* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EOC Review 2015 answer key A
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
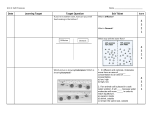
Name: _KEY_________ Semester 1 EOC Review Sheet Period: ________________ 1) State the three parts of the Cell Theory: a. All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. c. All cells are produced from other cells. 2) What two organelles are only in a plant cell? Why? Chloroplast and cell wall Cell Wall – supports and protects the cell. Required because plants the lack skeletal structures of animals. Chloroplasts – green organelles in plants that capture energy from the sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. Plants are autotrophs which photosynthesize. Animals are heterotrophs and must eat food. 3) What organelle is larger in the plant than the animal? Why? The vacuole so it can store water for photosynthesis and food (sugar) for respiration. 4) Explain the function(s) of the following organelles: (Be sure you can identify these in a picture!) a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities and is where the genetic information is stored. b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use (respiration) to carry out its functions c. Cell membrane –the next barrier within the cell wall – all cells have membranes - controls what substances come into and out of the cell d. Chloroplast – green organelles in plants that capture energy from the sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell (photosynthesis) e. Cell wall – a rigid layer of nonliving material (composed of cellulose) that surrounds the cells of plants to give shape and support. f. Vacuole – storage areas within the cell for food, wastes and water g. Cytoplasm – the area between the nucleus and the cell membrane where the organelles are found. 5) What are specialized cells? Cells that are shaped differently to perform a certain job or function. 6) Give three examples of specialized cells. Nerve cells send messages- Have fatty coating to insulate electrical messages. Muscle cells allow for movement- Extra Mitochondria to get the energy for movement. Red blood cells transport gases- Lack a nucleus so it has space to carry the gasses. Bones make blood since they cant reproduce. Egg cells provide nourishment for a developing embryo and give rise to all the future cells in the organism (reproductive cell)- Yolk of an egg with the egg white providing the nutrition. 7) Red blood cells lack a nucleus. What might they not be able to do? Reproduce (mitosis), direct activities, have students give examples 8) In plants with a certain disease, the composition of the cell membrane is not normal. What process would it have trouble doing? Any of these: Passive transport: osmosis and diffusion, Active transport and Photosynthesis…even protection. 9) Which part of the cell is semi-permeable and regulates the movement of molecules across it? The cell membrane 10) Define homeostasis. An organism’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment in spite of the changes in the external or internal environments. 11) List the 5 levels of organization in order. Cells – tissue – organs- organ system - organism 12) List and give an example of the four types of body tissues. Muscular: heart, skeletal muscles, smooth muscle lines digestive tract Epithelial: skin, lines organs Nervous: brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves Connective: bone, cartilage, blood, ligaments 13) Cell Processes a. What is selective permeability? The cell membrane allows some substances to pass through while others cannot. Also known as semi-permeable. b. Define passive transport: the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without the use of cellular energy a. ex. Define diffusion: the process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until reaching equilibrium. the main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane Example of diffusion: candle, chocolate milk, air freshener, gas exchange, etc. Draw a picture of diffusion and explain what is happening in the picture using the words high concentration and low concentration A substance in high concentration is moving to an area where it is in low concentration. ex. Define osmosis: the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. Example of osmosis: drinking water, exhaling, body cells or red blood cells losing/gaining water. What conditions promote osmosis? The amount (concentration) of dissolved substances, the amount (concentration) of water. Draw a picture of osmosis and explain what is happening in the picture using the words high concentration and low concentration. Water molecules moving across a semi-permeable membrane from high to low concentration. c. Define active transport: the movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy. 14) The movement of oxygen out of the lungs and into the blood happens because of __diffusion_______. 15) How does photosynthesis help living things? It is the process that creates food so they can eat and oxygen they can break down food into a useable form of energy. 16) What happens during photosynthesis? b. What types of living things carryout photosynthesis? Green plants or autotrophs c. Definition: The process by which plants and some other organisms capture the energy in sunlight and use it to make food (glucose sugar). d. Equation: Sunlight CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Carbon dioxide plus water and sunlight yields (in the presence of a chloroplast) glucose, oxygen e. Organelle used: __Chloroplast__________________ f. Draw a picture of the organelle and label what goes in and what comes out: g. What would happen to the cell if this organelle stopped working? It would no longer be able to convert sunlight energy into chemical energy. It would lose its source of energy (fuel). 17) What happens during respiration? a. What types of living things carryout cellular respiration? All living things carry out cellular respiration. Autotrophs and heterotrophs (plants and animals). b. Definition: using oxygen to transform glucose into chemical energy called ATP using an organelle called a mitochondria. Water and carbon dioxide are released along with energy during this process. c. Equation: C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy (ATP) Glucose plus oxygen yields Carbon dioxide, water, and energy d. Organelle used: _mitochondria. e. Draw a picture of the organelle and label what goes in and what comes out: f. What would happen to the cell if this organelle stopped working? The organism would not be able to convert food energy into chemical energy and all cell/life processes would stop. The organism would not be able to survive or maintain homeostasis. 18) What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? The two are reciprocal or reverse processes. The products of one process are the raw materials of the other which creates a cycle. 19) Plants undergo both photosynthesis and respiration. What do plants release during photosynthesis and then use during respiration? Oxygen 20) The six characteristics of living things: 1. Cellular organization 2. Reproduction 3. Responds to the environment 4. Growth and development 5. Energy use 6. Chemicals of life 21) 4 Basic needs of all living things: 1. Food 2. Water 3. Shelter/Space 4. Oxygen 22) Explain how to find the total magnification of a specimen when viewed using the microscope: Eyepiece magnification X Objective lens magnification = total magnification. *Label with unit “x”. Use the table above to answer the following questions. 23) What is the Independent variable? The type of organism 24) What is the Dependent variable? The number of organisms in a field. 25) What conclusions can be drawn from the data? There are more organisms in a field in the month of July compared to May and September. Grasshoppers, birds and spiders are highest in number during the month of July. For the table and image above: 26) What is the manipulated variable? Water temperature 27) What is the responding variable? Carbon dioxide produced per minute 28) What conclusions can be drawn from the data? 40oC (warm water) is the temperature that produces the most carbon dioxide bubbles per minute. 29) Does the experiment demonstrate cellular respiration or photosynthesis? How do you know? Cellular respiration because carbon dioxide is also produced as a result of this chemical process. 30) Name a specialized cell and organ for one of the systems and explain how its form helps its function. (see specialized cell notes or system notes) Cell: __Neuron Organ: _Brain/Spinal cord Form helping function: the long axon allows for chemical messages to be sent quickly, the finger like structures of the dendrites quickly and accurately receive messages. The fat of the myelin sheath ensures the message travels uninterrupted. For the chart above: 31) What is the Independent variable? _Type of Bread____________ 32) What is the Dependent variable? ___Presence of Mold_________ 33) What should be changed about this experiment to make it more accurate? The temperature should be For the chart above: 34) What is the Independent variable? ___The color of the light______ 35) What is the Dependent variable? _____The mass of the plant _____ 36) What conclusions can be drawn from the data? White light produces the greatest increase in plant mass 37) Briefly describe the function of each of the following systems: Circulatory – transports nutrients throughout the body and fights disease. Skeletal- provides shape, support, protection, storage of fats and minerals, produces blood cells. Respiratory – allows for exchange of gases (O2 & CO2) with the environment to support cellular respiration. Muscular – enables movement, generates heat. Nervous – sends and receives messages both internally and externally with the environment. Digestive – breaks down food into a useable form the body cells can use. Excretory – eliminates excess water, mineral and nitrogen (urea). 38) Give an example of how 2 or more body systems work together to function? The circulatory system delivering blood to all of the cell of the body & the respiratory system providing oxyegen to the cell for cellular respiration. Both system work together to remove cell waste carbon dioxide and water vapor. 39) Explain how plants have the ability to perform similar functions organs/tissues that allow it to do so: Function Organ Organ System/Organ/Tissue System/Organ/Tissue Used in Plants Used in Mammals Roots, root hairs (epidermal Digestive System, intestines, Obtaining cells) absorption (villi cells) nutrients Circulation of materials Xylem (water and minerals) and phloem (sugars) leaves (stomata) gas exchange Circulatory System, heart, blood vessels, (muscle cells) Support Woody and herbaceous stems Skeletal System, bones, (bone cells-Connective tissue) Gas Exchange Leaves are the organs where gas exchange occurs, stomata and guard cells are the specialized cells where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with the environment. Respiratory System, lungs, (alveoli cells) the human body by describing the How does it carryout a similar function in plants as in animals? Plants absorb water from soil using roots and osmosis, we use the digestive system to absorb water and osmosis transports water to body cells. Materials are actively and passively transported to cells using a system of vessels, we use arteries, capillaries and veins. Also, epidermal cells line plant and animal tissue so that diffusion and osmosis can take place. Plants use cell wall and cellulose to provide support for the organism, this is more of an exoskeleton, we use an endoskeleton made of calcium. We use lungs and a system of tubes called bronchi/bronchioles that transport gases and allow gases to be exchanges in the ends of the tubes called alveoli. Plants exchange gasses through their leaves. 40) List and define the two major types of observations. Qualitative - Observations dealing with descriptions based on your senses. Quantitative- Observations dealing with numbers and/or measurements. 41) What is a controlled experiment? An experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time. To ensure validity, there should be a control for comparison and the experiment should be repeated multiple times. 42) Define Independent and Dependent Variable. Independent – I chose the variable. It is the experimental variable that is being tested. Dependent – The variable I measured (it depends). It responds to the change you are testing. 43) On a graph the X-Axis represents the _Independent_________ Variable and the Y-Axis Represents the __Dependent___________ Variable. 44) What does the T.A.I.L acronym stand for? Title – Axis – Interval – Label 45) How did the invention of the microscope allow the cell theory to be developed? The invention of the microscope enabled scientists to discover the cell and learn more about it. 46) Why do plant cells have both a chloroplast and a mitochondria but animal cells have only a mitochondria? The chloroplast creates glucose for the plant (autotroph). The mitochondria coverts glucose into cellular energy that ALL LIVING things need to survive. 47) How do plants capture energy from the sun and make it usable for living systems? Plants capture light energy from the sun. Using the chloroplast organelle. The chloroplast chemically converts carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into glucose and oxygen. The energy is used by the plants but also stored for animals to consume as food. Plants begin all food chains. Niko Tinbergen (1907-1988) was a Swedish Ethologist (animal behaviorist) famous for studying animals in their native habitats. One of his classic experiments involved a bird called the black-headed gull (Larus ridibundus). Black-headed gulls build nests of twigs on the ground and lay light brown eggs that are covered with dark brown spots. However, the inside of the egg is white in color. Tinbergen noticed that adult gulls pick up the eggshells shortly after a chick has hatched, and fly them to a location far from the nest, where they are left. Since this behavior required expending energy and time that could have been spent feeding and protecting the chicks, Tinbergen wanted to know why the birds did this. Problem: Why do black-headed gulls remove eggshells from the nest? Hypothesis: The white interior of the shell is not camouflaged and attracts predators to the nest. Therefore, the gulls remove the shells to decrease predation. Test: Tinbergen and his co-workers collected gull eggs and painted 69 of them white and left 68 of them with their natural color. (Statistically, these numbers are close enough to be considered equal.) The researchers then scattered the eggs next to a gull breeding area and observed from a nearby blind. Predation rates were recorded for white versus natural colored eggs. Data: Original Number of Eggs Eggs Taken by Predators Eggs Not Taken ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------White Eggs 69 43 26 Natural Eggs 68 13 55 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------a. Do the results of this experiment support the hypothesis? Why, Why not? The results do support the hypothesis because white eggs were taken more often (43/69) than the natural eggs (13/68). b. Are you 100% sure (without a doubt) that your hypothesis is correct? (Is it proven?) Scientists are never 100% sure of the validity of a hypothesis. They should always continue testing to collect more and more data. c. If you were working with Tinbergen, what would you suggest be done next? Scientist can increase sample size and repeat the experiment multiple times to increase the validity of their results. d. Identify the independent and dependent variables. Independent= Color or Egg Dependent= Number of Eggs Taken vs. Number of Eggs Not Taken