsion provided by tiny cilia in the wall; also the site of fertilization Carries urine from the bladder Where the fetus develops Receives the male penis ...
... Directs an ovum (egg) from the ovary into the oviduct Contains follicles in which ova (eggs) are produced Carries an ovum to the uterus, with propulsion provided by tiny cilia in the wall; also the site of fertilization Carries urine from the bladder Where the fetus develops Receives the male penis ...
File - Hawk Nation Biology
... Fill in the blanks with the correct kingdom. __Archaebacteria______ – extremophiles (live in extreme locations) ___Eubacteria________ – bacteria that live in the same habits as humans ____Protista_________ – eukaryotic organisms that are not plant, animal or fungus ____Fungi___________ – eukaryotic ...
... Fill in the blanks with the correct kingdom. __Archaebacteria______ – extremophiles (live in extreme locations) ___Eubacteria________ – bacteria that live in the same habits as humans ____Protista_________ – eukaryotic organisms that are not plant, animal or fungus ____Fungi___________ – eukaryotic ...
28 - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... • Inner cell mass develops into embryonic disc (subdivides into epiblast and hypoblast) • Three primary germ layers form; extraembryonic ...
... • Inner cell mass develops into embryonic disc (subdivides into epiblast and hypoblast) • Three primary germ layers form; extraembryonic ...
Invertebrates
... No germ layers Germ layers: layers of cells formed in the embryonic stage No specialized organs: group of tissues working together to perform a specific ...
... No germ layers Germ layers: layers of cells formed in the embryonic stage No specialized organs: group of tissues working together to perform a specific ...
Chapter 33 Section 1 Vocabulary
... The body wall of a sponge is composed of two layers of cells that are separated by a jellylike substance called mesohyl. The body is supported by a skeleton made of sponging, spicules, or both. Choanocytes which line the inside of a sponge beat their flagella, thus drawing a current of water int ...
... The body wall of a sponge is composed of two layers of cells that are separated by a jellylike substance called mesohyl. The body is supported by a skeleton made of sponging, spicules, or both. Choanocytes which line the inside of a sponge beat their flagella, thus drawing a current of water int ...
Female - El Camino College
... a. These pills contain a combination of synthetic _________ & progesterone (_________) b. They prevent follicle development and ovulation by feedback inhibition of ____ & ____ c. Women stop taking the pill one week of every 3 weeks so the endometrium can be shed in __________ d. The pill does not pr ...
... a. These pills contain a combination of synthetic _________ & progesterone (_________) b. They prevent follicle development and ovulation by feedback inhibition of ____ & ____ c. Women stop taking the pill one week of every 3 weeks so the endometrium can be shed in __________ d. The pill does not pr ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy
... a. These pills contain a combination of synthetic _________ & progesterone (_________) b. They prevent follicle development and ovulation by feedback inhibition of ____ & ____ c. Women stop taking the pill one week of every 3 weeks so the endometrium can be shed in __________ d. The pill does not pr ...
... a. These pills contain a combination of synthetic _________ & progesterone (_________) b. They prevent follicle development and ovulation by feedback inhibition of ____ & ____ c. Women stop taking the pill one week of every 3 weeks so the endometrium can be shed in __________ d. The pill does not pr ...
Review #9 – Chapters 40 – 51
... a. Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth b. Skeletal, vascular, and smooth c. Skeletal, cardiac, and rough d. Skeletal, cardiac, and striated e. Skeletal, vascular, and smooth ...
... a. Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth b. Skeletal, vascular, and smooth c. Skeletal, cardiac, and rough d. Skeletal, cardiac, and striated e. Skeletal, vascular, and smooth ...
organ
... cell-tissue-organorgan system-organism 38. From least complex to most complex, what is the correct order of the levels of organization of a multicellular organism? – organ ...
... cell-tissue-organorgan system-organism 38. From least complex to most complex, what is the correct order of the levels of organization of a multicellular organism? – organ ...
F15 ap-2a-quiz-1-6 - My Anatomy Mentor
... Which term would be used to describe a membrane lining the surface of the organ within the body cavity found on the lateral sides within the thoracic cavity? Write the complete name for the specific serous membrane that this describes. ...
... Which term would be used to describe a membrane lining the surface of the organ within the body cavity found on the lateral sides within the thoracic cavity? Write the complete name for the specific serous membrane that this describes. ...
Stem Cells and Ethics
... study of all stem cell types, since we're not sure yet which one will be the most useful for cell replacement therapies. An additional ethical consideration is that iPS cells have the potential to develop into a human embryo, in effect producing a clone of the donor. Many nations are already prepare ...
... study of all stem cell types, since we're not sure yet which one will be the most useful for cell replacement therapies. An additional ethical consideration is that iPS cells have the potential to develop into a human embryo, in effect producing a clone of the donor. Many nations are already prepare ...
Levels of Organization
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
7th Spring Final Exam Review 2016
... 65. Your lungs give oxygen to your capillaries through which structures? ...
... 65. Your lungs give oxygen to your capillaries through which structures? ...
Levels of Organization - Darlington Middle School
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
5 Levels of Organization Notes
... Here are the cells we saw before, but if you look closely, you can see that they all look similar. Nerve cells working together make nerve tissue, and skin cells make up a special type of epithelial tissue. ...
... Here are the cells we saw before, but if you look closely, you can see that they all look similar. Nerve cells working together make nerve tissue, and skin cells make up a special type of epithelial tissue. ...
NoB1ch06QUICKcheck-ed
... What is the function of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets? Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to all tissues of the body and also carry some carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs. White blood cells are active in defence against infection through phagocytosis of foreign ...
... What is the function of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets? Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to all tissues of the body and also carry some carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs. White blood cells are active in defence against infection through phagocytosis of foreign ...
7th Grade
... individual, occurring commonly among insects and certain other arthropods. vegetative propagation - Production of a new plant from a portion of another plant, such as a stem or branch. budding - Being in an early developmental stage. ...
... individual, occurring commonly among insects and certain other arthropods. vegetative propagation - Production of a new plant from a portion of another plant, such as a stem or branch. budding - Being in an early developmental stage. ...
Biology Study Guide
... food and water won’t enter it. 17. How does the diaphragm make breathing more efficient? It causes the lungs to expand towards the abdomen, so it makes a bigger surface for oxygen absorption. 18. Define the three main parts of the circulatory system: heart, blood and blood vessels. Heart: the main o ...
... food and water won’t enter it. 17. How does the diaphragm make breathing more efficient? It causes the lungs to expand towards the abdomen, so it makes a bigger surface for oxygen absorption. 18. Define the three main parts of the circulatory system: heart, blood and blood vessels. Heart: the main o ...
Levels of Organization
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
1 - SchoolNotes
... Systemic anatomy is a term that refers to ________________________________ Homeostasis can best be described as ___________________________________ The smallest living units of structure and function in the body are _____________ An organ is one organizational step lower that a ______________ What o ...
... Systemic anatomy is a term that refers to ________________________________ Homeostasis can best be described as ___________________________________ The smallest living units of structure and function in the body are _____________ An organ is one organizational step lower that a ______________ What o ...
What is osmosis?
... Molecules move constantly and randomly. You might smell perfume when you walk past someone who is wearing it. The perfume molecules move freely throughout the air. This random movement of molecules from an area where there are more of them into an area where there are fewer of them is called diffusi ...
... Molecules move constantly and randomly. You might smell perfume when you walk past someone who is wearing it. The perfume molecules move freely throughout the air. This random movement of molecules from an area where there are more of them into an area where there are fewer of them is called diffusi ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.