* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
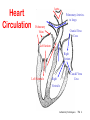
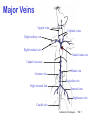
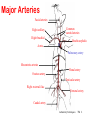
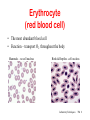
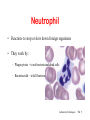
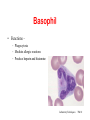
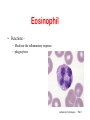
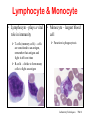
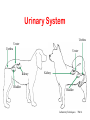
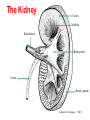
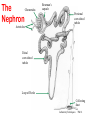
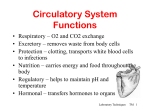
Circulatory System Functions Laboratory Techniques TM 1 Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resource Standards Addressed • AS.07.01. Design programs to prevent animal diseases, parasites and other disorders and ensure animal welfare. – AS.07.01.02.a. Explain methods of determining animal health and disorders. Laboratory Techniques TM 2 Circulatory System Functions • Respiratory – O2 and CO2 exchange • Excretory – removes waste from body cells • Protection – clotting, transports white blood cells to infections • Nutrition – carries energy and food throughout the body • Regulatory – helps to maintain pH and temperature • Hormonal – transfers hormones to organs Laboratory Techniques TM 3 Heart Circulation Aorta Pulmonary Arteriesto lungs Pulmonary Veins Cranial Vena Cava Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle Caudal Vena Cava Right Ventricle Laboratory Techniques TM 4 Major Veins Jugular veins Cephalic veins Right axillary vein Right brachial vein Cranial vena cava Caudal vena cava Ovarian vein Renal vein Testicular vein Right external iliac Femoral vein Saphenous vein Caudal vein Laboratory Techniques TM 5 Major Arteries Facial arteries Right axillary Right brachial Common carotid arteries Brachiocephalic Aorta Pulmonary artery Mesenteric arteries Renal artery Ovarian artery Testicular artery Right external iliac Femoral artery Caudal artery Laboratory Techniques TM 6 Structure of Blood Blood is composed of : 40% cells and %60 plasma The cells that in the blood are: Erythrocytes (red blood cells) Leukocytes (white blood cells) Platelets Laboratory Techniques TM 7 Erythrocyte (red blood cell) • The most abundant blood cell • Function – transport O2 throughout the body Mammals – no cell nucleus Birds & Reptiles –cell nucleus Laboratory Techniques TM 8 Neutrophil • Function- to stop or slow down foreign organisms • They work by: – Phagocytosis – to eat bacteria and dead cells – Bacteriocidal – to kill bacteria Laboratory Techniques TM 9 Basophil • Functions – – Phagocytosis – Mediate allergic reactions – Produce heparin and histamine Laboratory Techniques TM 10 Eosinophil • Functions – – Moderate the inflammatory response – phagocytosis Laboratory Techniques TM 11 Lymphocyte & Monocyte • Lymphocyte – plays a vital role in immunity T-cells (memory cells) – cells are sensitized to an antigen, remember that antigen and fight it off next time • Monocyte – largest blood cell Function is phagocytosis B-cells – divide to form many cells to fight an antigen Laboratory Techniques TM 12 Thrombocyte • Function – – Hemostasis (clotting) – stop bleeding by adhering to damaged vessels and clumping together, release proteins that help form a clot Laboratory Techniques TM 13 Urinary System Urethra Ureter Urethra Ureter Kidney Bladder Kidney Bladder Laboratory Techniques TM 14 The Kidney Cortex Medulla Renal artery Renal pelvis Ureter Renal capsule Laboratory Techniques TM 15 The Glomerulus Nephron Bowman’s capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Arterioles Distal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Collecting duct Laboratory Techniques TM 16