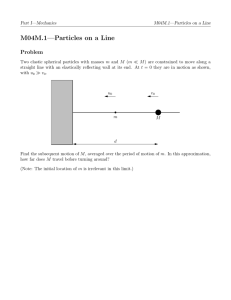
Chapter 5
... One electron enters each orbital until all orbitals contain one electron with parallel spins. ...
... One electron enters each orbital until all orbitals contain one electron with parallel spins. ...
MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS r0 r0
... i) For most polymers, determination of the molecular weight by osmotic pressure measurements and by light scattering give different values; ii) Polymer solutions show large deviations from ideality; iii) Rubber warms up if it is stretched adiabatically (for a metal spring, only a very small temperat ...
... i) For most polymers, determination of the molecular weight by osmotic pressure measurements and by light scattering give different values; ii) Polymer solutions show large deviations from ideality; iii) Rubber warms up if it is stretched adiabatically (for a metal spring, only a very small temperat ...
Chapter 5
... One electron enters each orbital until all orbitals contain one electron with parallel spins. ...
... One electron enters each orbital until all orbitals contain one electron with parallel spins. ...
Text S4) Diabatic Surface Hopping: Theory and Implementation
... then in regions of strong coupling (large h 1 t 2 ), part of the population will transfer to the other state and part will remain on the old state. For classical trajectories this implies spawning another trajectory. When single trajectories are computed using an ab initio wavefunction to comput ...
... then in regions of strong coupling (large h 1 t 2 ), part of the population will transfer to the other state and part will remain on the old state. For classical trajectories this implies spawning another trajectory. When single trajectories are computed using an ab initio wavefunction to comput ...
The QT interval on the ECG is measured from the beginning of the
... theory that a Lifshitz transition occurs in which the system closes the bulk bandgap to become a semimetal and then re-opens it to become a quantum spin Hall insulator. The spin orbits induce an energy gap in the graphene, which leads to the formation of a new two-dimensional electronic state. This ...
... theory that a Lifshitz transition occurs in which the system closes the bulk bandgap to become a semimetal and then re-opens it to become a quantum spin Hall insulator. The spin orbits induce an energy gap in the graphene, which leads to the formation of a new two-dimensional electronic state. This ...
Fluorescence Spectroscopy 1.0 Emission – the mirror image
... 4.0 Fluorescence quenching and energy transfer The quantum yield gives the intrinsic fraction of the molecules that decay by a emitting light. In addition, the fluorescence emission can be further quenched by: 1. Collisional quenching – molecular collisions in solution 2. Intersystem crossing – conv ...
... 4.0 Fluorescence quenching and energy transfer The quantum yield gives the intrinsic fraction of the molecules that decay by a emitting light. In addition, the fluorescence emission can be further quenched by: 1. Collisional quenching – molecular collisions in solution 2. Intersystem crossing – conv ...
Total
... VIII (8 points) List the symmetry elements of NO2 molecule, construct the group multiplication table, name the point group to which it belongs, point out the normal subgoups and check up the table by multiplication table rule. ...
... VIII (8 points) List the symmetry elements of NO2 molecule, construct the group multiplication table, name the point group to which it belongs, point out the normal subgoups and check up the table by multiplication table rule. ...
Sections 6.3-6.5
... Bohr Model of the Atom • Electrons move in certain, specific, circular orbitals • Smaller orbit = lower energy level • Assigned the allowable electron orbitals the principle quantum number, n. • 1st orbit= lowest energy: n=1 • 2nd orbit= 2nd lowest energy: n=2 ...
... Bohr Model of the Atom • Electrons move in certain, specific, circular orbitals • Smaller orbit = lower energy level • Assigned the allowable electron orbitals the principle quantum number, n. • 1st orbit= lowest energy: n=1 • 2nd orbit= 2nd lowest energy: n=2 ...
Electromagnetically induced transparency
... drive a resonant transition in a three-level atomic system, the absorption of a weak probe laser field can be reduced or eliminated provided the two resonant transitions are coherently coupled to a common state. EIT was first observed in lambda type system of strontium vapors using high pulsed laser ...
... drive a resonant transition in a three-level atomic system, the absorption of a weak probe laser field can be reduced or eliminated provided the two resonant transitions are coherently coupled to a common state. EIT was first observed in lambda type system of strontium vapors using high pulsed laser ...
Defense Presentation
... analyze an oscillator’s motion with its quantum dynamics continuously throughout external interaction, with a more unified model than what we’ve seen in the literature ...
... analyze an oscillator’s motion with its quantum dynamics continuously throughout external interaction, with a more unified model than what we’ve seen in the literature ...
Principles of Operation of Semiconductor Quantum Dots
... ground state of many-particle problem by filling particles one by one into lowest energy levels that are not already occupied, one can consider the problem as pertaining to those of one particle states. ...
... ground state of many-particle problem by filling particles one by one into lowest energy levels that are not already occupied, one can consider the problem as pertaining to those of one particle states. ...
12.3 Assembly of distinguishable Particles
... calculated as Wtotal = WA x WB thus: f (WA x WB) = f (WA) + f (WB) The only function for which the above relationship is true is the logarithm. Therefore: S = k · lnW where k is the Boltzman constant with the units of entropy. ...
... calculated as Wtotal = WA x WB thus: f (WA x WB) = f (WA) + f (WB) The only function for which the above relationship is true is the logarithm. Therefore: S = k · lnW where k is the Boltzman constant with the units of entropy. ...
Review: Quantum mechanics of the harmonic oscillator
... Why are ladder operators useful? • We are typically interested in expressions such as or ...
... Why are ladder operators useful? • We are typically interested in expressions such as or ...
Dissociation energy of the Ar-HN complex
... from fitting the line positions to a linear molecule Hamiltonian keeping the lower state constants fixed: v 0 = 2505.40 + 0.10 (band A), 2707.34 + 0.05 (B) and 2755.62 + 0.05 c m - I (C). Large uncertainties in the origin values result from the fact that they are most sensitive to transitions involv ...
... from fitting the line positions to a linear molecule Hamiltonian keeping the lower state constants fixed: v 0 = 2505.40 + 0.10 (band A), 2707.34 + 0.05 (B) and 2755.62 + 0.05 c m - I (C). Large uncertainties in the origin values result from the fact that they are most sensitive to transitions involv ...
Inorganic Physical Methods
... There is another way of separating the information according to frequency, and this involves the interference phenomena that are also responsible for the dispersive effect of a diffraction grating. If interference effects can be made to alter the amplitude of the total radiation reaching the detecto ...
... There is another way of separating the information according to frequency, and this involves the interference phenomena that are also responsible for the dispersive effect of a diffraction grating. If interference effects can be made to alter the amplitude of the total radiation reaching the detecto ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.